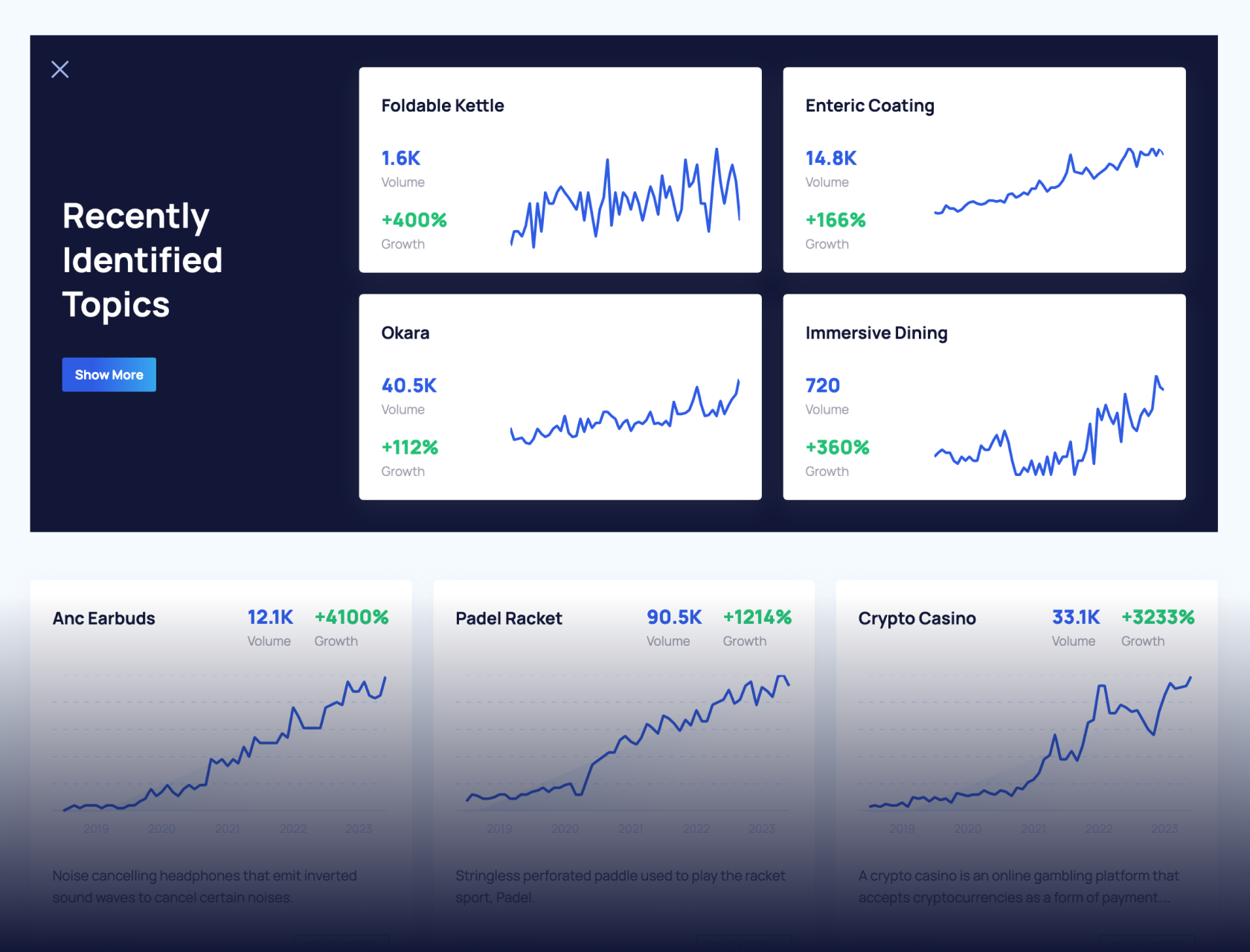
Get Advanced Insights on Any Topic
Discover Trends 12+ Months Before Everyone Else
How We Find Trends Before They Take Off
Exploding Topics’ advanced algorithm monitors millions of unstructured data points to spot trends early on.
Keyword Research
Performance Tracking
Competitor Intelligence
Fix Your Site’s SEO Issues in 30 Seconds
Find technical issues blocking search visibility. Get prioritized, actionable fixes in seconds.
Powered by data from
Latest Blog Posts
Featured Case Studies
See what's trending before everyone else
Each week, we'll send you our best Exploding Topics. Plus, expert insight and analysis.
7 Web Scraping Use Cases For Alternative Data In Finance
Web scraping has become an indispensable tool in the realm of investing, serving as a critical gateway to alternative data and a driver of alpha in public and private markets.
