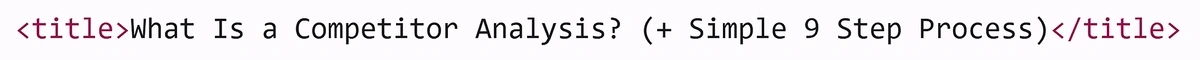Get Advanced Insights on Any Topic
Discover Trends 12+ Months Before Everyone Else
How We Find Trends Before They Take Off
Exploding Topics’ advanced algorithm monitors millions of unstructured data points to spot trends early on.
Keyword Research
Performance Tracking
Competitor Intelligence
Fix Your Site’s SEO Issues in 30 Seconds
Find technical issues blocking search visibility. Get prioritized, actionable fixes in seconds.
Powered by data from
13 Ways to Improve On Page SEO (+ Free Checklist)
On page SEO can be your ticket to improving your rankings in search results.
Better rankings can lead to more sales, better brand recognition, and a larger customer base.
Today, we’ll show you how to improve your on page SEO with straightforward tips you can implement without hiring an expert.
Make a copy of our free on page SEO checklist.
As you read through this guide, check off the items in your checklist to make sure your page is completely optimized.
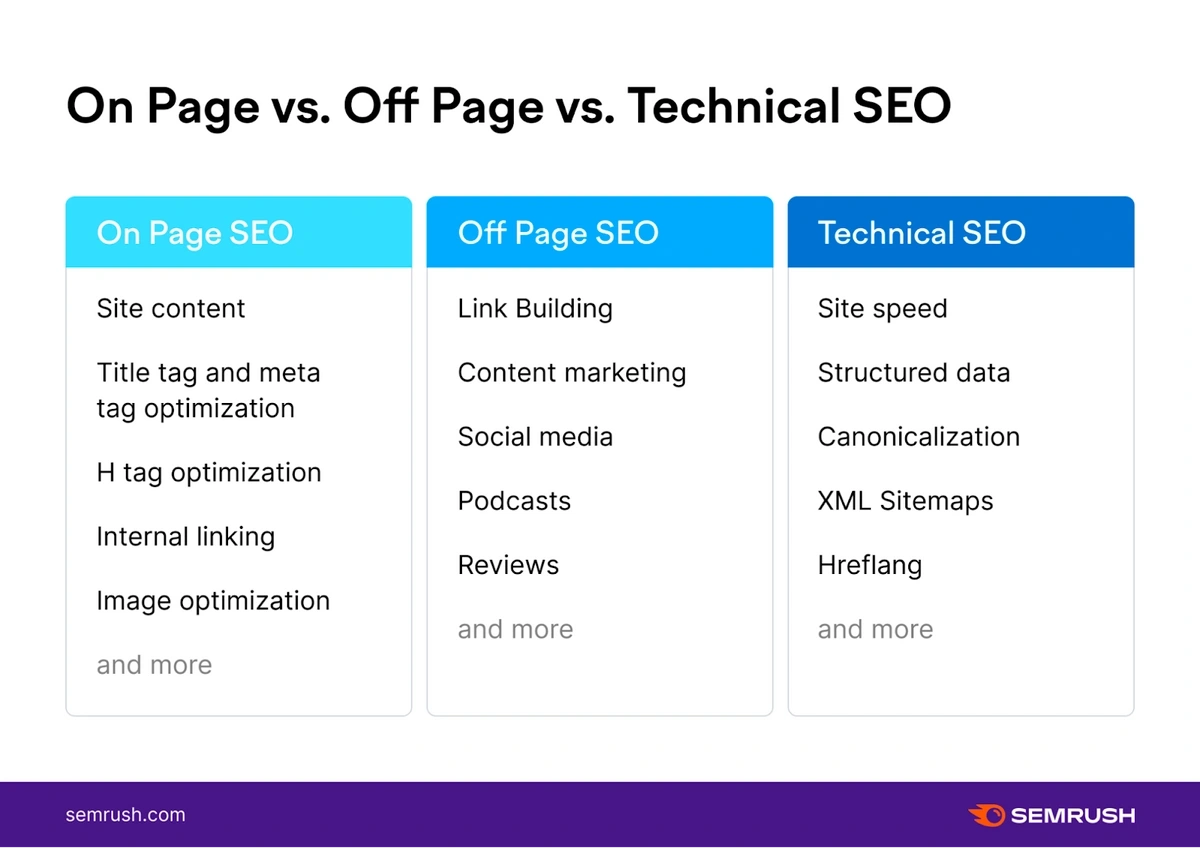
What Is On Page SEO?
On page SEO (also known as on-site SEO) involves optimizing your web page and its content for search engines. This helps it to rank higher in search results.
For example, one on page SEO technique is adding keywords to your content to help search engines understand what the page is about.
Other types of SEO include off page SEO—the activities you do outside of your website to improve your rankings. This might include link building (getting backlinks from other websites to your site), or technical SEO.
Why Is On Page SEO Important?
Improving your on page SEO can help boost your rankings in search engine results pages (SERPs).
And you can drive more traffic to your site through those higher rankings.
Good on page SEO can also improve the overall user experience on your site.
For example, keyword-rich headers within blog posts can help people find specific sections in your article. Users may be more likely to click around and become a follower of your brand when they can easily find the information they’re looking for.
And adding descriptive alt text to your images makes them more accessible to a wider audience.
Get More Search Traffic
Use trending keywords to create content your audience craves.
13 Ways to Improve On Page SEO
In Google Drive, save our free on page SEO checklist and run through the steps below.
The checklist has a space for you to check off each item as you complete it.
1. Include Keywords in Your Title Tag
Search engines use title tags to help them understand what a page is about. Include your target keyword (the keyword you want to rank for) in your page’s title tag.
