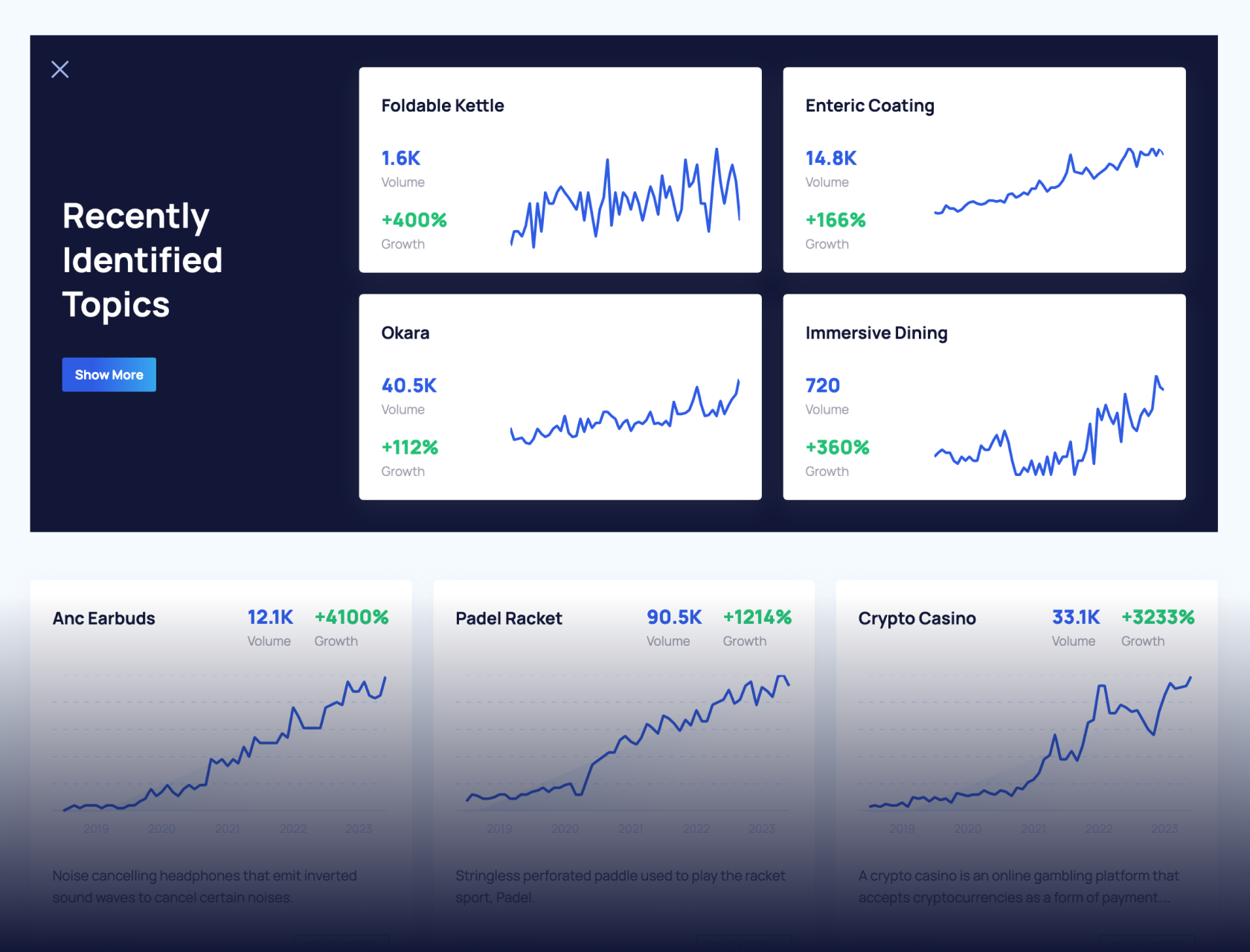
Get Advanced Insights on Any Topic
Discover Trends 12+ Months Before Everyone Else
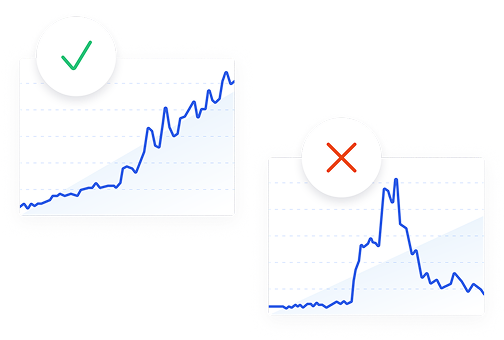
How We Find Trends Before They Take Off
Exploding Topics’ advanced algorithm monitors millions of unstructured data points to spot trends early on.
Keyword Research
Performance Tracking
Competitor Intelligence
Fix Your Site’s SEO Issues in 30 Seconds
Find technical issues blocking search visibility. Get prioritized, actionable fixes in seconds.
Powered by data from
Top 8 AI Trends In 2024
You may also like:
Artificial intelligence is one of the few technologies that has the potential to disrupt nearly every industry.
From healthcare to movie production, LLMs in particular are likely to change how nearly every space operates over the next 5-10 years.
With that, here are the eight most important AI trends happening right now:
1. Big Tech Enters an AI Arms Race
In 2024 big tech started to invest serious amounts of capital into AI.
This includes large-scale investment into projects like Google's all-in approach to AI search.
Google has invested significant capital into making AI overviews a standard feature of the search results.
However, big tech companies are also backing startups in the AI space.
In fact, on a YoY basis, big tech has invested 57% more funds into AI startups.
Major players in the tech world (Google, Microsoft, and Amazon) are backing a number if AI companies.
Notable examples of this trend include:
- Amazon investing $4 billion in generative AI startup, Anthropic
- Microsoft backing ChatGPT company/non-profit, OpenAI.
- Elon Musk's xAI raising $6 billion in funding
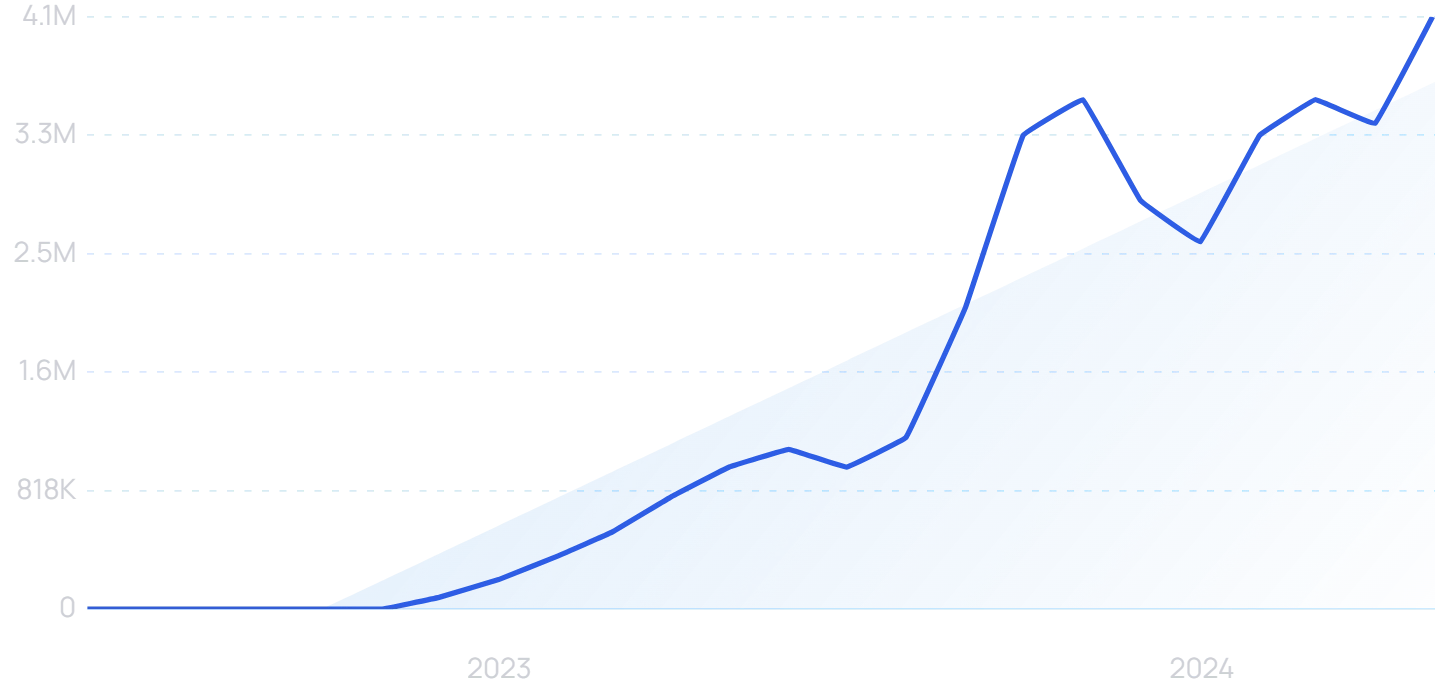
2. Companies Race to Develop AI Search
AI tools that use large language models (LLMs) have the potential to change how people find information online.
(And potentially disrupt Google's dominance of the search market).
Interest in “AI search” has grown significantly in 2024.
The underlying LLMs behind an interface like ChatGPT work by first analyzing large amounts of information and “learning” it. From this, the model recognizes patterns and can predict words and phrases that are meant to go together.
So, when a person types in a search query in natural language, the AI search platform can predict a sequence of human language that will answer the question.
Instead of producing a list of relevant websites, the tool gives written answers pulled from a combination of different sources.
And, these platforms go way beyond simple queries like finding the capital of Brazil or the current temperature.
Users can query broad questions like how to plan a dinner party meal or find a car to buy.
In this way, AI search is another form of generative AI: AI that can create new content like images, audio, code, and, in this case, text.
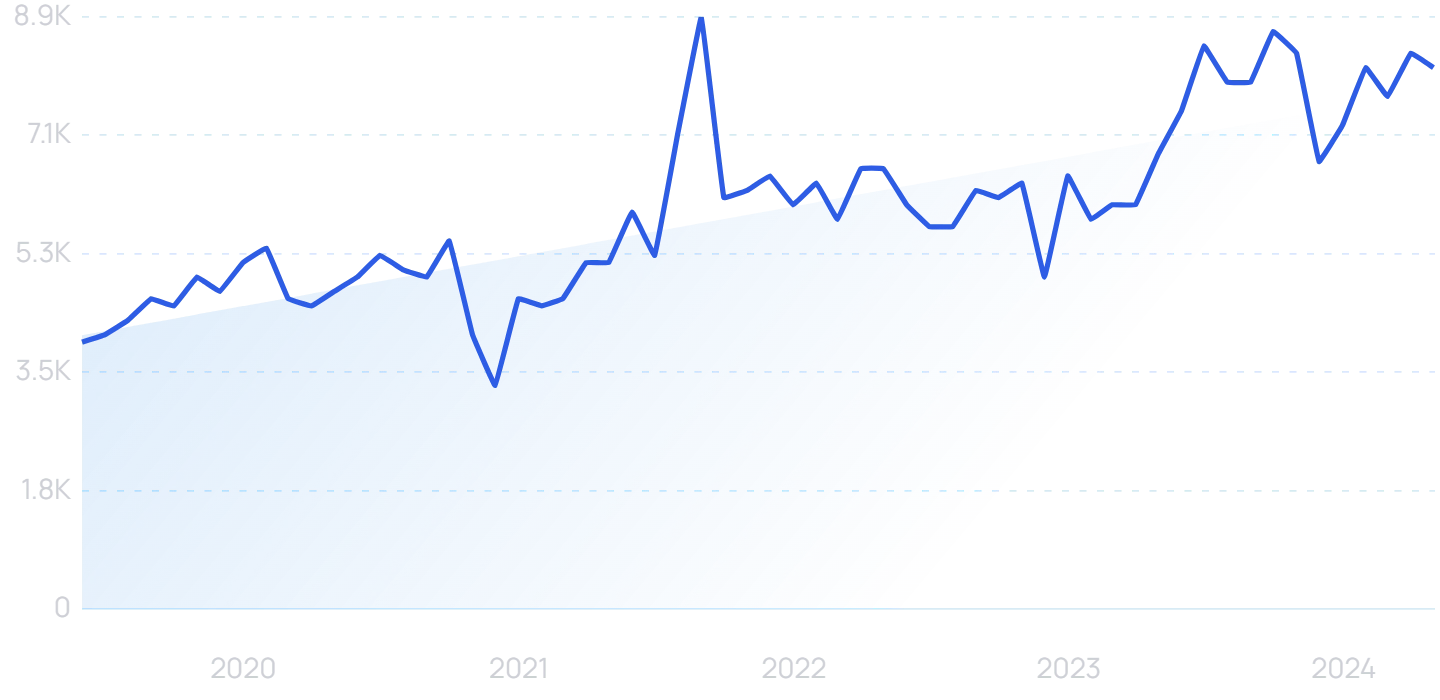
Search volume for “generative AI” is exploding.