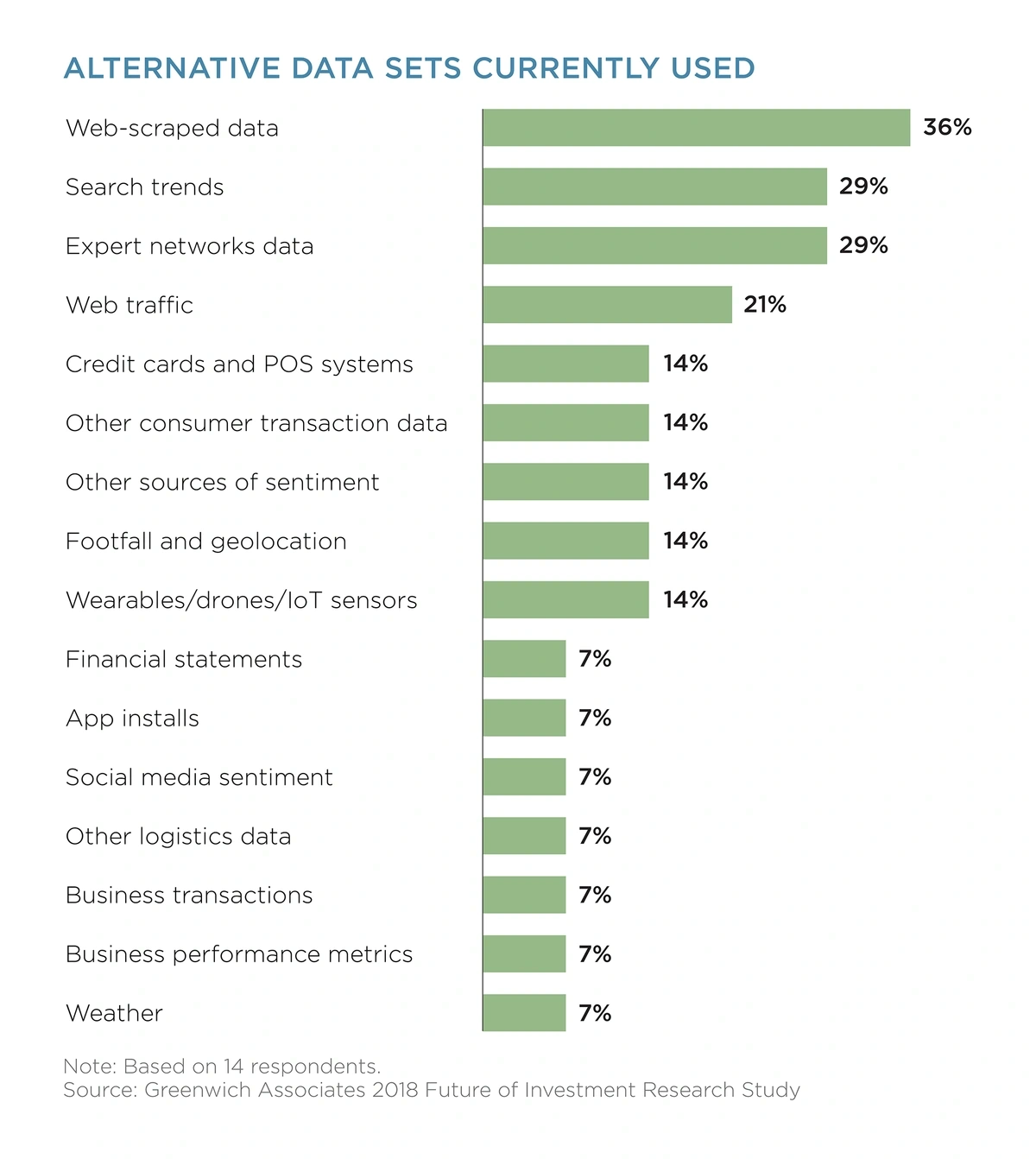
As Thomson Reuters research shows, the average investment firm invests $900,000 annually in alternative data, with web-scraped data emerging as the frontrunner.
Source: Thomson Reuters & Greenwich Associates
Web scraping refines unstructured data gathered from public sources into structured, actionable insights, steering investors toward untapped opportunities and strategies.
Here are a few case studies showcasing how web scraping fuels alternative data:
1. Market Sentiment
For portfolio managers and capital allocators, web scraping reveals one of the most valuable facets of alternative data: real-time market sentiment.
Analyzing the sentiment behind a tweet—positive, negative, neutral—can forecast stock trajectories based on public perception.
This method's potency was exemplified in a study analyzing over 4 million tweets about the DJIA, NASDAQ, and major tech firms, revealing a strong correlation between Twitter sentiment and stock prices.
Furthermore, a 2022 survey highlighted that over 61% of hedge funds were integrating social media data into their strategies that year, from 25% in 2017.