A title tag is an HTML element that provides the title of a web page. Like this:
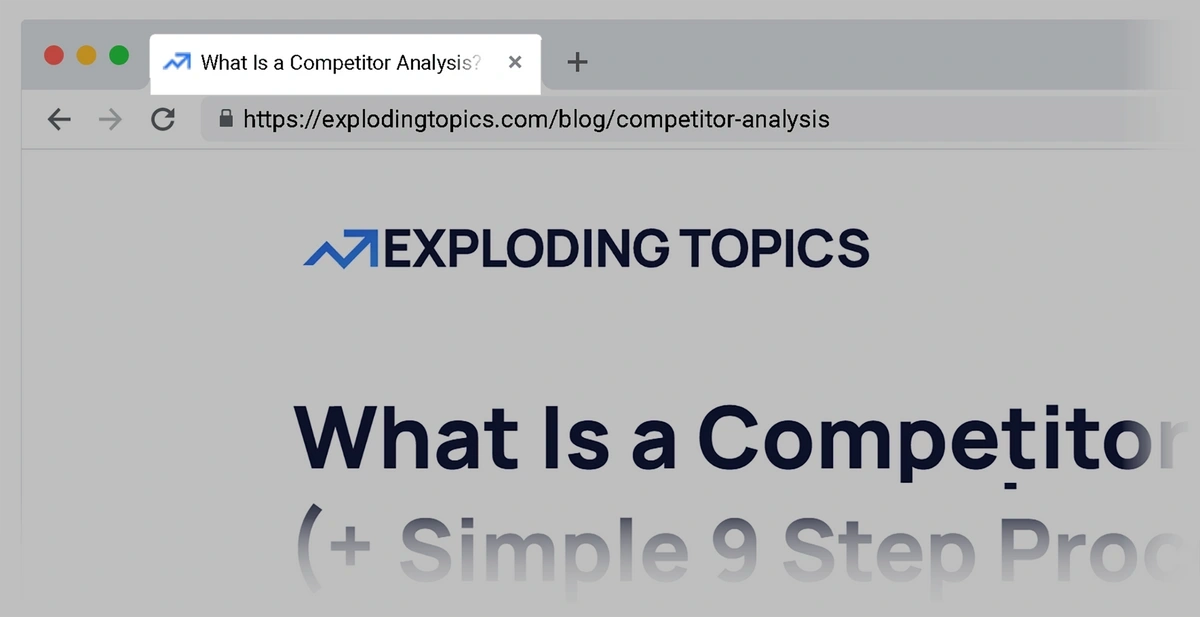
It’s not visible on the actual web page. But it can appear on your browser tab:
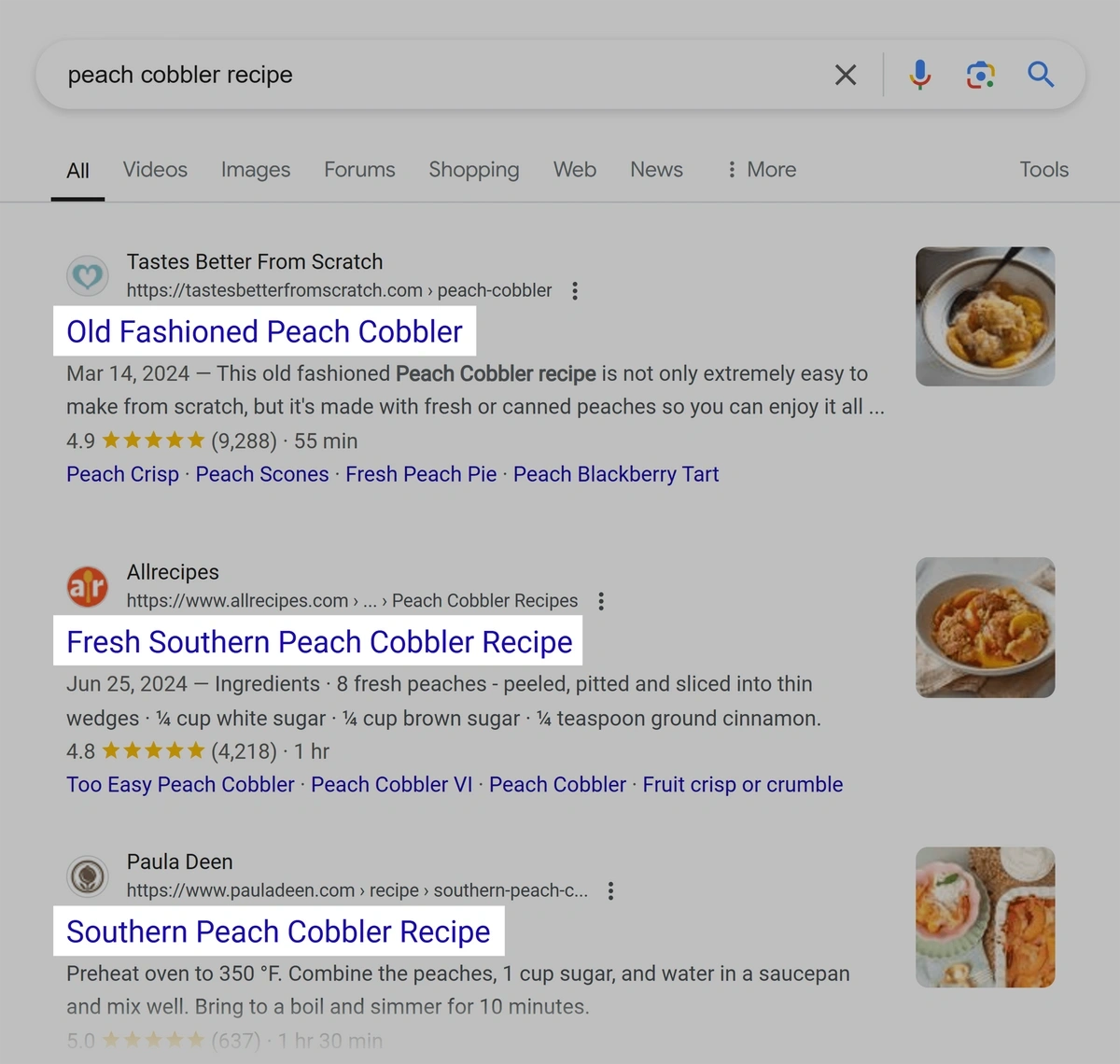
Search engines may also display your title tag in search results:
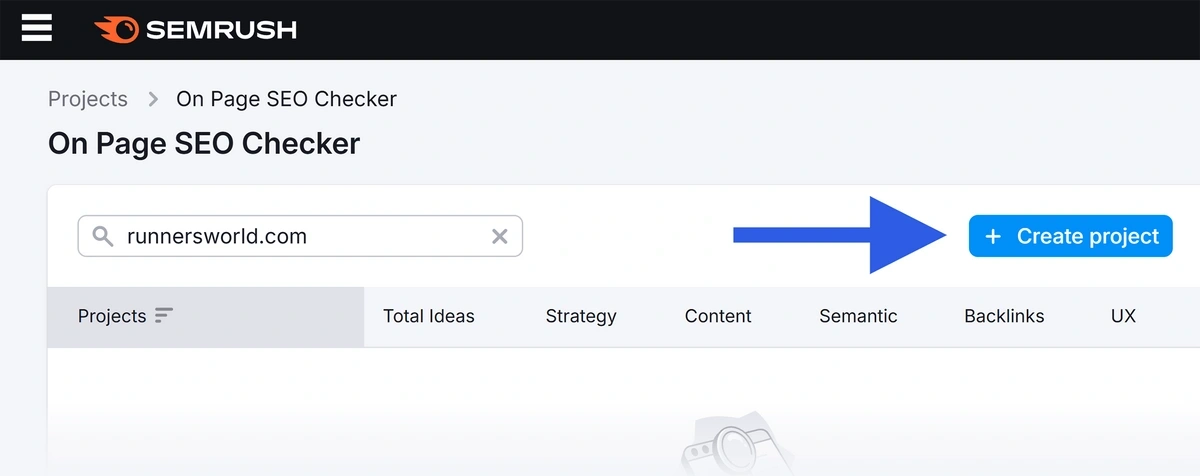
The Semrush On Page SEO Checker analyzes all your page’s title tags and tells you which ones to optimize for target keywords.
To check your title tags, open the tool and click “+ Create project.”