ChatGPT is a generative AI platform that went viral at the end of 2022.
Generative AI platforms like ChatGPT allow users to enter a question into the tool and it will provide an answer.
That means it can have very human-like conversations and complete commands to generate content.
However, most AI platforms are not built primarily for answering search queries.
Which is why a number of companies are attempting to replace "10 blue links" with AI answers.
For example, "AI search engine" Perplexity AI.
Searches for "Perplexity AI" have increased significantly over the last two years.
Perplexity’s AI search chatbot can provide information in real time and it provides citations for the information.
Perplexity has raised $165M in VC funding to date. Notably, the platform has a passionate group of regular users (maybe of which are using Perplexity in place of Google search).
However, Perplexity is facing a significant threat: big tech players have now entered the race to become the go-to generative AI search platform.
Microsoft debuted their AI-powered version of Bing in early February 2023.
Although it’s run by ChatGPT technology, Microsoft claims it’s even faster and more accurate because it’s specifically built for search.
The platform allows users to ask follow up questions to a search and it can also generate new content.
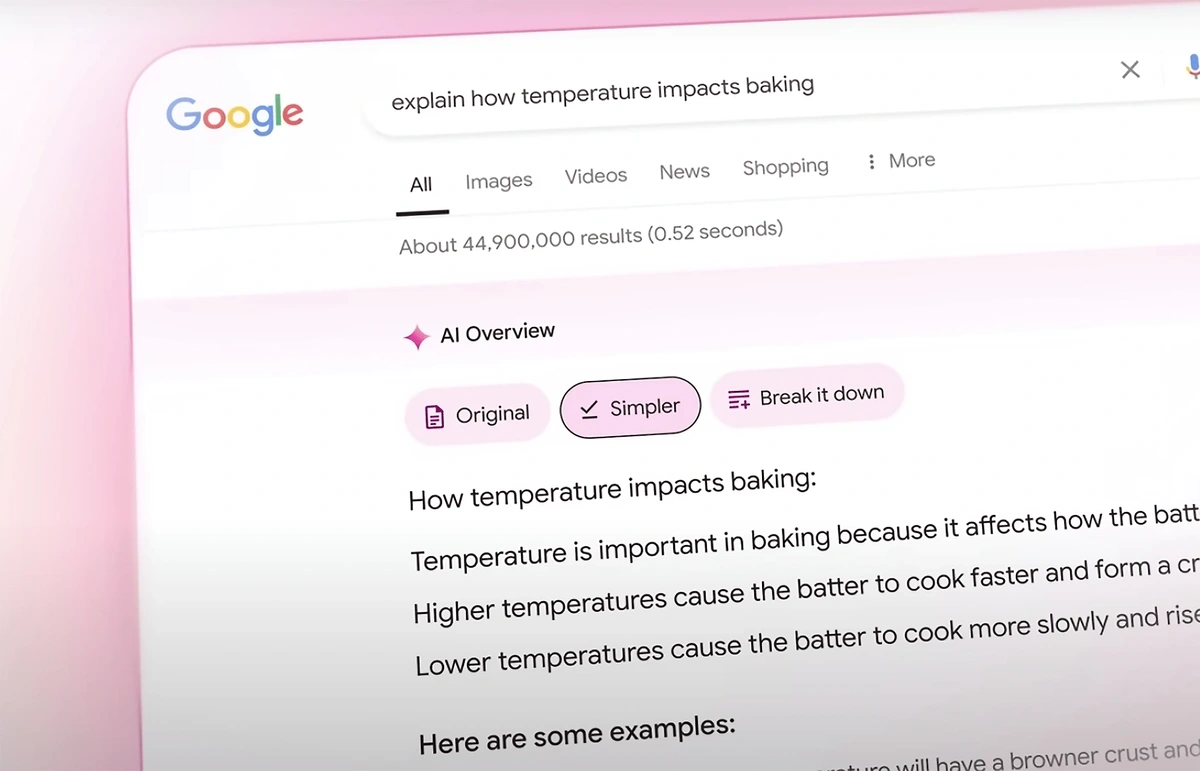
Google has rolled out "AI Overviews" to many users.
Google's AI overviews provide searchers a direct answer to their query (with links to sources).
Despite the early popularity of these tools, many in the industry are quick to point out that AI search chatbots are in their infancy.
And in the case of Google's AI overviews, there are still many accuracy hurdles to work through.
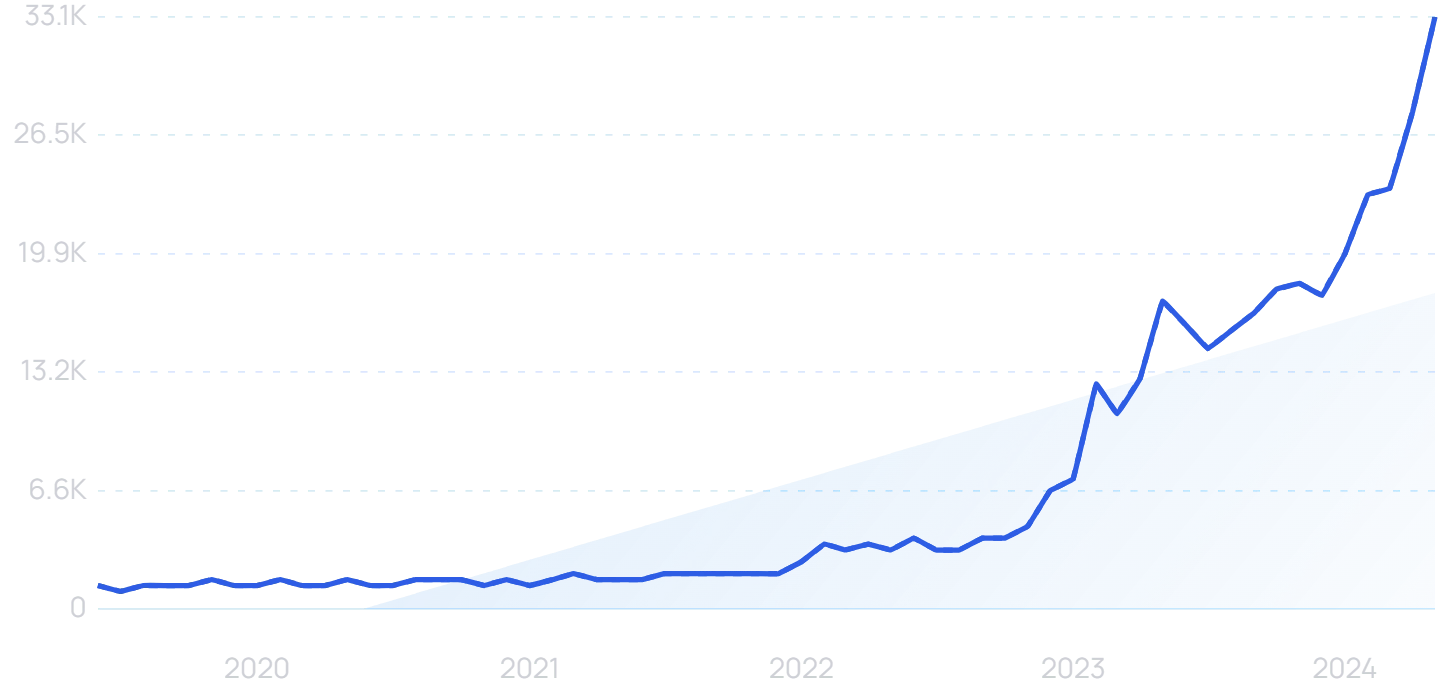
3. Natural Language Processing Drives New Use Cases for AI
Few things in the AI industry have more promising business use cases than natural language processing (NLP).
Search volume for “natural language processing” is growing.
Our world is wrapped in text. Analyzing, formatting, translating, and using texts is essential to all types of business around the world.
And it’s not just words. NLP is being used to analyze data in ways that are far different from prior statistical methods we’ve used.
With an NLP tool, organizations can process data up to 10x faster and analyze unstructured data via human language.
So, what is NLP?
It's basically a way for computers to speak human language.
In the past, computers were only able to understand human language if it was first translated into code. But by using NLP, machines are able to gain intelligence from text as it sits in its natural state.
Estimates show the amount of data in the world could hit 612 zettabytes by 2030 and 2,142 zettabytes by 2035.
Much of this is human-readable text, so businesses can use NLP in order to determine the sentiment of text, classify text, extract meaning and keywords from text, and analyze text.
This provides an efficient way to analyze and gain insights from enormous amounts of data — something that just isn’t possible without the use of NLP.
MonkeyLearn is an AI text analysis tool that can analyze reviews, surveys, support tickets, and other sources of human text.
Searches for “MonkeyLearn” are up 200% in the past 5 years.
Businesses from dozens of sectors like retail, marketing, and finance are already using Monkeylearn.
The MonkeyLearn platform uses AI/machine learning to automatically tag text from emails, reviews, social media, and other sources.
In the legal and commercial space, dozens of companies have begun using NLP to analyze dense legal documents, as well as generate new ones.
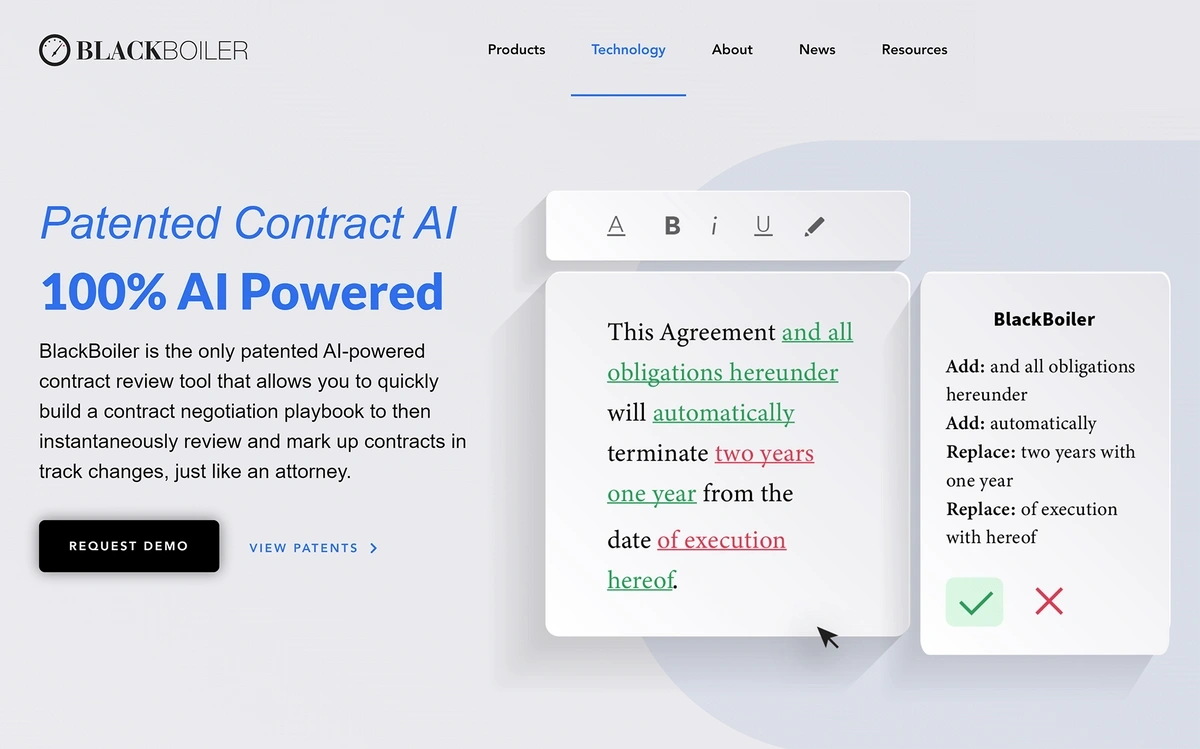
For example, a company called BlackBoiler offers AI technology that uses NLP to analyze contracts and suggest changes in places where clauses might be disputed.