Source: Arxiv
2. Alpha Generation
Web scraping enables investors to stay ahead of traditional market data, accessing a stream of real-time data for more timely decision-making.
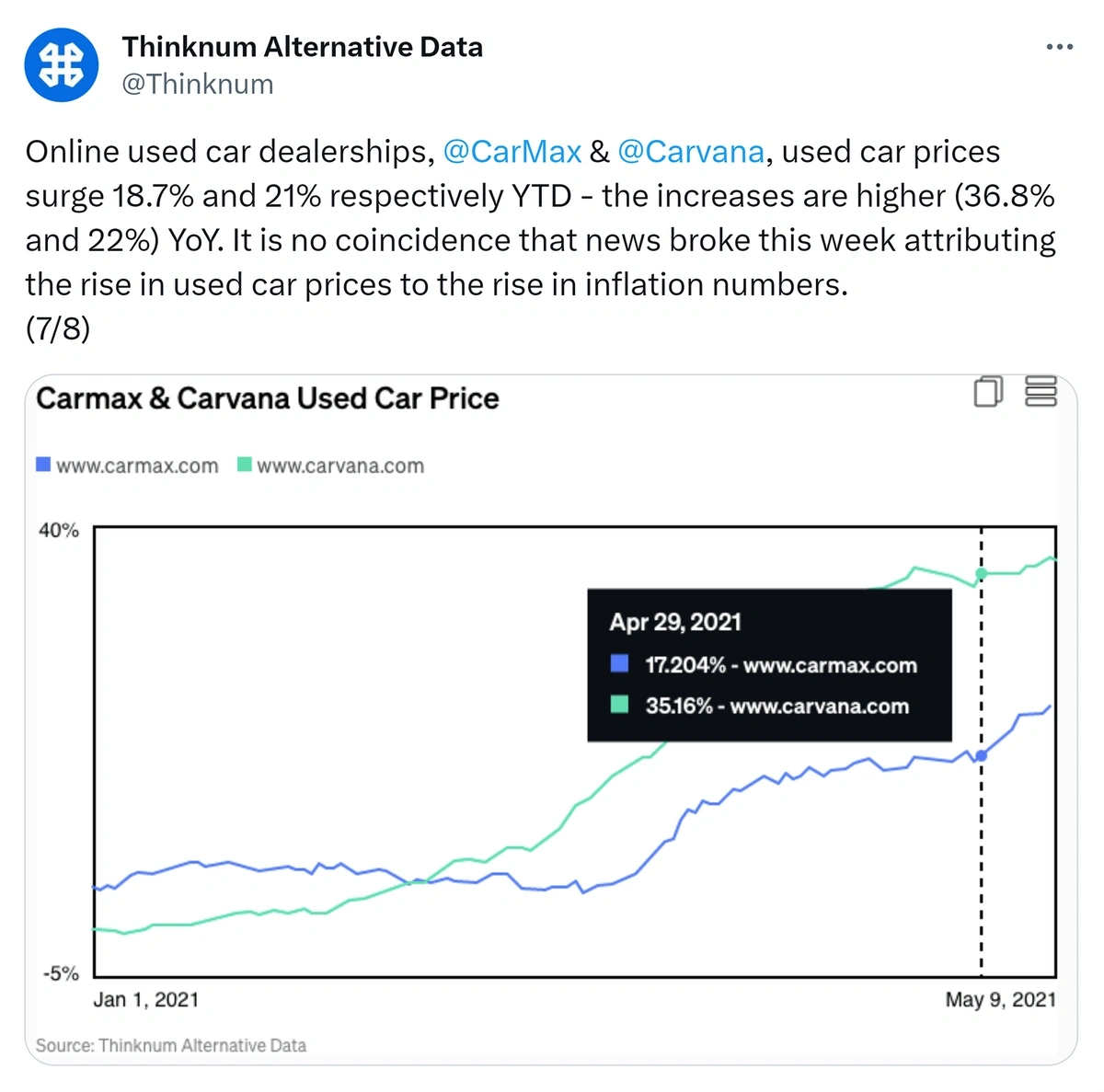
During the COVID pandemic, used car prices and the stock prices of online dealerships like Carvana (CVNA) soared.
As the effects of the pandemic subsided, Carvana’s stock fell 89% from its 2021 peak.
Investors with access to Thinknum's car inventory data would have been forewarned. Thinknum scrapes the web to track real-time inventory of all major online dealerships.
Dwindling inventory would have signaled lower sales and profits to tech-savvy investors, who could adjust their investment strategy accordingly.
Source: Twitter
3. VC Scouting
Exploding Topics is a trend-spotting tool that is changing how investors identify opportunities.