Next, configure the On Page SEO Checker for your site.
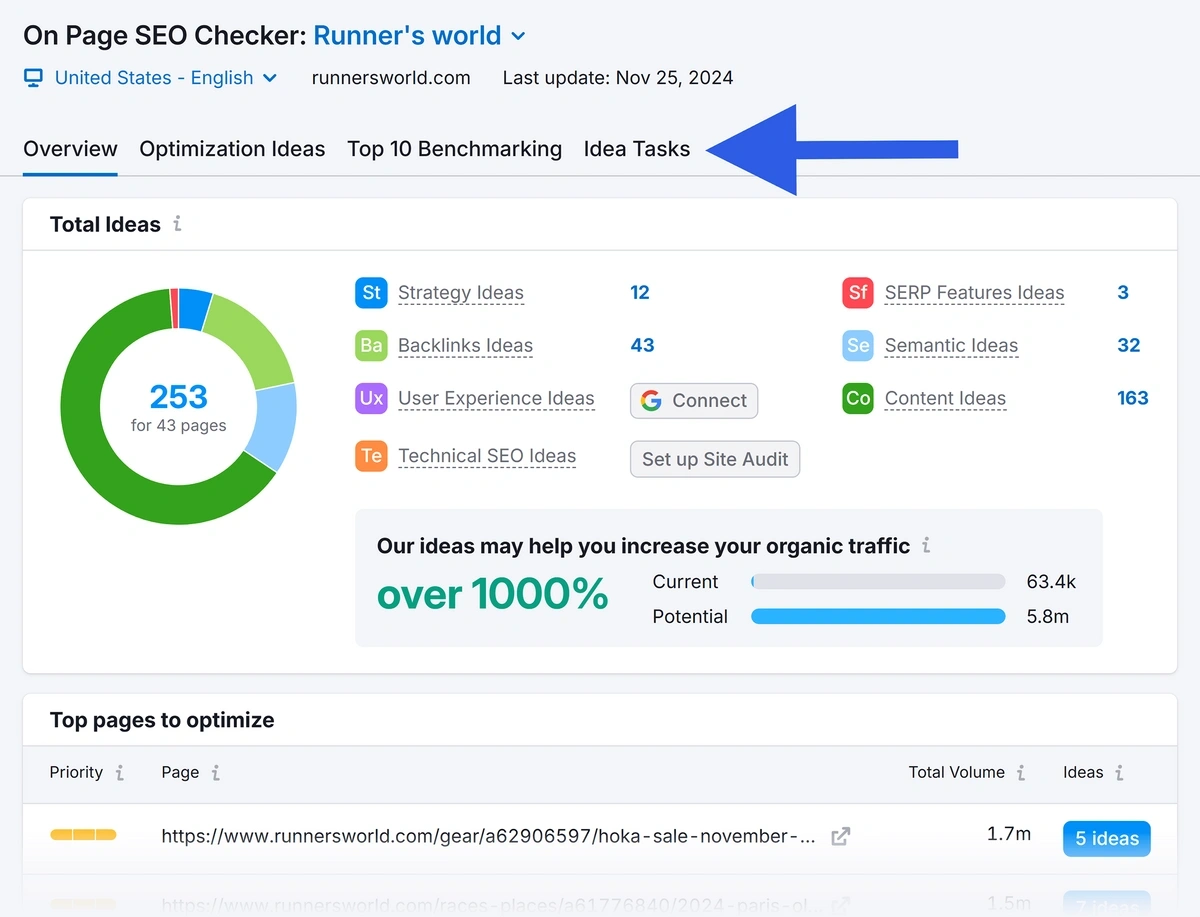
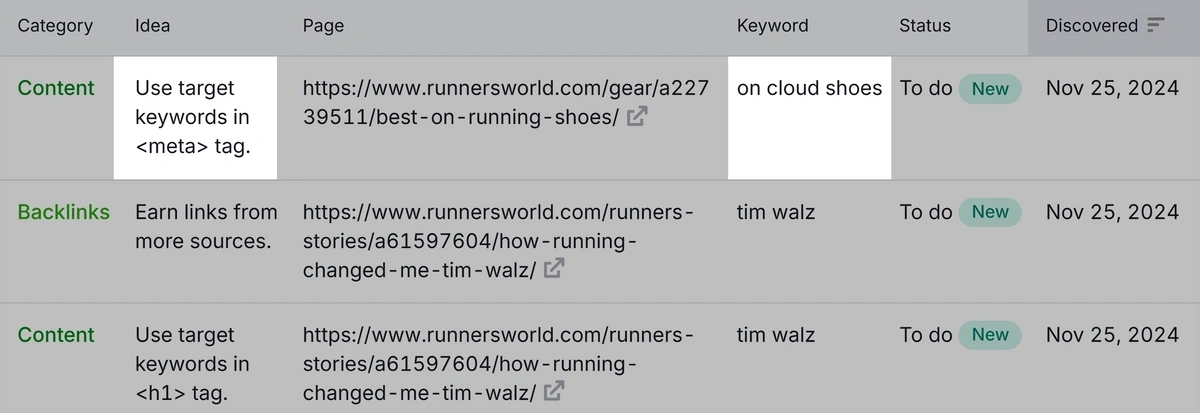
You’ll then see a page like the image below. Click the “Idea Tasks” tab.
Scroll to the list of ideas. Look for “<title> tag” in the “Idea” column and apply these ideas to your title tags. The “Keyword” column tells you which keywords to add.
Here are some other ways to optimize your title tags:
- Keep title tags between 50 and 60 characters: Search engines may truncate them in the SERPs if they’re too long
- Make each title tag unique: This ensures users and search engines know the purpose of each page
- Target one keyword within each title tag: Adding too many keywords to a title tag can confuse users and search engines as to what the page is about
- Make your title tag similar to your H1 tag: Similar titles and H1 tags (see below) reinforce what your page is about to both users and search engines
2. Optimize Your H1 Tag
H1 tags are your web page’s main title. They appear on your site for users to see (unlike title tags).
Including keywords helps people and search engines understand what your page is about. Like this H1 tag for a blog post:
Semrush’s On Page SEO Checker also identifies which pages have H1s worth optimizing.