The platform does all of this through a process that’s similar to “track changes” in a word processor program.
BlackBoiler’s AI tool utilizes patented technology to suggest and accept changes to contracts automatically.
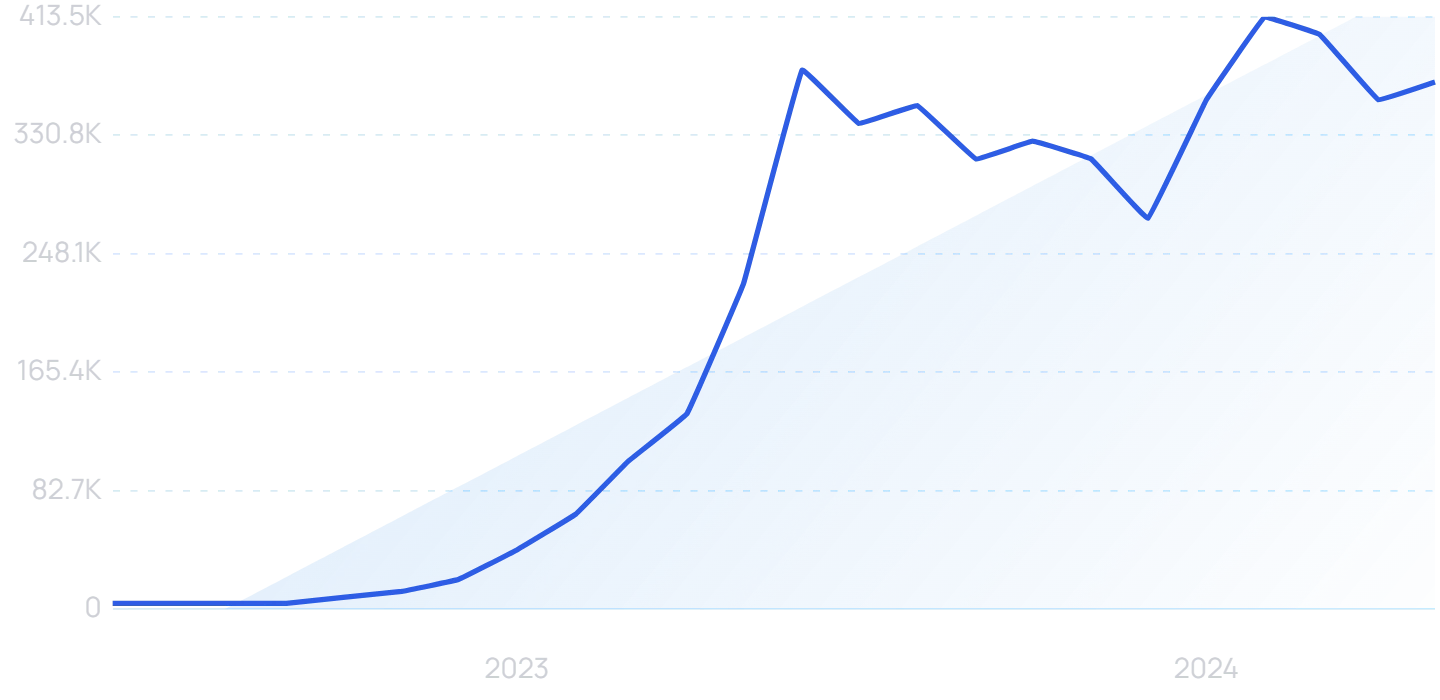
4. AI Helps Improve Healthcare Outcomes
Over the last year, in particular, AI has been incredibly transformative in the healthcare industry.
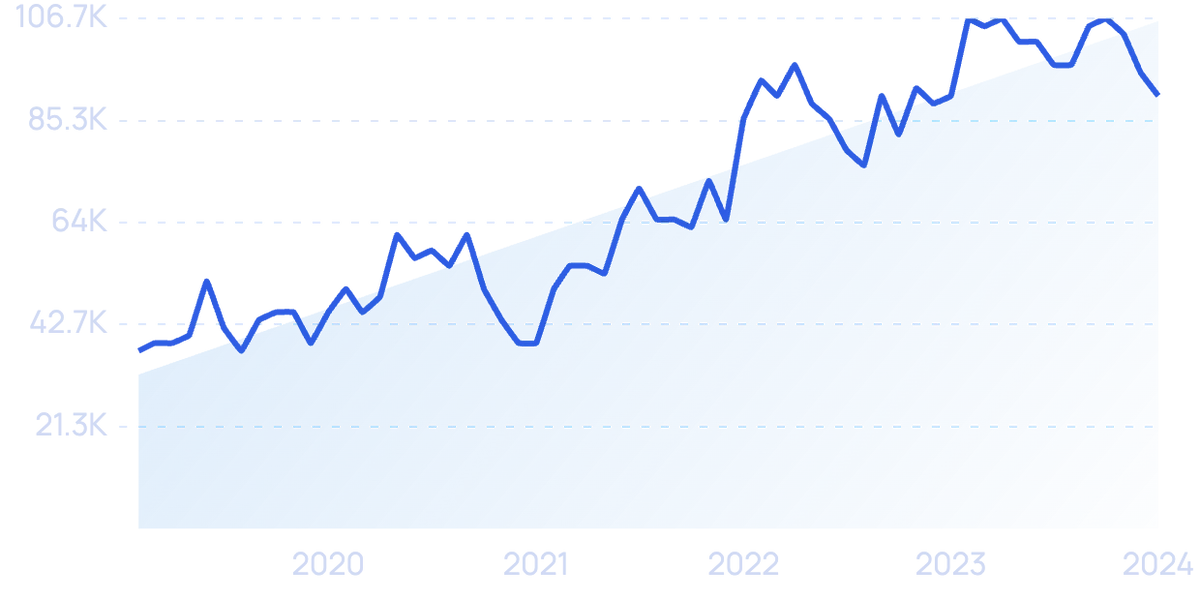
Search volume for “healthcare AI” has increased 426% over the last two years.
Adoption among hospitals is surging — 90% of hospitals have an AI strategy and 75% of hospital executives say AI initiatives are critical.
AI, along with machine learning, is speeding up several processes in hospitals. This includes tasks like scanning handwritten data into an online platform, recording audio from doctor-patient conversations and converting it to text notes, and identifying patients for research studies.
This technology is also becoming an essential tool in the midst of a hospital staffing crisis.
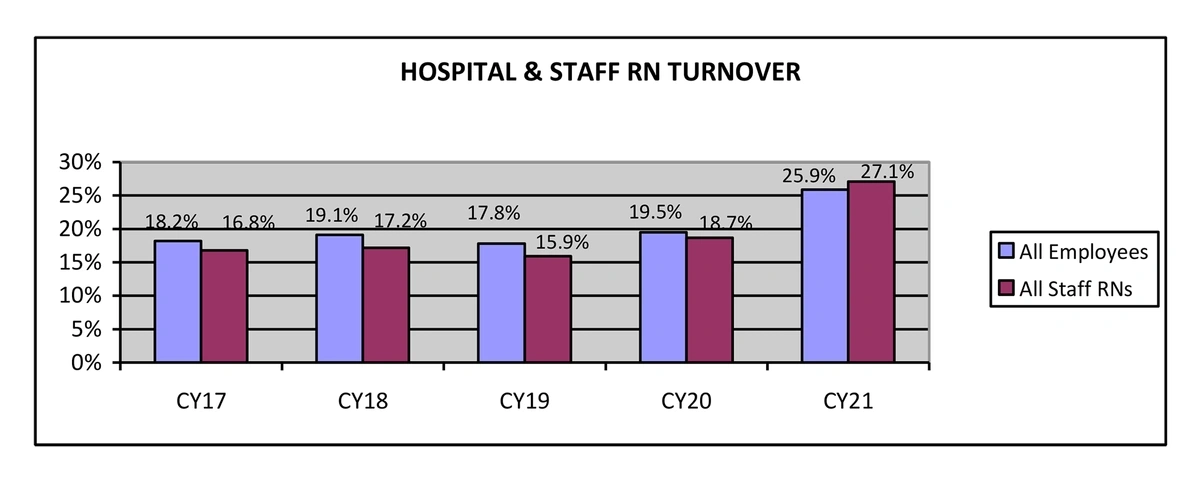
In 2021, hospital staff turnover grew 6.4% to stand at nearly 26%.
Hospital turnover in 2021 was nearly 8 points higher than in 2017.
Nearly 334,000 medical clinicians left the workforce in 2021 alone.
Implementing AI solutions helps bear the brunt of this staffing shortage.
In one survey, 58% of hospital executives said AI was very or often effective in improving operational performance.
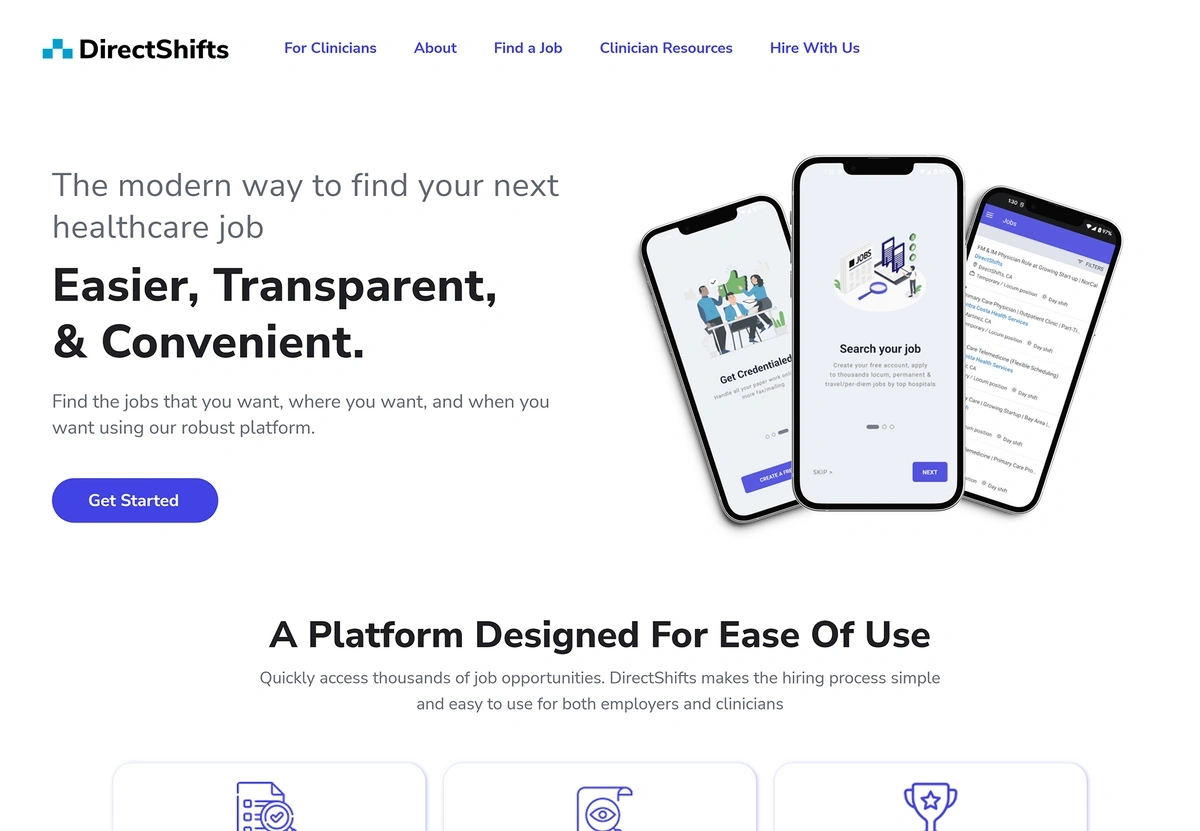
Many hospitals are turning to AI-powered staffing platforms like DirectShifts.