The company’s technology continuously crawls a multitude of online data sources such as social media, company websites, news outlets, blogs, and online communities.
This approach allows investors and entrepreneurs to find rapidly-growing industries, companies, and trends.
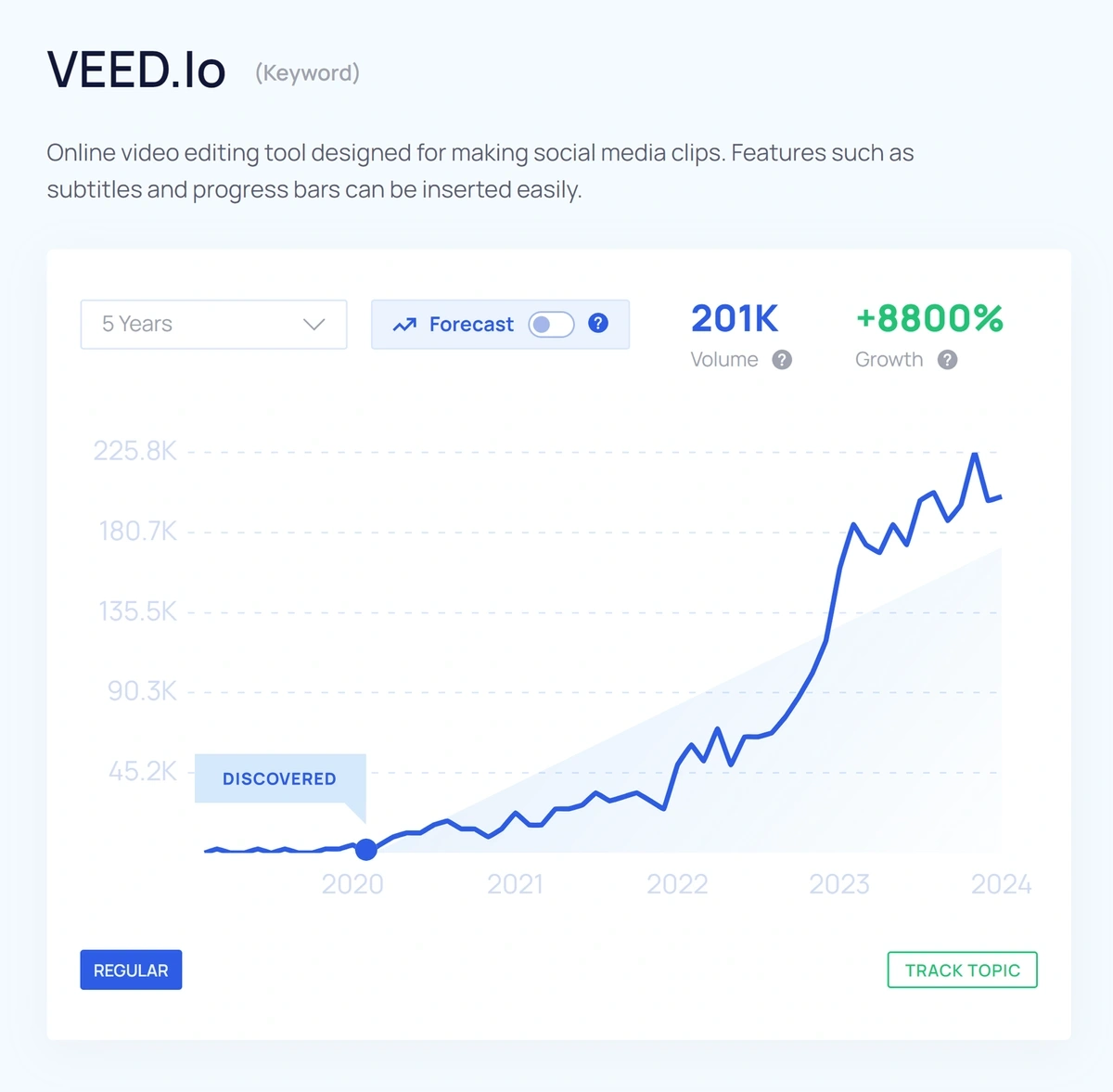
A notable example is VEED.io, an online video editor identified early by Exploding Topics. When it was first flagged in December 2020, VEED.io’s website received 137,000 visits a month. Fast forward three years, and organic search results jumped nearly 30-fold.
Source: Exploding Topics
4. Competitive Analysis
74% of U.S. product searches start on Amazon.
Scraping pricing from Amazon and other platforms is pivotal to e-commerce players, as it allows them to leverage Amazon's extensive product selection and consumer reliance on its pricing as a benchmark.
Armed with alternative data, e-commerce companies can tailor dynamic pricing strategies and marketing tactics with an eye on the competition.