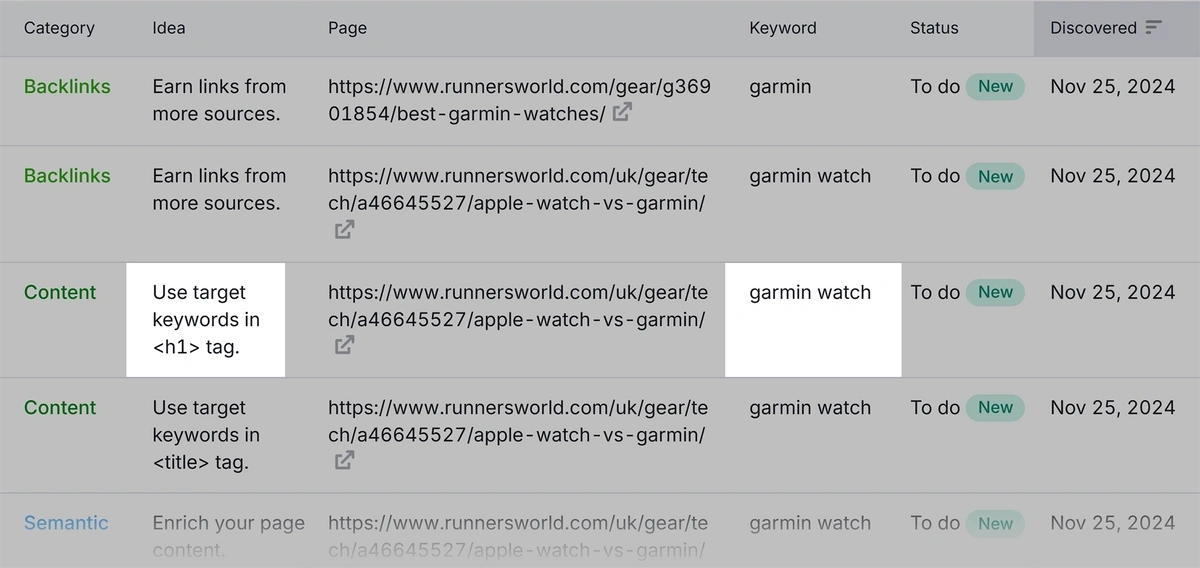
Head back into the “Idea Tasks” tab in the On Page SEO Checker.
Look through the “Ideas” column for H1-tag-specific ideas. Again, the “Keyword” column tells you which keyword to use in your H1 tag.
3. Write Keyword-Rich and Click-Worthy Meta Descriptions
Meta descriptions are short summaries of a web page. Writing unique and relevant meta descriptions can increase click-through rates and drive more organic (unpaid) traffic to your site.
Search engines may show the meta description you set for your page in the search results. But they may auto-generate descriptions based on what users search for instead.
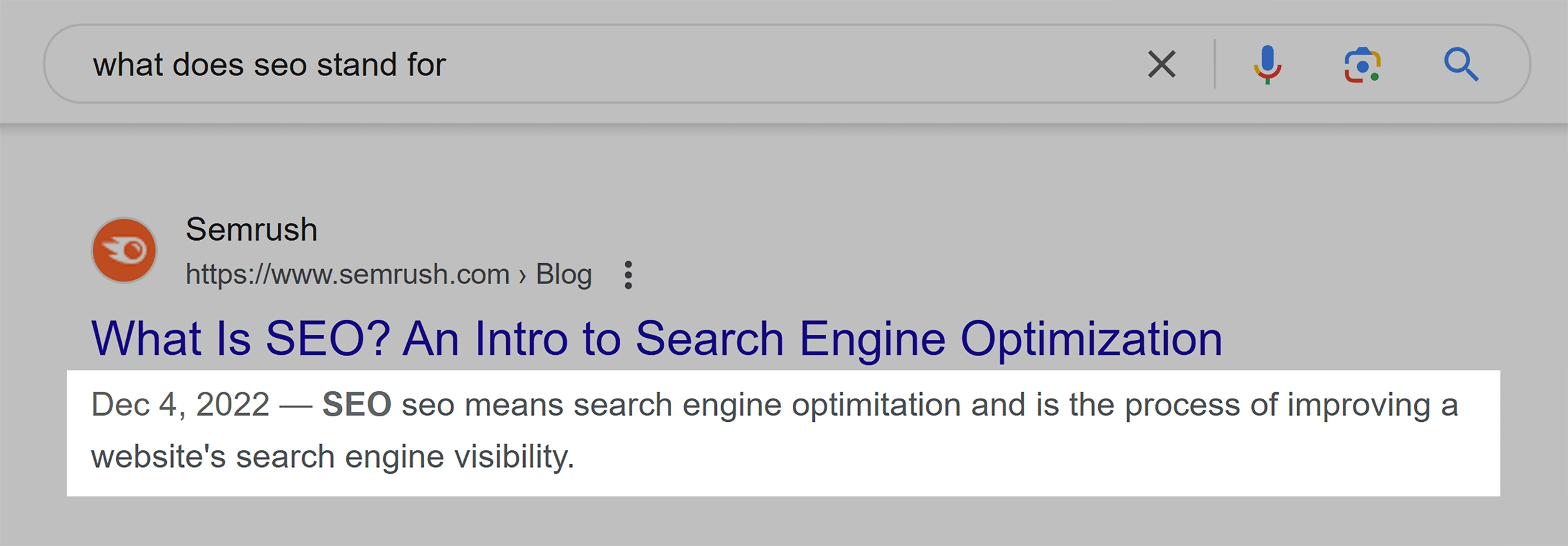
For example, Google uses Semrush’s meta description for the search “what does SEO stand for”:
This meta description directly answers the user’s query.
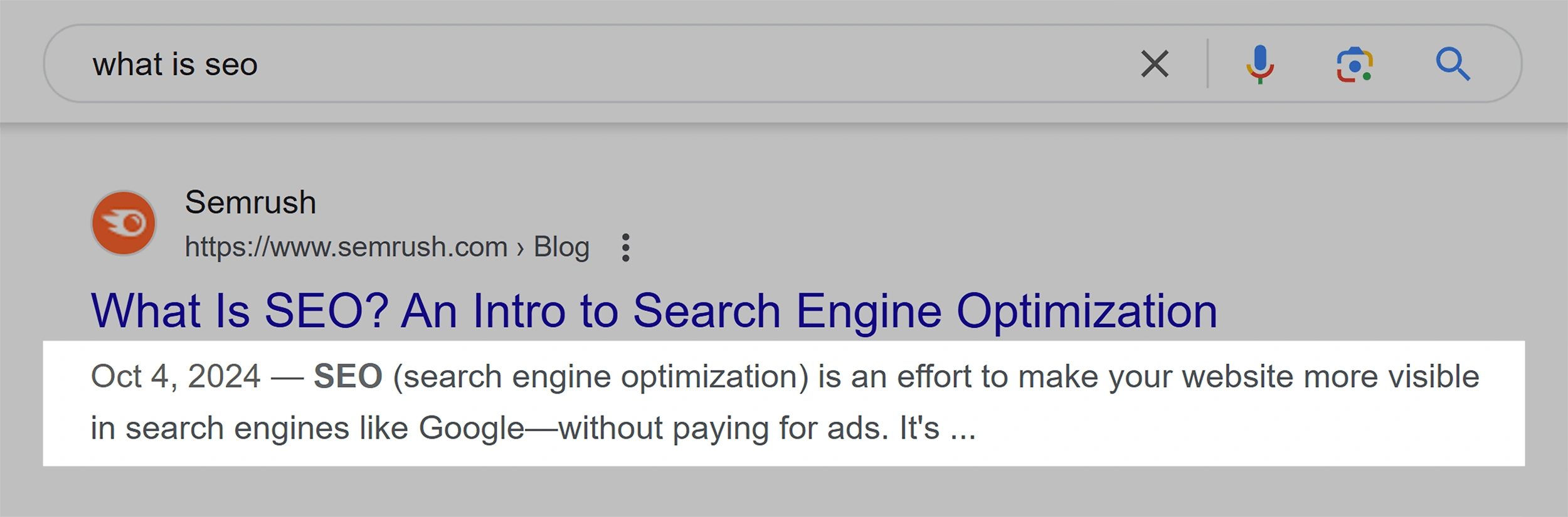
However, Google changed the meta description for the query “what is SEO?” to something more relevant to the specific question:
Here are a few tips to write useful meta descriptions that satisfy users and search engines:
- Keep meta descriptions to around 105 characters: This reduces the chance of search engines truncating them in mobile search results
- Give the searcher what they want: Answer the user’s main question or provide key details that show them your content is what they’re looking for
- Add a call to action (CTA): This entices a searcher to click through to your content
Want to Spy on Your Competition?