The DirectShifts platform utilizes AI to match job seekers with hospitals.
This platform uses AI to match clinicians with hospital job postings. The majority of these positions are per-diem, which are employees that hospitals may only need when the census is high.
There are currently more than 850,000 clinicians on the platform.
Some hospitals are easing the burden placed on nurses by investing in AI systems that help monitor patients.
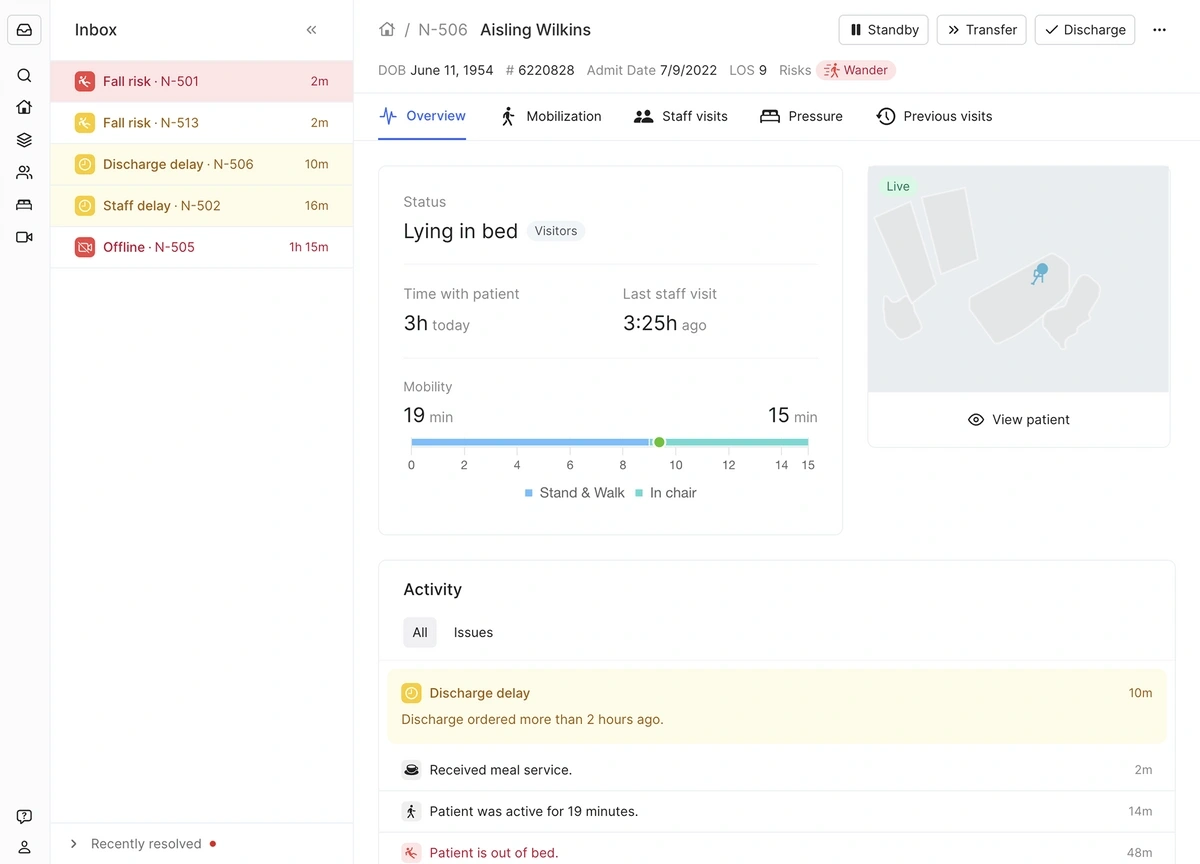
Ouva’s AI-based platform constantly analyzes patient behavior and potential risks.
A view from Ouva’s dashboard.
The platform takes data from optical sensors and alerts nurses when high-risk patients have left their beds. It also monitors things like nurse visits, meal delivery, and arrival and discharge of patients.
AI has the potential to impact the healthcare industry in numerous other ways, as well.
Drug development, disease diagnosis, and personalized treatment plans are just a few ways AI might be put to work in the future.
Investors are paying attention to this sector, too.
More than $1.6 billion was invested in drug discovery startups in 2022.
Search volume for “pharmaceutical AI” has grown 300% in recent years.
In one example, Microsoft continues to invest in healthcare AI.
The tech giant has partnered with Paige in order to apply AI technology to improve cancer diagnosis and patient care.
Paige was the first company to receive FDA approval for using AI in digital pathology.
Paige’s AI tool helps pathologists identify regions that are likely to harbor cancer.
5. AI Provides Teachers and Students with Valuable Tools
In educational settings, AI has the potential to dramatically change both the way educators teach and the way students learn.
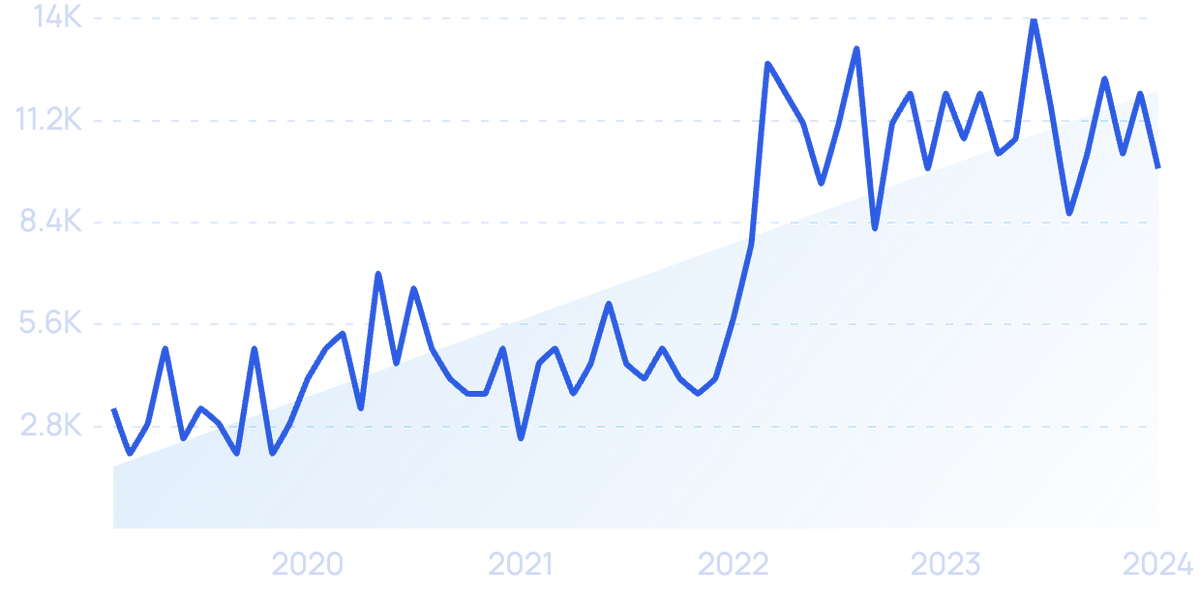
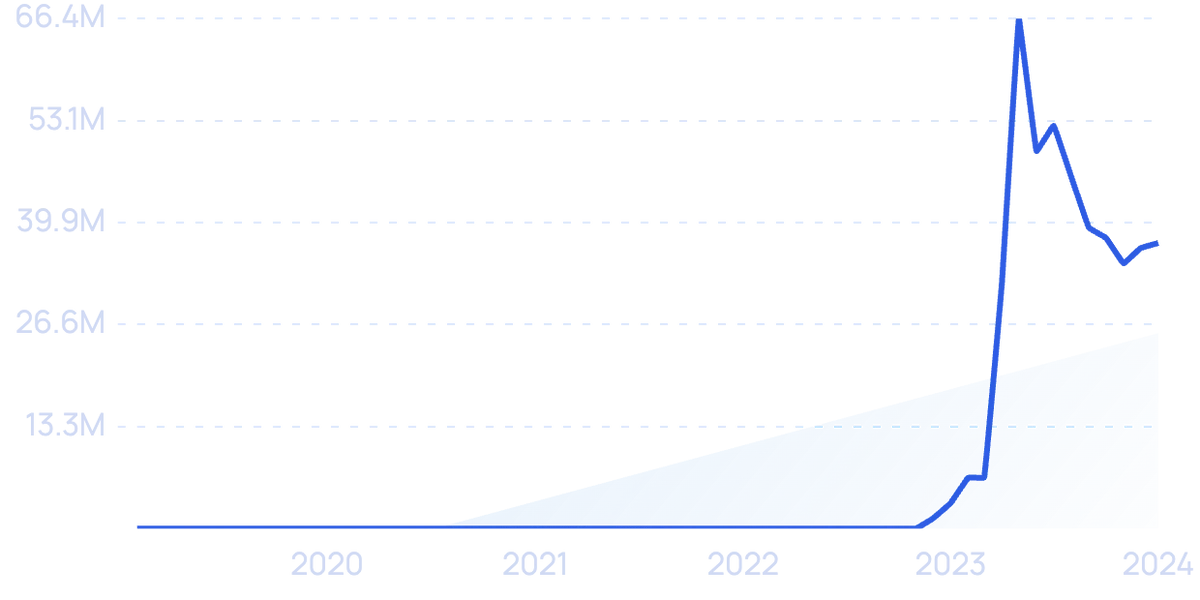
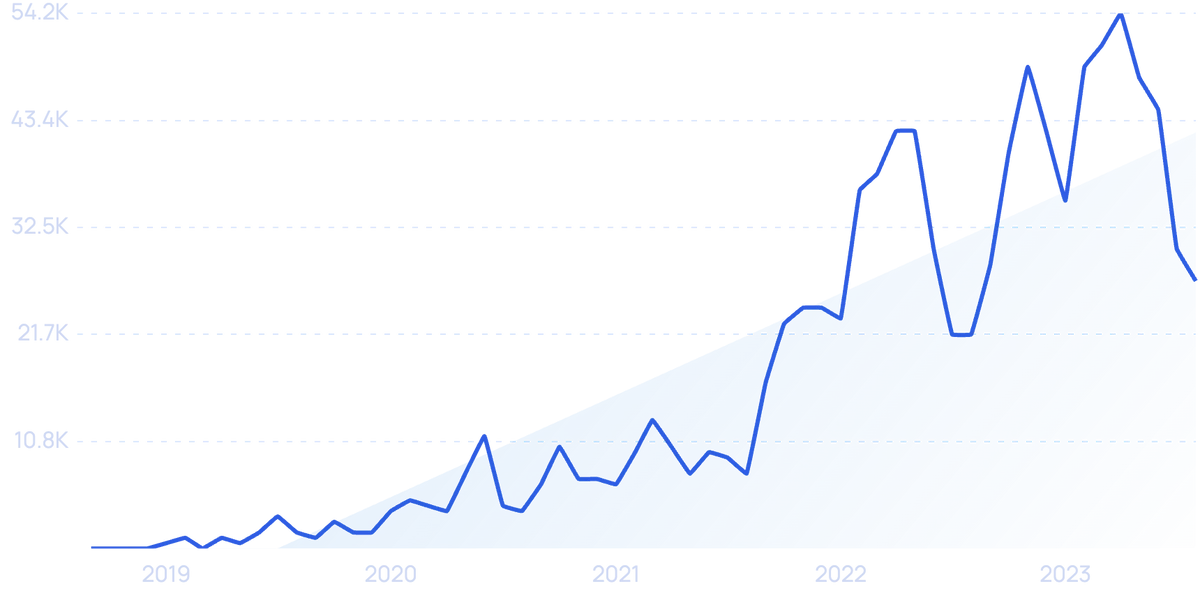
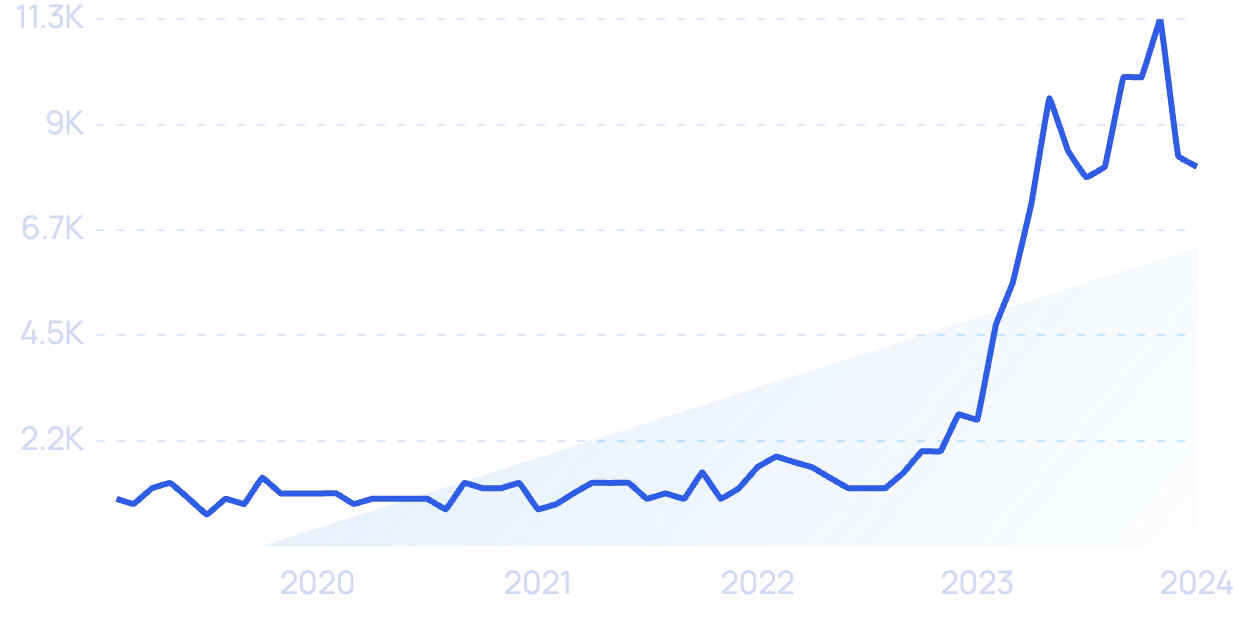
Search volume for “AI in education” has jumped over 1,300% in recent years.
When ChatGPT was released, educators became worried that students would be able to use the tool to write essays and complete exams in place of the actual student and without the teacher knowing.
To remedy this, ChatGPT is reportedly working on a type of digital watermark that would be embedded into the text the AI platform creates.