Insights extend beyond pricing; scraping tools like SpyFu reveal competitors' pay-per-click (PPC) strategies, providing data on keyword pricing and traffic and enabling smarter decisions on budget allocation.
Source: SpyFu
5. Consumer Intelligence
For companies large and small, it’s not enough to take reviews at face value.
When web scraping is coupled with natural language processing (NLP), companies are able to unlock deeper insights into customers’ wishes and pain points.
While pet company Chewy’s 78% 5-star rating on TrustPilot is impressive, deeper analysis was crucial to inform improvements in customer experience.
Chewy used web scraping tool MonkeyLearn to build granular sentiment analysis reports. By processing thousands of reviews, MonkeyLearn enabled Chewy to further refine its services and product strategy.
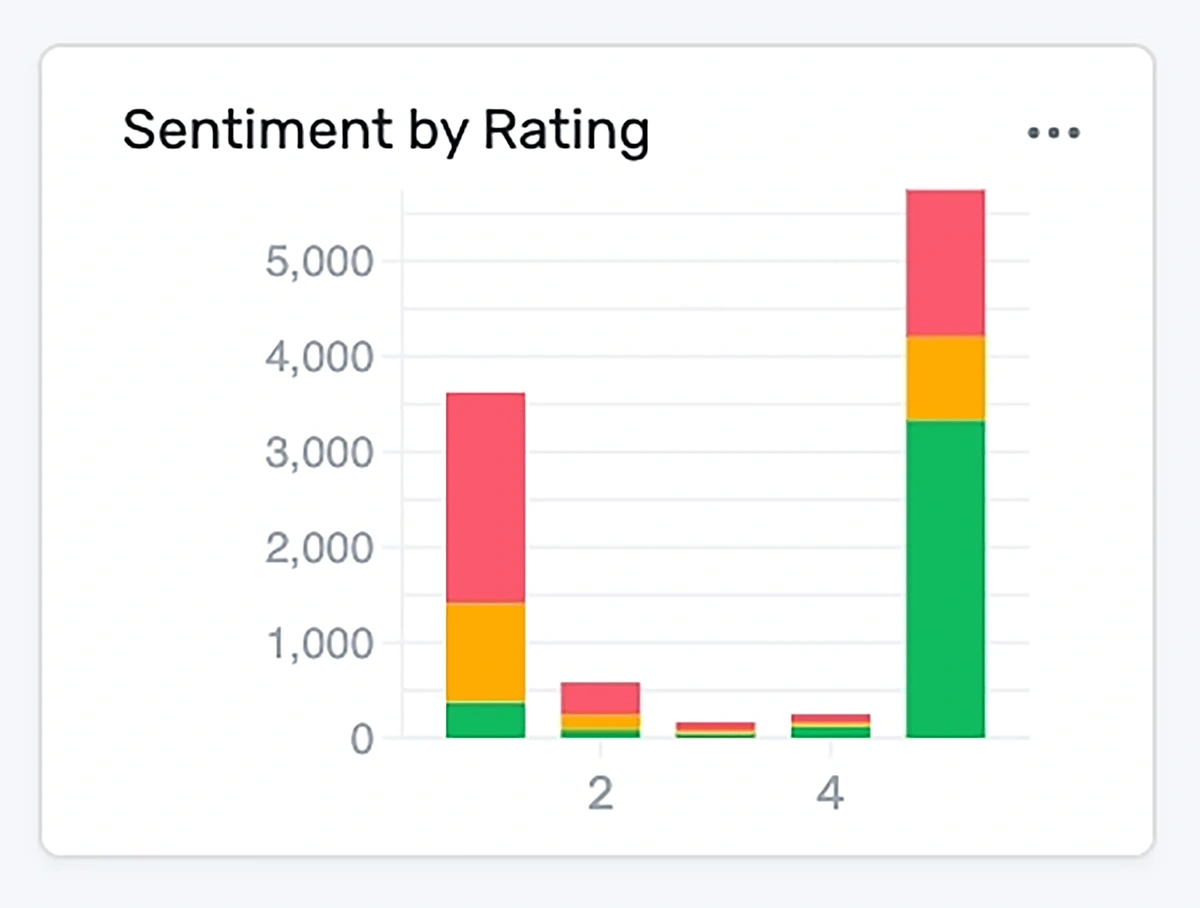
For example, MonkeyLearn’s dashboard drills down into how sentiment changes over time, by review rating, and by topic.
Sentiment by review rating exposes a goldmine of nuanced information unavailable elsewhere: the negative sentiment sections of positive reviews (and vice versa) offer unique perspectives of customers’ psychology.
Source: MonkeyLearn
Sentiment by topic, in the same vein, pairs sentiment with specific product and service features, allowing the company to map out what’s working and what’s not.