Explore competitors’ website traffic stats, discover growth points, and expand your market share.
It’s also worth checking for pages on your site with duplicate meta descriptions or pages that are missing them entirely. Look for opportunities to add your target keywords.
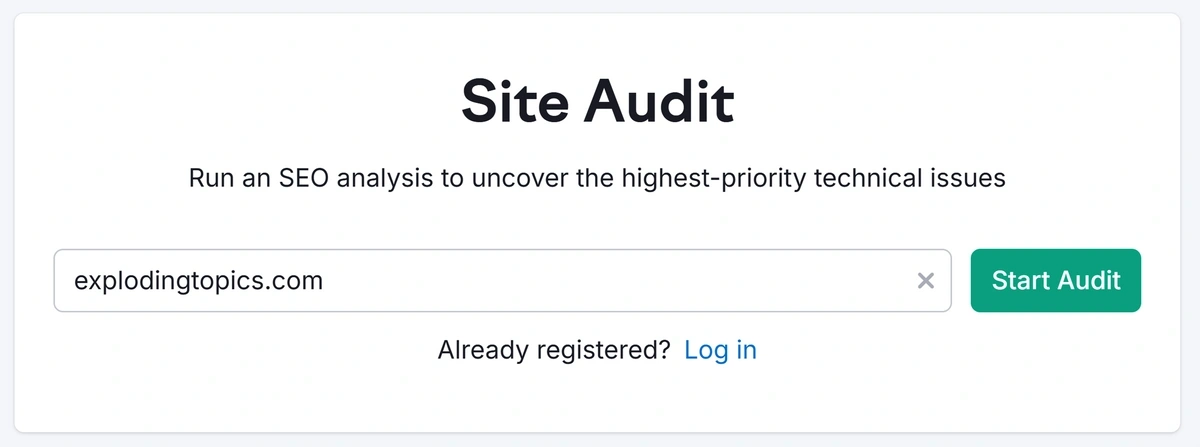
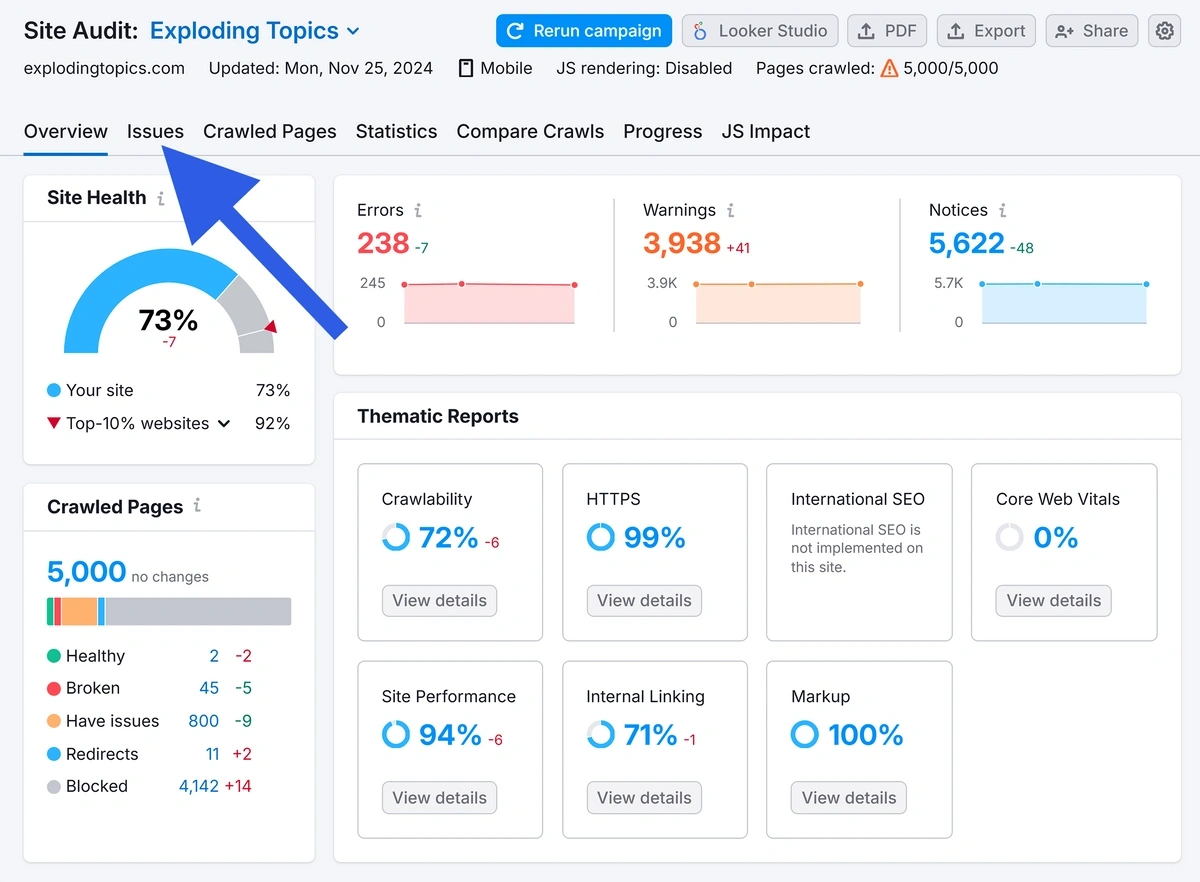
First, check that you don’t have any missing or duplicate meta descriptions by running a Site Audit with Semrush.
Open the Site Audit tool, enter your domain, and click “Start Audit.”