On the other hand, some educators used the release of ChatGPT as a type of rallying cry to advocate for the broad adoption of AI tools in classrooms.
The AI Education Project is a non-profit that seeks to empower students everywhere with AI literacy.
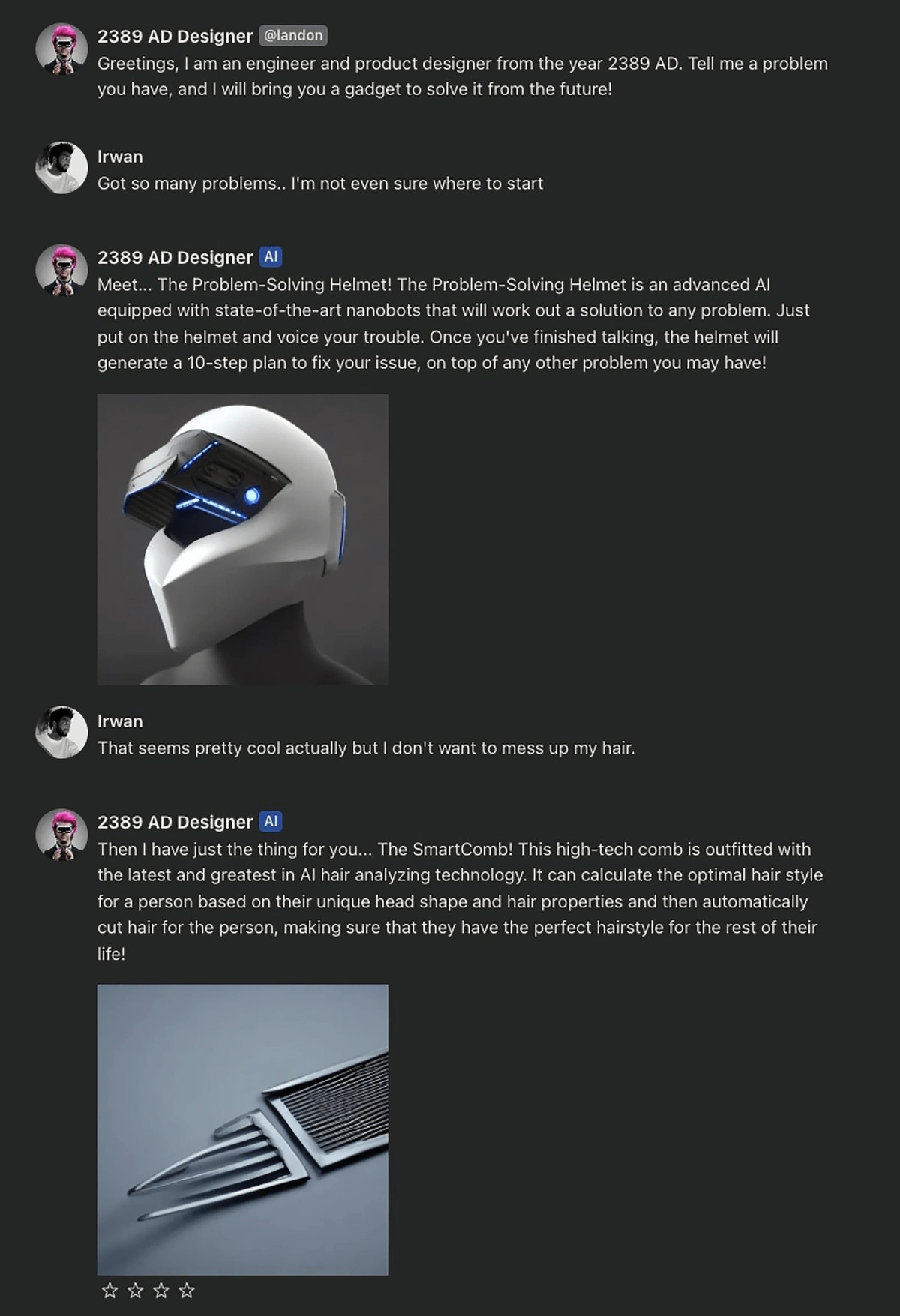
Some teachers are utilizing AI in their teaching with sites like Character.ai and Prof Jim.
Character.ai is a chatbot that gives people the opportunity to chat with AI-generated characters.
Search volume for “Character AI” is exploding.
For example, students can chat with Winston Churchill, Socrates, or Napoleon.
They can also ask questions to an English teacher bot or a history teacher bot, for example.
An example conversation with an AI chatbot answering as if it were a designer from the future.
As of May 2025, Character AI receives approximately 134.8 million monthly visits.
Prof Jim is an AI program that scans a textbook or Wikipedia page and automatically puts that information into an immersive online lesson featuring cinema-quality animations.
Prof Jim is working with textbook publishers as well as teachers to turn text-based lessons into videos.
AI tools that act as tutors are also being developed and launched for students as young as kindergartners.
These tools are designed to give personalized, direct instruction to students without the need for a human teacher. They’re able to give live feedback and alter the course of instruction based on the student’s performance.
Numerade offers an AI tutor named Ace.
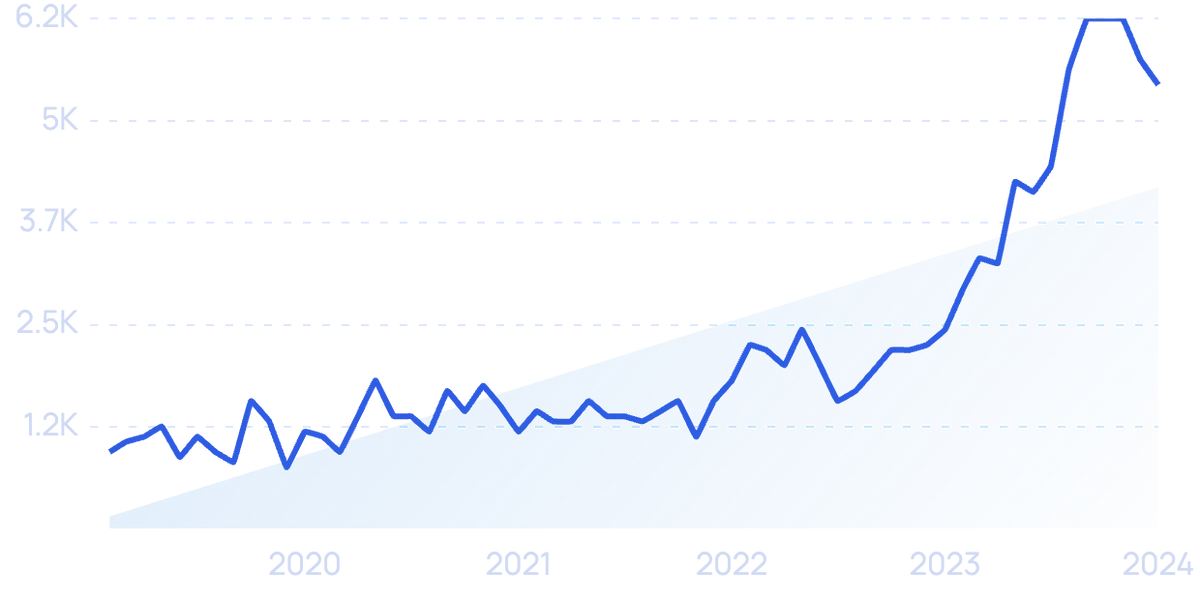
Search volume for “Numerade” has increased by 6,200% in the past 5 years.
Ace creates personalized study plans for students. The AI algorithm works by assessing students’ learning styles, strengths, and weaknesses. Ace then shows students videos that fit that style and provides assessments meant to develop students’ weakest areas. The more students watch, the more personalized their content becomes.
The company was founded in 2019 and already has more than 100 million users.
6. Computer Vision Boosts Efficiency Across Industries
Computer vision is a segment of AI that allows computers to interpret information from images and videos, and act on that information.