6. Real Estate Investing
Web scraping is changing how institutional real estate investors gather market insights.
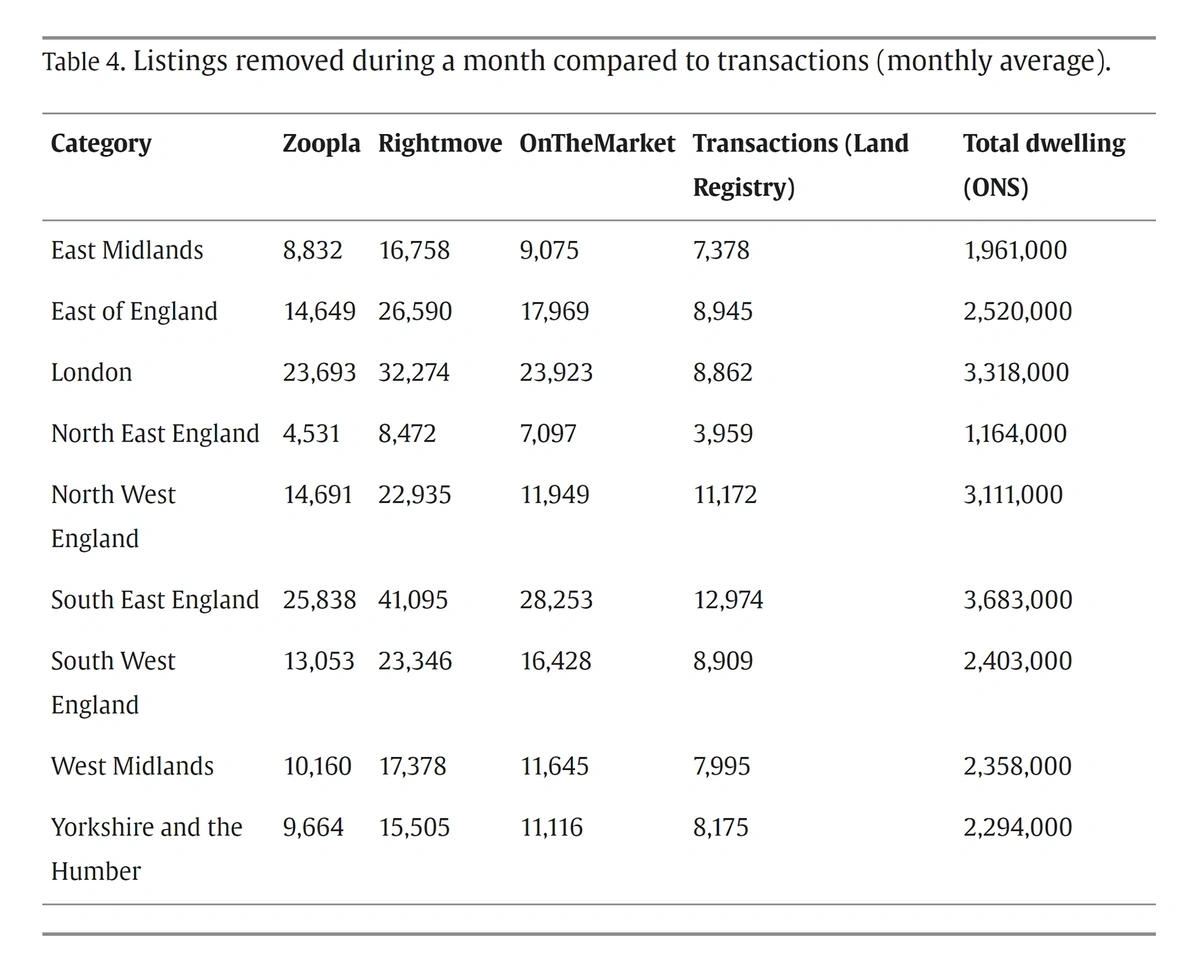
By extracting data daily from UK real estate websites, researchers built a rich, granular database that provided far more value to investors than traditional housing statistics.
This approach offered a unique perspective to sellers, enabling them to monitor new listings and price fluctuations over time.
Additionally, matching scraped selling prices with official transaction records revealed how much bargaining power buyers had at a given point in time - a novel insight.
During the COVID-19 crisis, these tools proved invaluable, highlighting market stasis, seller caution, and diverging price trends between rural areas and London.
Source: Science Direct
7. Due Diligence
When VC and private equity firms deploy capital, due diligence extends beyond financials to include a thorough online vetting of target companies and their key personnel.
Web scraping plays an important role in this process, enabling funds to gather data from public records, lawsuits, and social media.