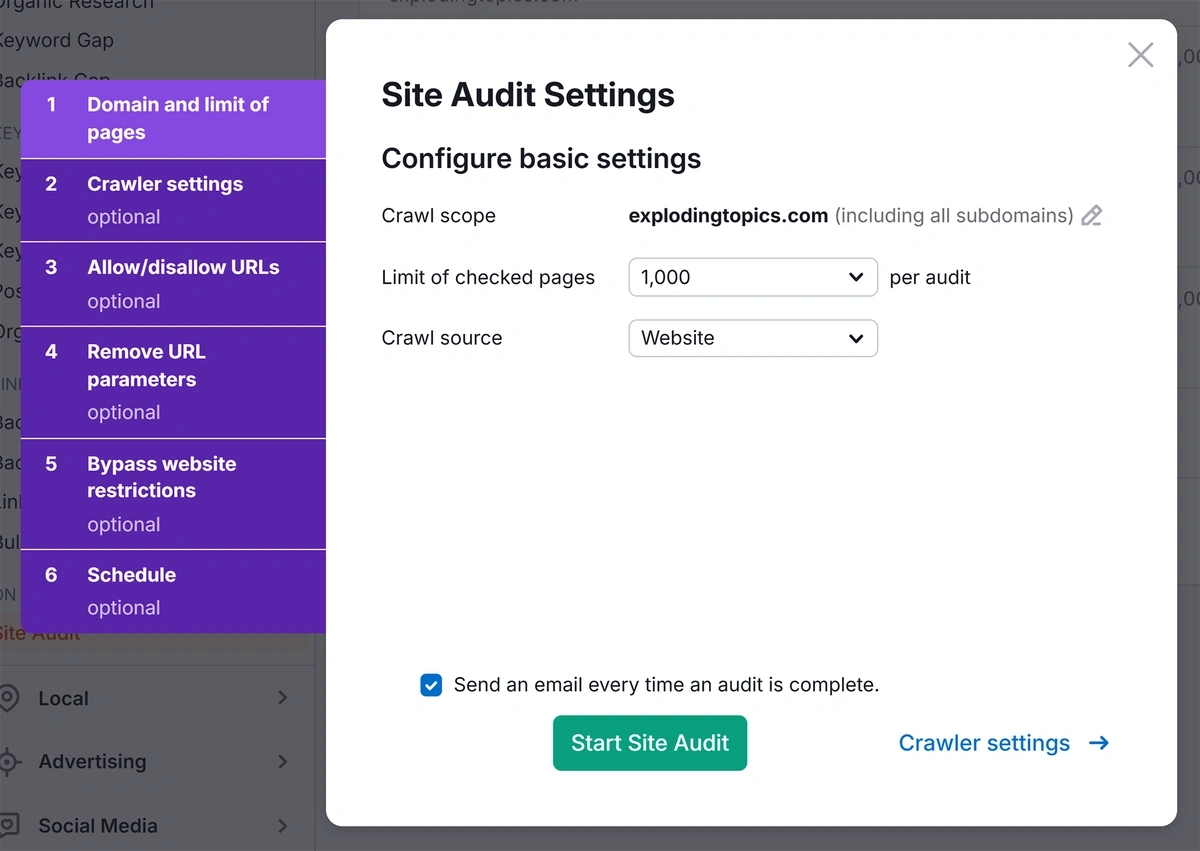
Configure your audit in the popup window and click “Start Site Audit” when you’re ready. (The Semrush configuration guide can help if you get stuck.)
Click the “Issues” tab when the audit is complete.
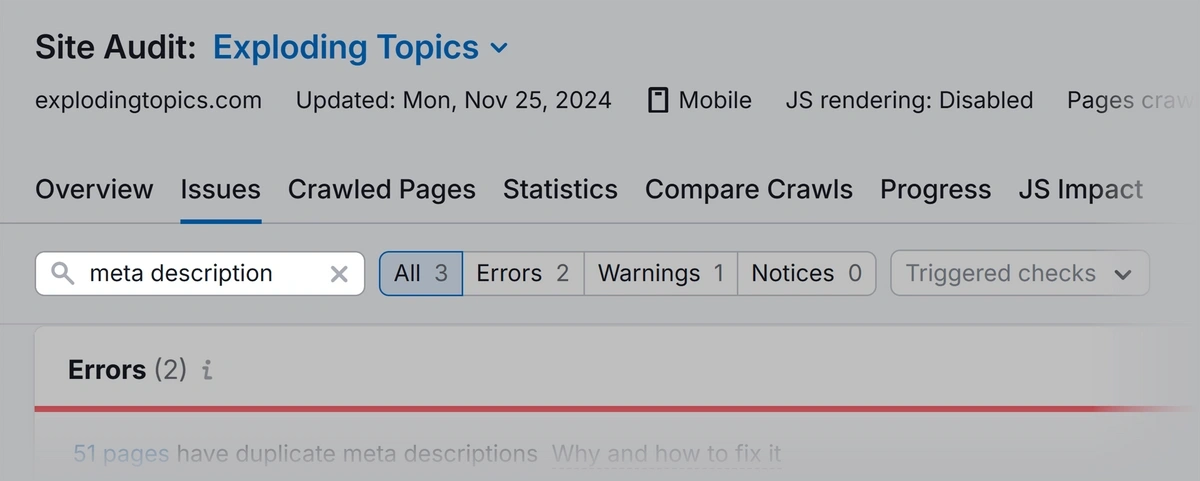
Write “meta description” in the search box. This brings up issues related to the meta descriptions on your site.
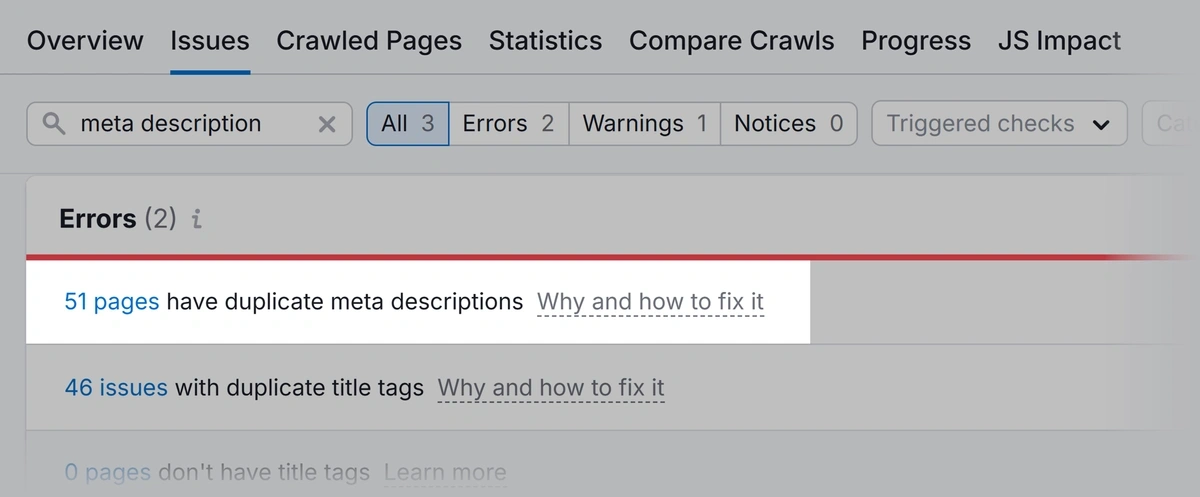
Look for any pages that have duplicate meta descriptions with the warning “# pages have duplicate meta description.”
Click the link to view a list of pages with this issue. Go through and rewrite the meta descriptions for these pages so they're all unique.