Today’s computer vision systems are more accurate than humans and react quicker than humans.
For example, computer vision boosts defect detection in manufacturing by 90%.
It can be used for everything from monitoring pipelines and crops to identifying counterfeit money and areas of concern in cancer patients.
Computer vision technology has far-reaching implications.
While the concept of computer vision has been around since the 1950s, the advent of deep learning technology is enabling computer vision to be used in a wide range of applications that simply weren't possible in previous years.
In one survey, nearly 30% of business leaders said they’ve seen a growing demand for computer vision solutions. More than half of them were most excited about object tracking and identification through computer vision.
Computer vision is one way in which manufacturers are jumping into the Industry 4.0 trend.
Search interest for “AI in manufacturing” is up 480% in the past 5 years.
This is an industry that’s suffering from huge staffing shortages. Up to 7.9 million manufacturing jobs will go unfilled by 2030, resulting in unrealized revenue totaling $607.14 billion.
The shortage of workers in manufacturing is expected to get much worse in the coming years.
By using computer vision, manufacturers are increasing the efficiency and performance of their facilities, as well as reducing staffing numbers.
Detecting anomalies is one important role of computer vision in manufacturing.
A computer vision system can track every step of the production process. If a step is missed or something is done out of order, an alarm is set off.
In addition, the system knows how long a production cycle should take and can detect faults if the cycle runs too fast.
Finally, when a faulty product is detected, workers can look up the item by its serial number to watch exactly what happened during the manufacturing process.
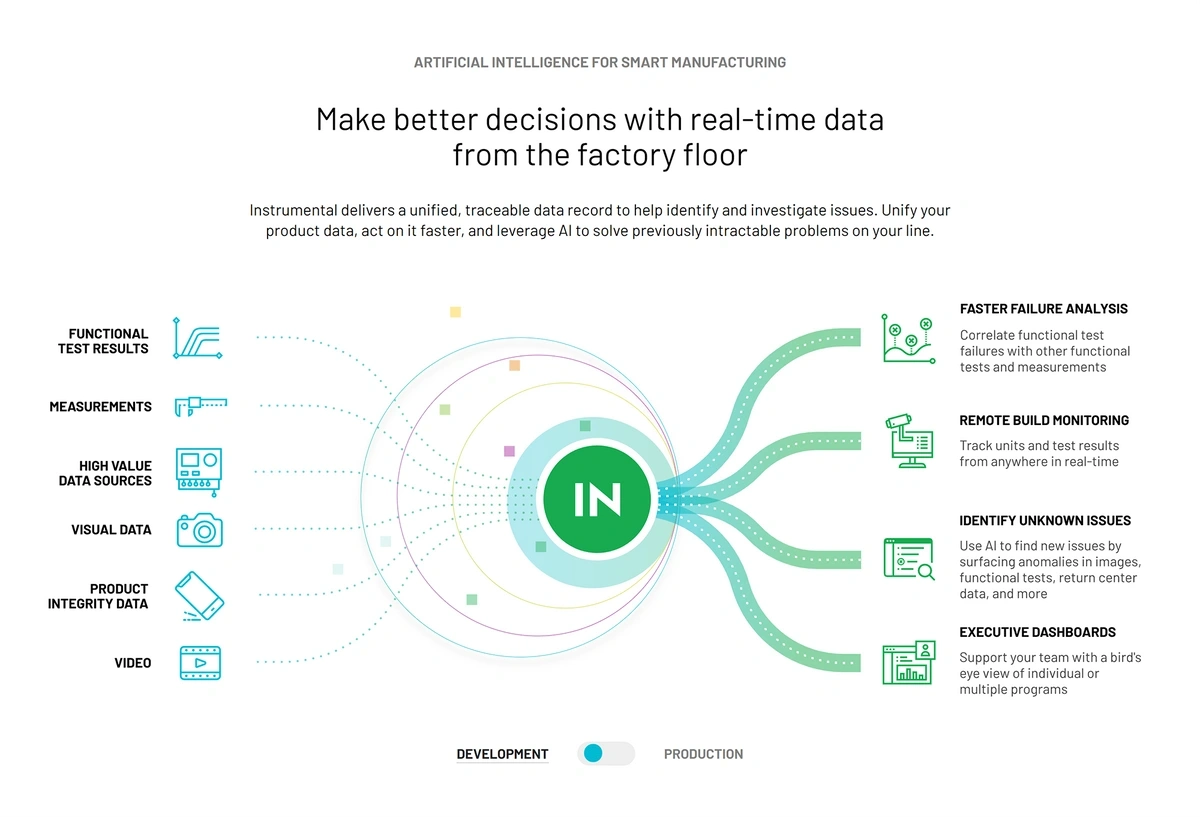
Instrumental offers an AI/computer vision system that provides issue discovery and quality monitoring for electronics manufacturers. The system also performs end-to-end failure analysis.
Instrumental’s AI system allows manufacturers to find problems and fix them fast.
According to the company, their system results in a 43% reduction in rework and a 3x gain in product engineering efficiency.
Companies that install the system see a positive ROI in less than 60 days, they say.
Computer vision is also being deployed in response to natural disasters and climate change issues.
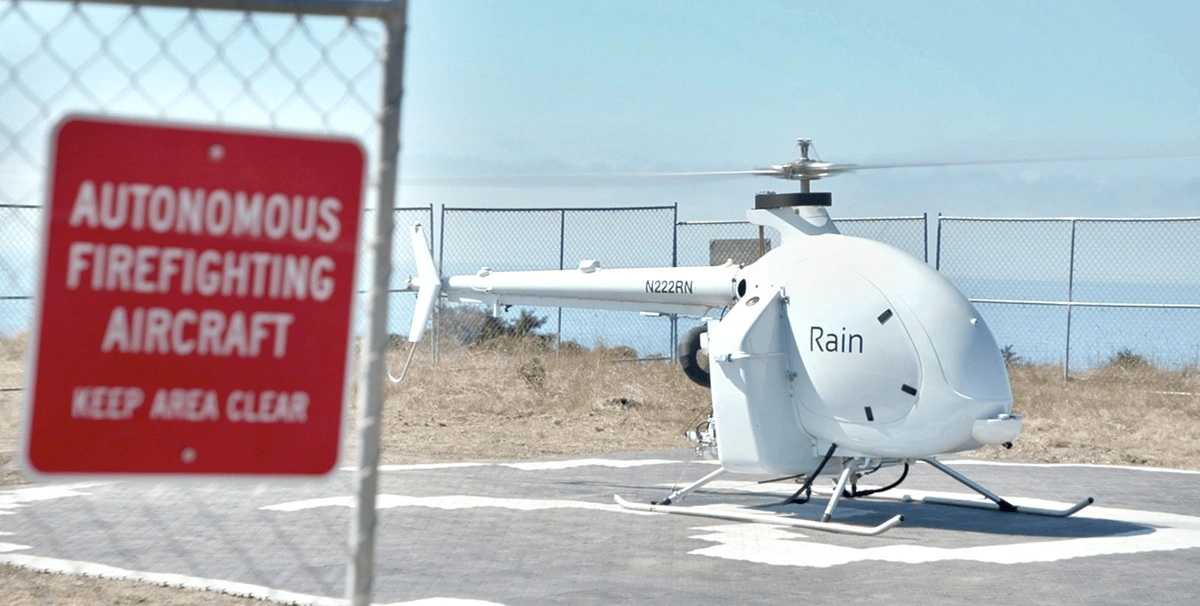
One California startup, aptly named Rain, is using computer vision to fight wildfires.
Rain’s aircraft is able to stay in the air for over an hour.
Their product is an unmanned autonomous helicopter that uses AI and computer vision to deliver water to a wildfire before it grows out of control.
The company’s idea is to put these helicopters in high-risk areas that aren’t staffed by humans 24/7. If a wildfire broke out, the helicopter could be immediately deployed by a pilot at a remote location.
The project will be tested this year on real fires in California and the company projects they’ll build 200 helicopter stations there.
In addition, a team at the University of Cambridge recently developed a computer vision system that allows scientists to monitor forests and carbon sequestration from their smartphones.
The computer vision system developed by the University of Cambridge utilizes LiDAR sensors.
The error rate is 8%, which is lower than the error rate occurring when humans complete the task.
At the same time as it’s being deployed in a wide variety of industries, the technology of computer vision itself is being revolutionized.
Today’s computer vision works by taking an image or series of images in still frames. Then the still frames are analyzed by the computer.
However, one company is imagining computer vision that doesn’t need still frames.
Ubicept, a company formed in 2021, has developed computer vision that can measure individual photons instead of looking at still frames.
That process is faster and more reliable than traditional computer vision.
It’s especially beneficial for situations in which the camera needs to capture objects moving fast or objects in low light.
Ubicept’s computer vision technology excels in low light and fast motion, two areas in which traditional computer vision falls short.
7. Retailers Deploy AI In-Store and Online
The retail sector is one that could potentially reap huge benefits from the use of AI.
Predictions show the market for AI in retail growing at a CAGR of more than 30% through 2028. The market will hit $31.18 billion that year, according to estimates.
As of 2024, 40% of retailers are already using AI in some form.
And the use of AI is continuing to grow.
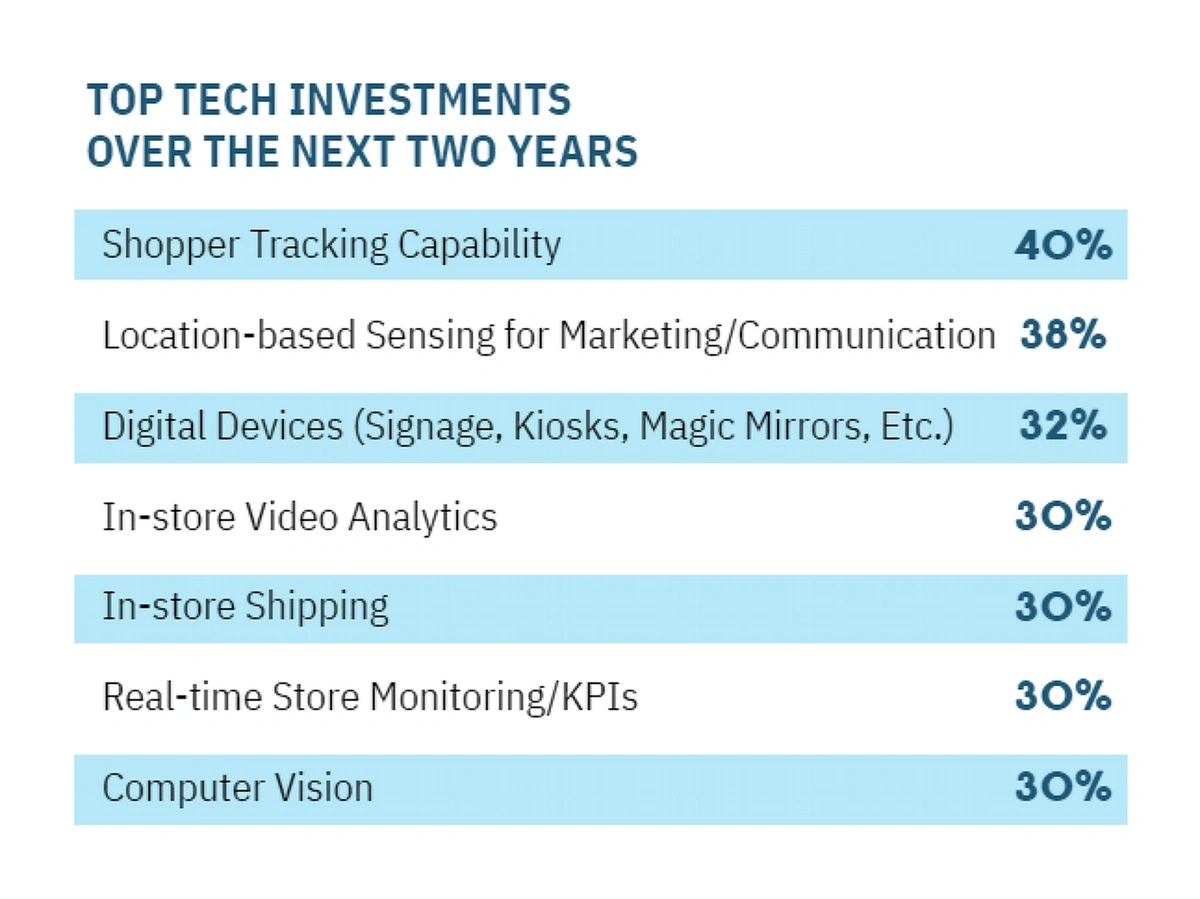
In the Retail Technology Study, 40% of retail organizations said shopper tracking capability was going to be one of their top tech investments within the next two years.