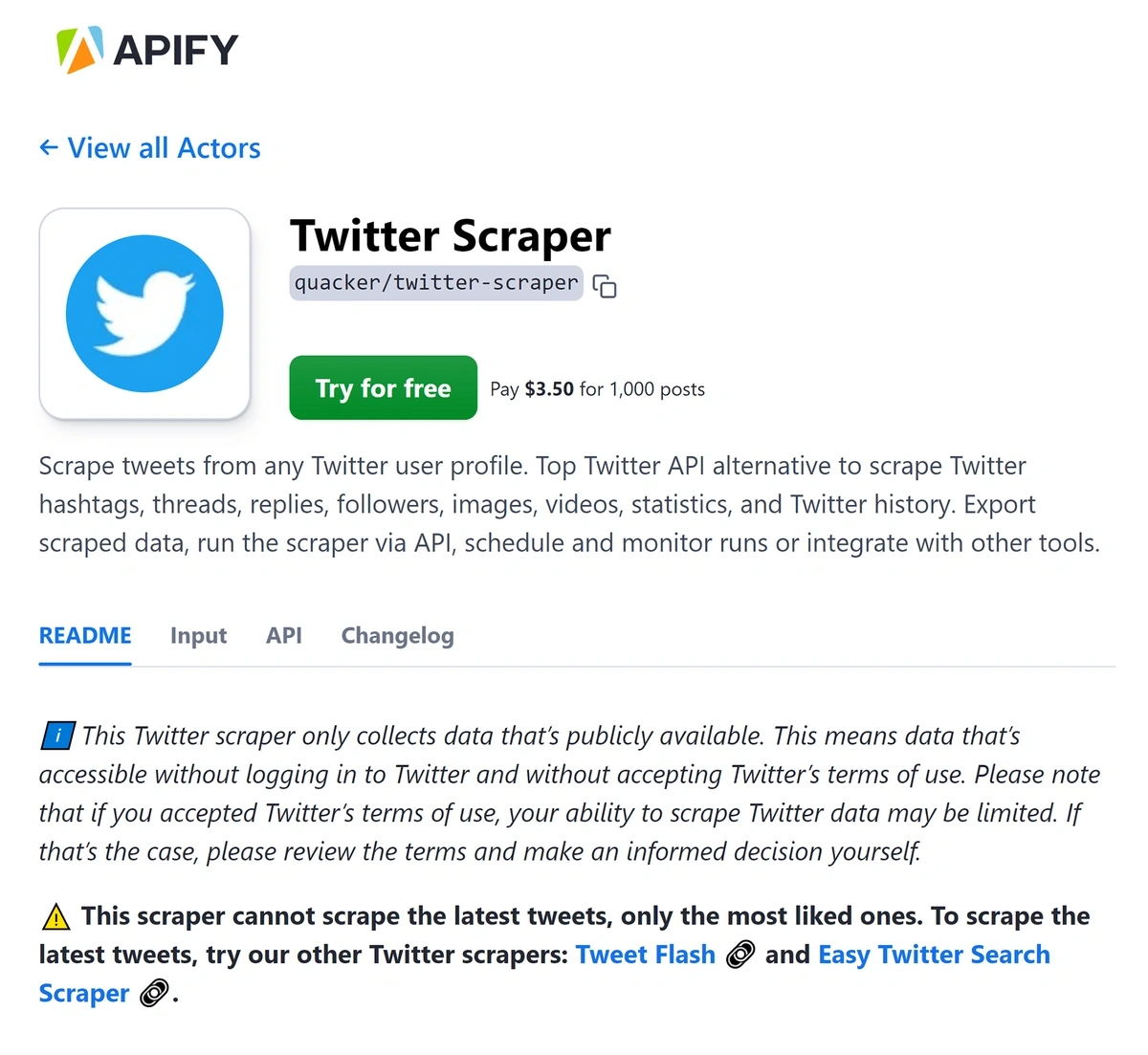
Tools like Apify's Twitter Scraper monitor a company's public sentiment, flagging potential issues related to founders' or staff's online behavior.
This approach offers investors a comprehensive understanding of potential risks, ensuring informed investment decisions.
Source: Apify
Trends and Challenges
Several key trends and challenges stand to shape the future of web scraping and alternative data.
The integration of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning is enhancing the sophistication of web scraping tools, enabling more advanced data analysis.