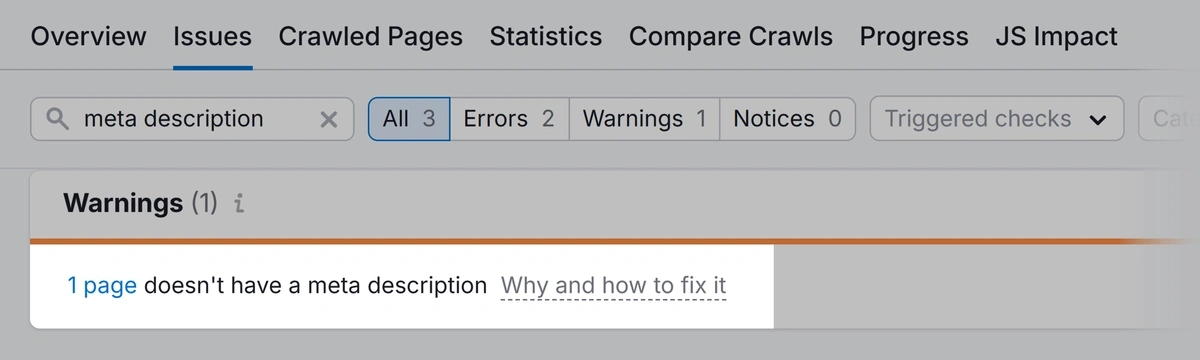
Then, look for a warning that reads “# pages don’t have meta descriptions.” Click the link to see which pages are missing them. Add relevant descriptions to those pages.
Finally, use the On Page SEO Checker to see which meta descriptions are missing keywords.
Head back into your On Page SEO Checker report and click the “Idea Tasks” tab. Look for meta description ideas. Like this one:
Use these insights to adjust your meta descriptions to make them more relevant to your page’s content. And potentially increase your click-through rates.
4. Logically Structure Headings on Your Page
Headings and subheading provide structure for the content on your page. They help people skim and find the sections they want to read.
Headings also help search engines understand what your content is about.
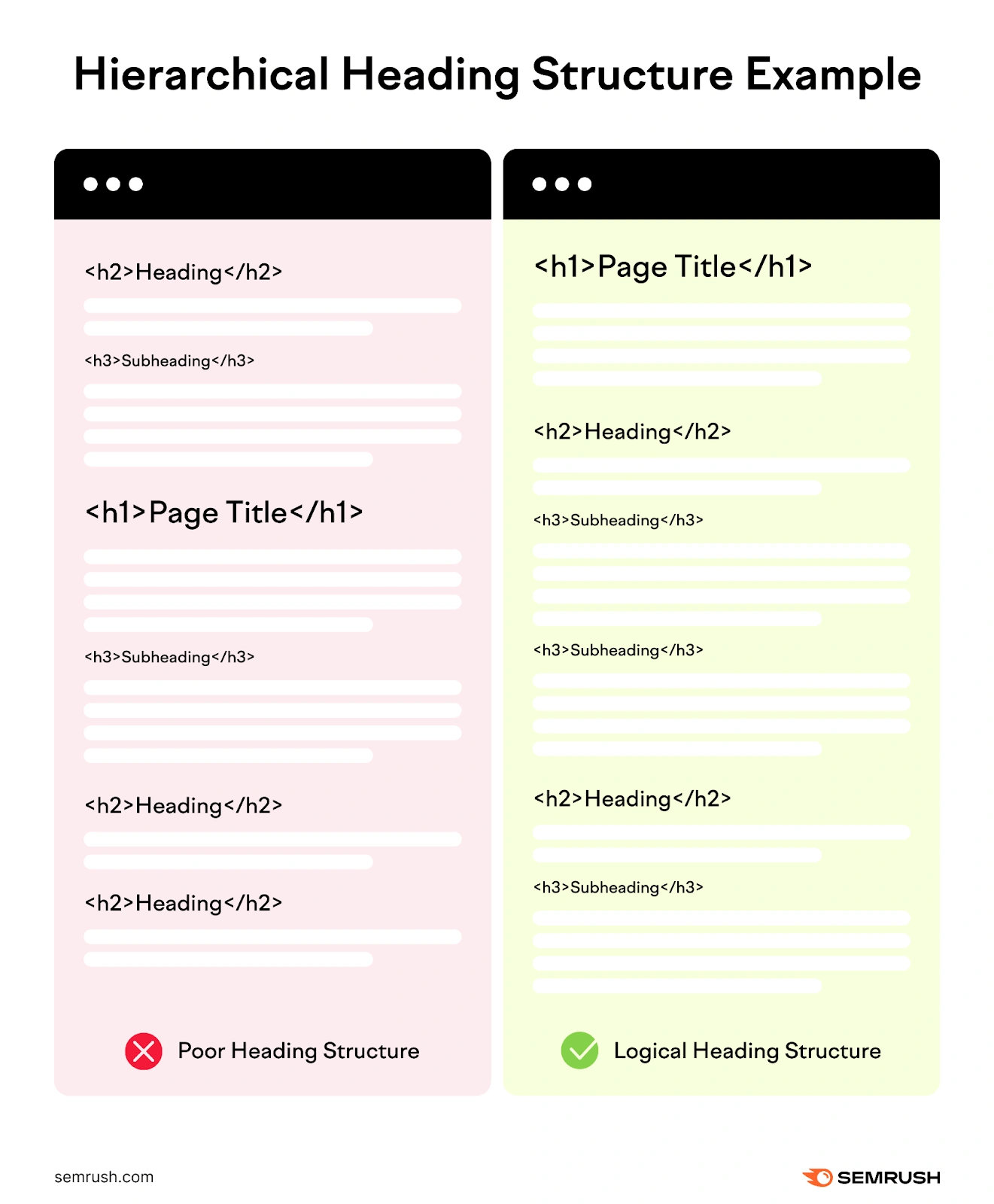
It's best to follow a hierarchical structure, from H1 (the top-level heading) through H6.
Here are a few tips for structuring your headings:
- The H1 tag should be the first heading on the page
- Each page should only have one H1: Pages can have multiple subheadings (H2, H3, etc.) but should only have one H1 tag related to the main topic
- Headings should follow a hierarchical order: Don’t, for example, go from H1 > H3
Here’s an example of a poor header structure compared to a more logical one:
5. Create Crawler-Friendly URLs
Descriptive URLs can improve your site structure (how pages on your site are organized) and user experience. They can also help search engines understand your content. This improves your chances of ranking for relevant search terms.