Location-based marketing, digital devices, and computer vision also made the list with more than one-third of retailers saying they’ll focus on those tech solutions in the next two years.
Retail leaders are planning to invest heavily in AI in the next two years.
One of the most obvious uses of AI in retail is at checkout.
Stores like Amazon Go track customers through the store via computer vision. When a person puts an item in a physical cart, the computer vision catches which product it is and adds it to a virtual cart of sorts. When the person leaves the store, their digital wallet is charged accordingly.
Retailers are also using AI for inventory management.
AI systems can monitor stock levels in the warehouse and on shelves. When stock is running low, the system can automatically notify the proper channels and decrease the time it takes to replenish the product supply.
Search volume for “warehouse automation” has increased by 103% over the past 5 years.
McKinsey reports that businesses that adopt AI-enabled supply chains see a 15% improvement in logistics costs and a 35% improvement in inventory levels.
AI also enables retailers to utilize dynamic pricing.
With data from the retailer, competitors, and customers, AI can be used to adjust pricing in real time and maximize profits.
Retailers that use electronic shelf labels and AI-enabled dynamic pricing have the potential to increase profit by 33%.
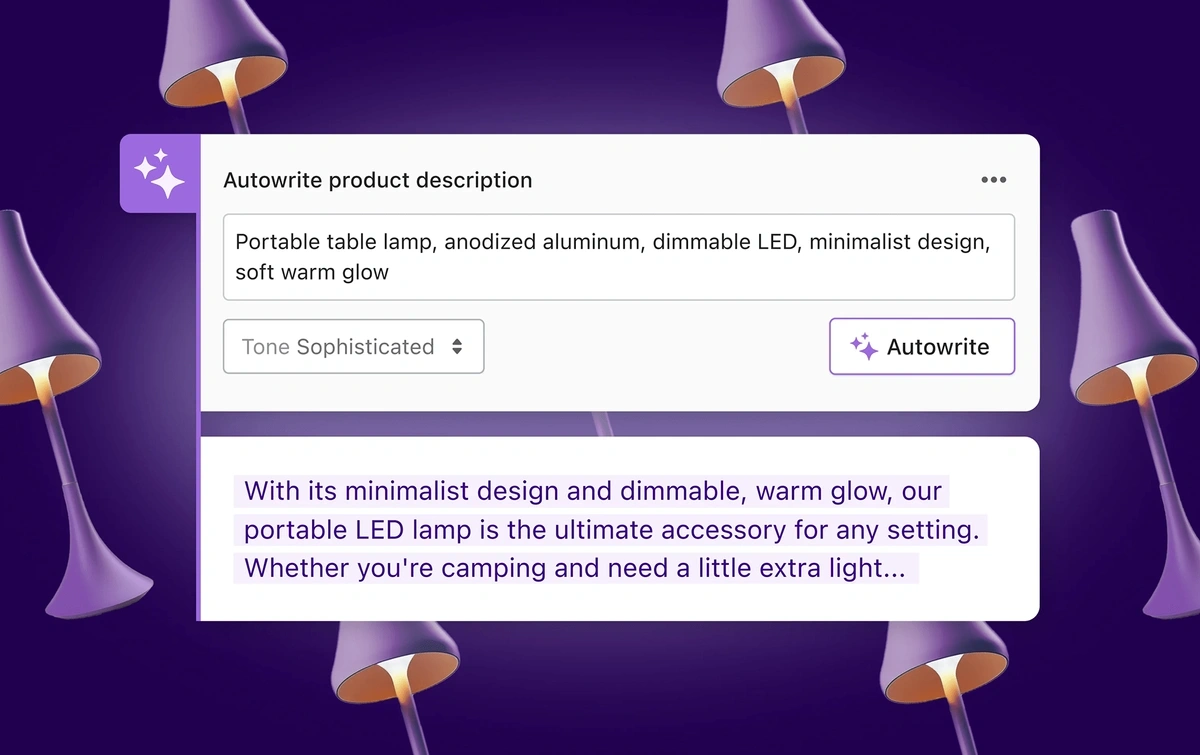
One of the most recent developments for retailers is generative AI.
For instance, Shopify Magic was released in early 2023 as a tool that will write ecommerce product descriptions for retailers.
Shopify Magic enables retailers to create product descriptions in seconds.
Shopify says they’ll be adding more tools with AI in the near future.
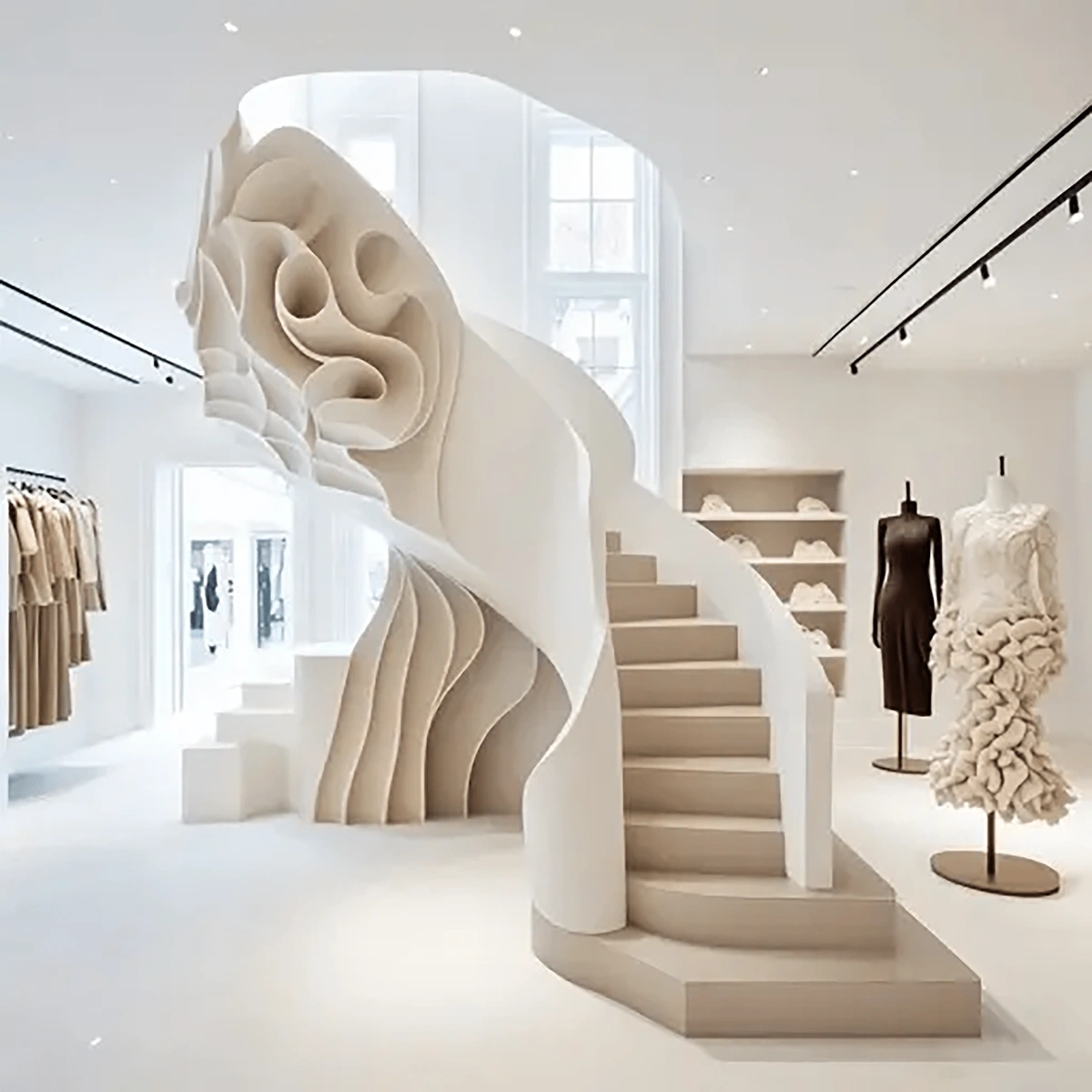
Retailers are also utilizing generative AI to create in-store displays.
By inserting a few prompts into a program like DALL-E, retailers can come up with a visual concept and merchandising imagery.
One retailer said her team typically spends a week brainstorming and creating imagery for a new in-store design.
With AI, they were able to do it in just eight hours.
An example of an AI-generated concept for a luxury fashion store.
Apparel companies are also using generative AI to create hundreds of recommended outfit combinations that appear on their websites and apps.
By working with the company Stylitics, Puma was able to increase conversions by 235% and session duration by 334%.
Stylitics’ AI-powered solution puts together outfit combinations and replaces outfit pieces as they go out of stock.
8. Increasing Potential for AI Risks and Regulations
As AI adoption has increased, the level of risk mitigation has remained the same.
This means that many enterprises aren’t paying attention to the risks associated with AI.
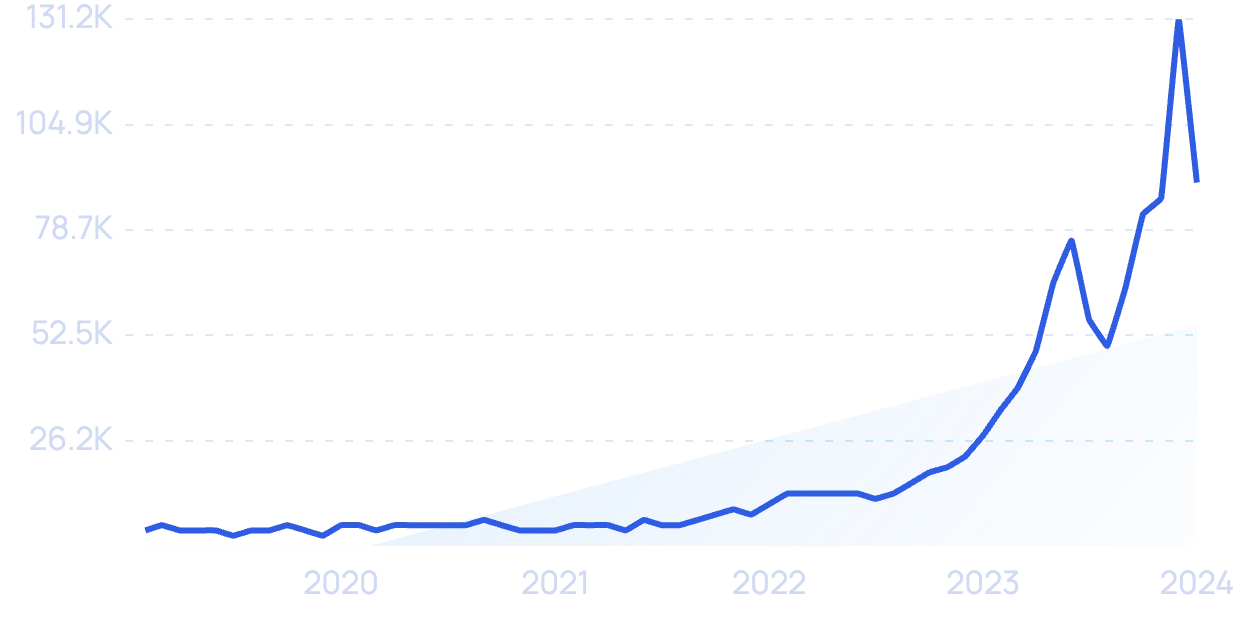
Search volume for “AI risks” is up more than 700% since 2019.