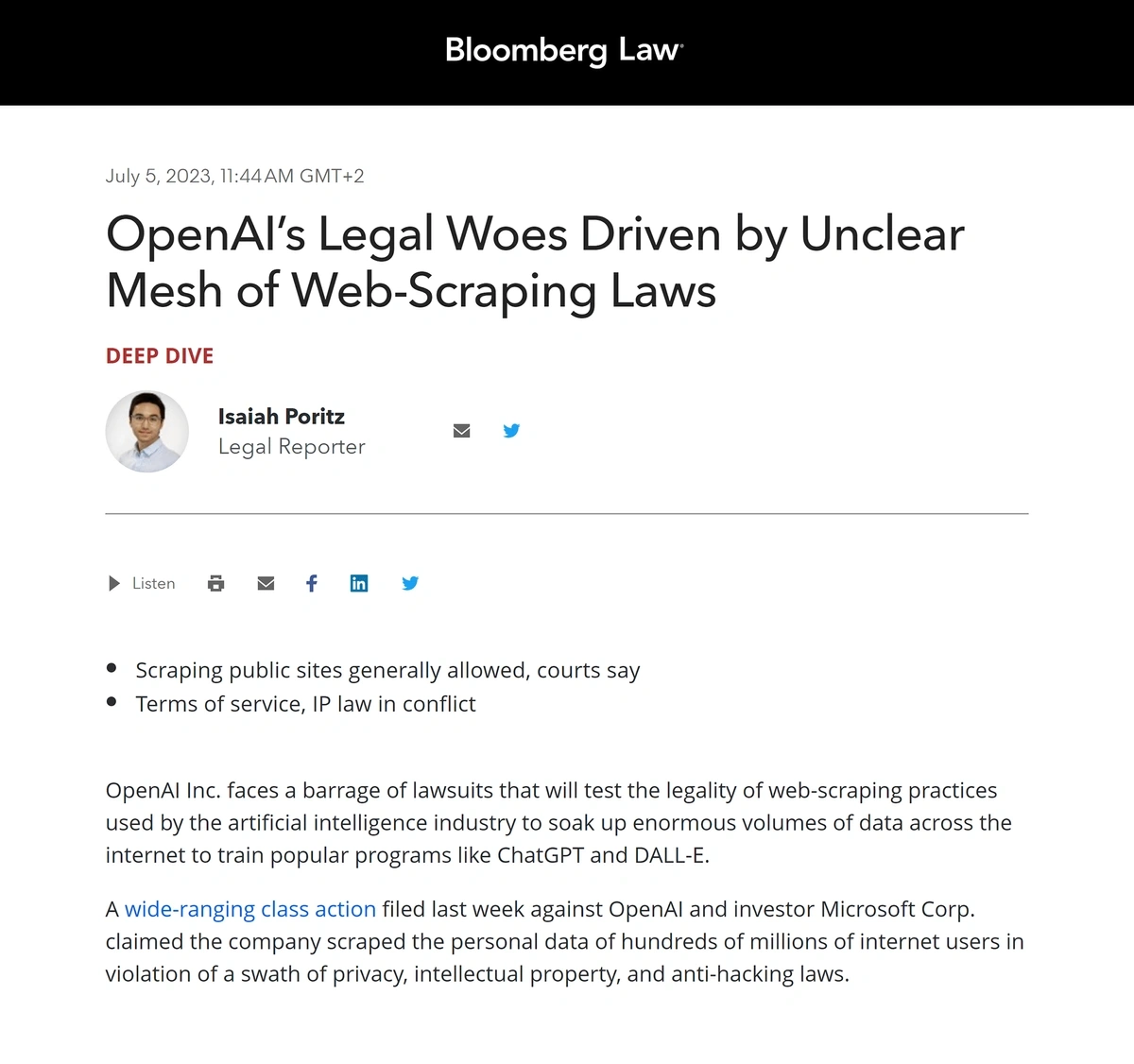
At the same time, AI systems utilize web scraping in order to train their large language models (LLMs) with a vast amount of information. The legal landscape surrounding access to this data remains complex and sometimes unclear.
The development of improved anti-scraping technologies by websites poses additional challenges, leading to an ongoing adaptation between scraping methodologies and countermeasures.
Source: Bloomberg Law
Conclusion
Regardless of legal and technical challenges, web scraping has proven transformative across many industry sectors.
Its ability to provide real-time market insights, to uncover competitive dynamics, and to delve into consumer psychology affirms its place as the main driver of alternative data.
The narratives and case studies presented in this article showcase its indispensability in today's data-driven investment landscape.
Stop Guessing, Start Growing 🚀
Use real-time topic data to create content that resonates and brings results.
Exploding Topics is owned by Semrush. Our mission is to provide accurate data and expert insights on emerging trends. Unless otherwise noted, this page’s content was written by either an employee or a paid contractor of Semrush Inc.
Share
Newsletter Signup
By clicking “Subscribe” you agree to Semrush Privacy Policy and consent to Semrush using your contact data for newsletter purposes
Written By


Josh is the Co-Founder and CTO of Exploding Topics. Josh has led Exploding Topics product development from the first line of co... Read more