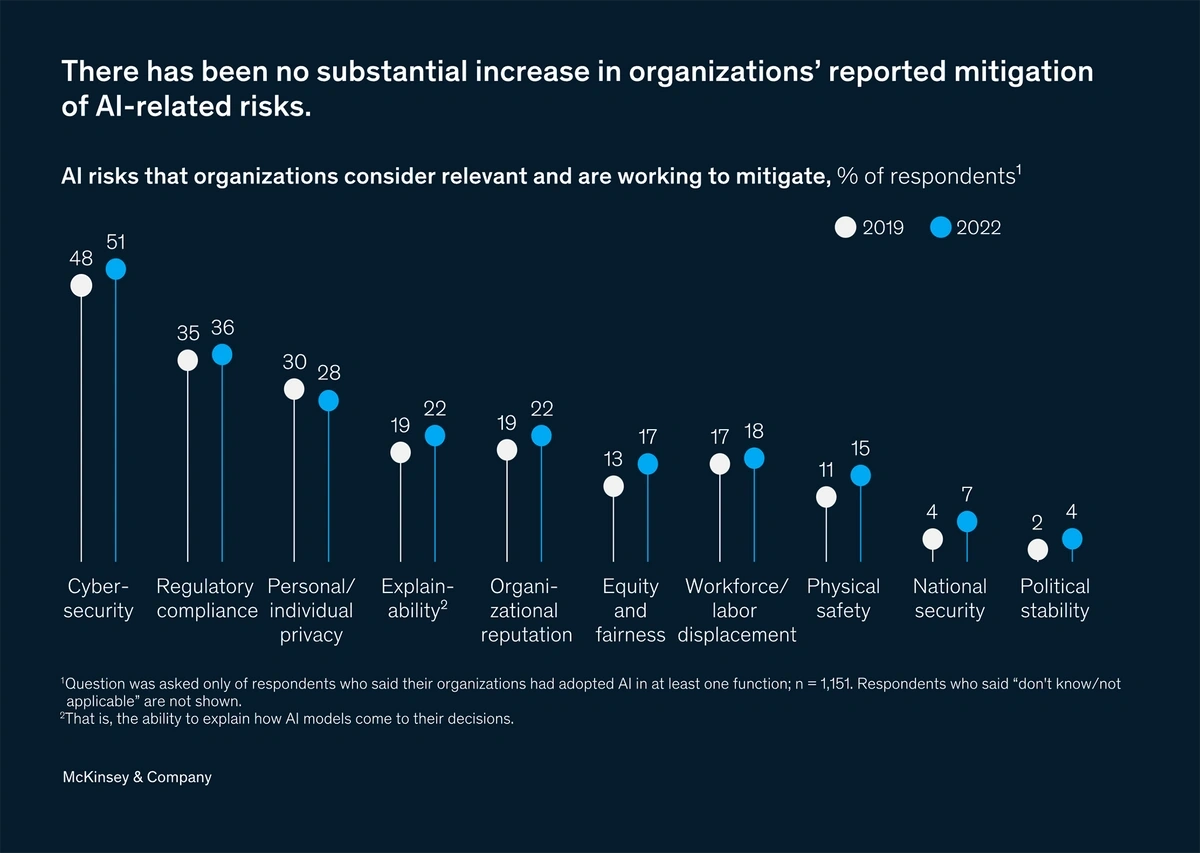
When looking at the past three years, a survey from McKinsey showed no substantial increase in the amount of attention companies are giving any AI-related risks. This includes cybersecurity, regulatory compliance, privacy, and explainability.
McKinsey called the lack of focus on AI risks “concerning.”
The list of potential risks is long — and it keeps growing.
The Wharton School created an extensive paper outlining the risks of using AI in business. Poor data quality, data attacks, lack of transparency, and bias were just a few of the topics discussed.
In recent months, there have been signs from companies, consumers, and the US government showing a shifting focus toward these risks and AI safety.
Another report from McKinsey shows that 72% of consumers believe that it’s important to know a company’s AI policy before they make a purchase.
In that same survey, 55% of business leaders said they’d suffered an AI incident in the past three years.
In another survey, nearly two-thirds of people in the US said they wanted regulations placed on AI in the near future.
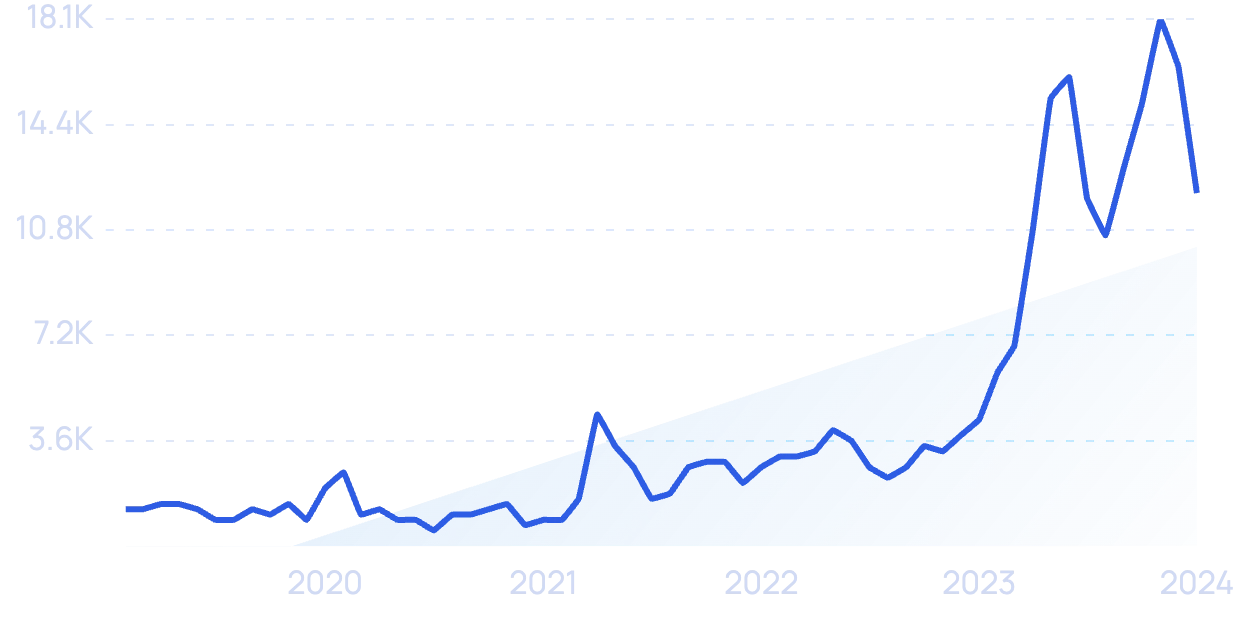
Search volume for “AI regulation” has increased by more than 857% in recent years.
However, outside of the EU, governments haven't been quick to offer up any laws or oversight.
As of May 2024, there haven’t been any bills proposed in Congress that would limit the reach of AI.
In late 2022, the White House released an AI Bill of Rights that was aimed at encouraging companies to police the use of AI within their ranks, but it has no authority.
The AI Bill of Rights encourages businesses to adequately assess their AI systems and correct potential problems.
However, federal agencies are upping their involvement in AI regulation.
The FTC, FDA, and CFPB are all acting in some way to curb the use of unethical AI.
In one case, the FTC took action against Weight Watchers for improperly collecting information from children and creating AI models from the data.
More federal-level action on AI regulation has taken place in Europe.
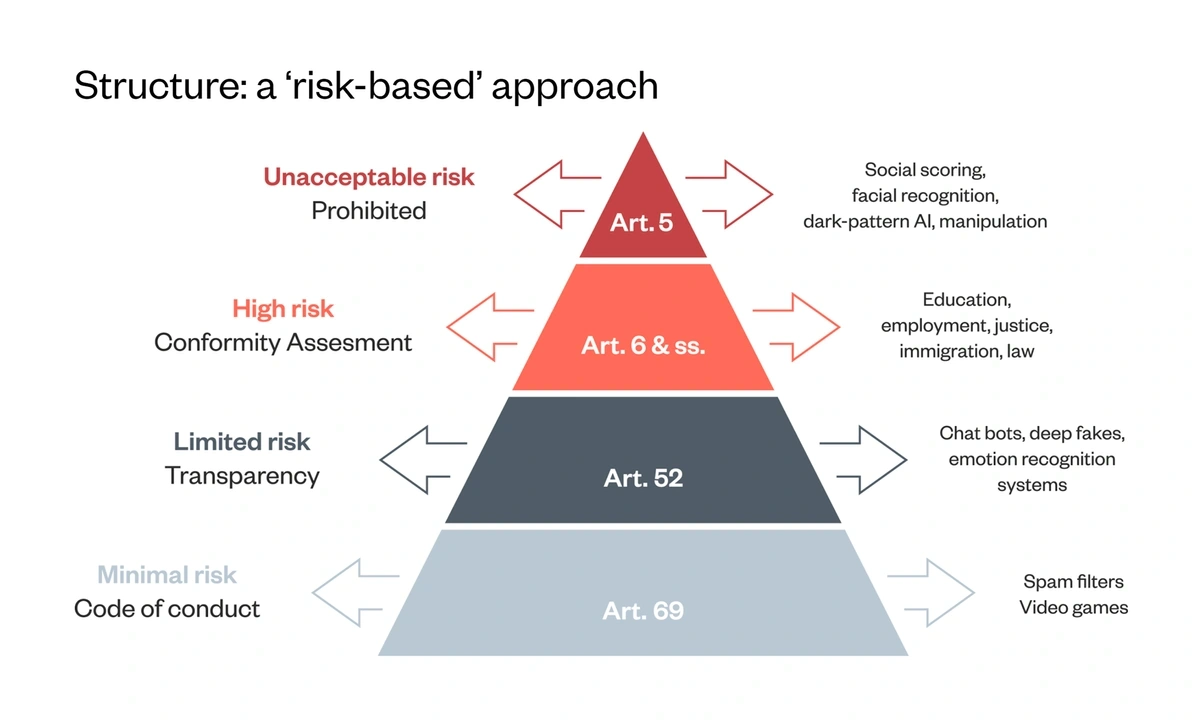
Search interest in “AI Act” is up more than 2,200%.
The AI Act looks at applications based on their level of potential risk.
Conclusion
That wraps up our list of the top AI trends to watch over the next few years.
Artificial intelligence, and the tech solutions it powers, will undoubtedly change the way businesses and individuals operate in the world.
In many industries, AI will drive the development of methods and processes that we’ve never seen before. This has the potential to increase efficiency, lessen the impact of the labor shortage, and prompt businesses to create new revenue streams.
However, the true risks of AI remain to be seen. In the coming years, the vulnerabilities of AI may be exposed, and governments, agencies, and consumers will have to decide how to balance the risks and benefits.
Stop Guessing, Start Growing 🚀
Use real-time topic data to create content that resonates and brings results.
Exploding Topics is owned by Semrush. Our mission is to provide accurate data and expert insights on emerging trends. Unless otherwise noted, this page’s content was written by either an employee or a paid contractor of Semrush Inc.
Share
Newsletter Signup
By clicking “Subscribe” you agree to Semrush Privacy Policy and consent to Semrush using your contact data for newsletter purposes
Written By


Josh is the Co-Founder and CTO of Exploding Topics. Josh has led Exploding Topics product development from the first line of co... Read more