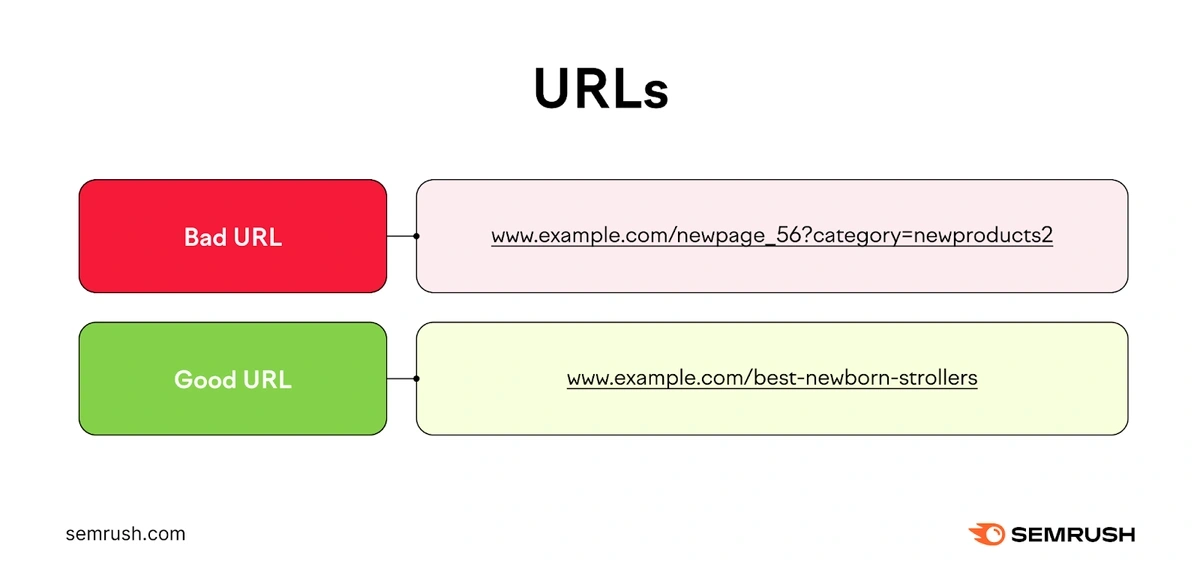
Good URLs:
- Are short (ideally fewer than five words)
- Contain keywords to help people and search engines understand what the content is about
- Use hyphens instead of underscores to represent spaces between words
- Don’t contain too many parameters (elements within URLs that filter and organize content)
Here’s an example of a good URL compared to a poor one:
Semrush Site Audit will check your site and tell you which URLs to optimize to improve your on page SEO.
Open the tool and head into your site’s audit that we started earlier.
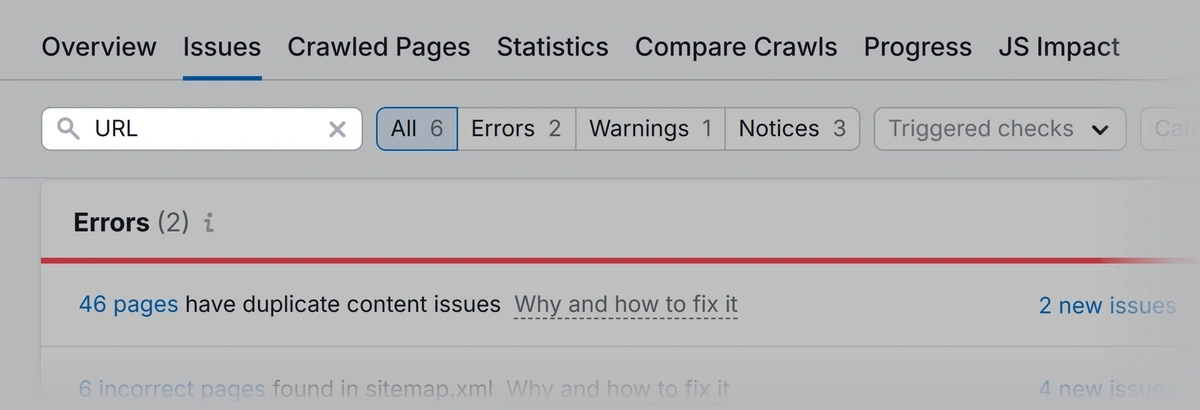
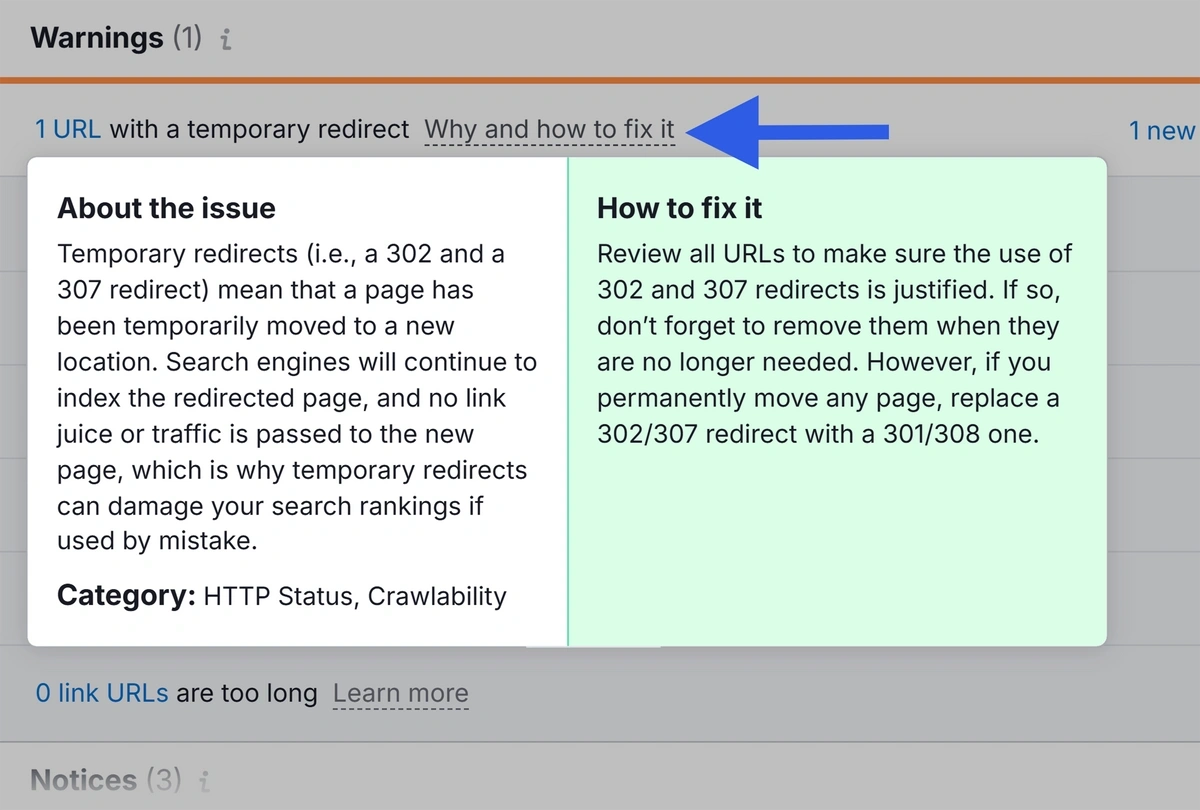
Head to the “Issues” tab and search for “URL.”
This shows any URL issues you may need to fix. Learn more by clicking “Why and how to fix it.”
6. Write Helpful Content That Matches User Intent
Writing quality content (like blog posts) can help drive organic traffic to your site.
When you create high-quality content that offers value, your site has a chance of appearing in the search results whenever someone searches for terms related to your business or niche.
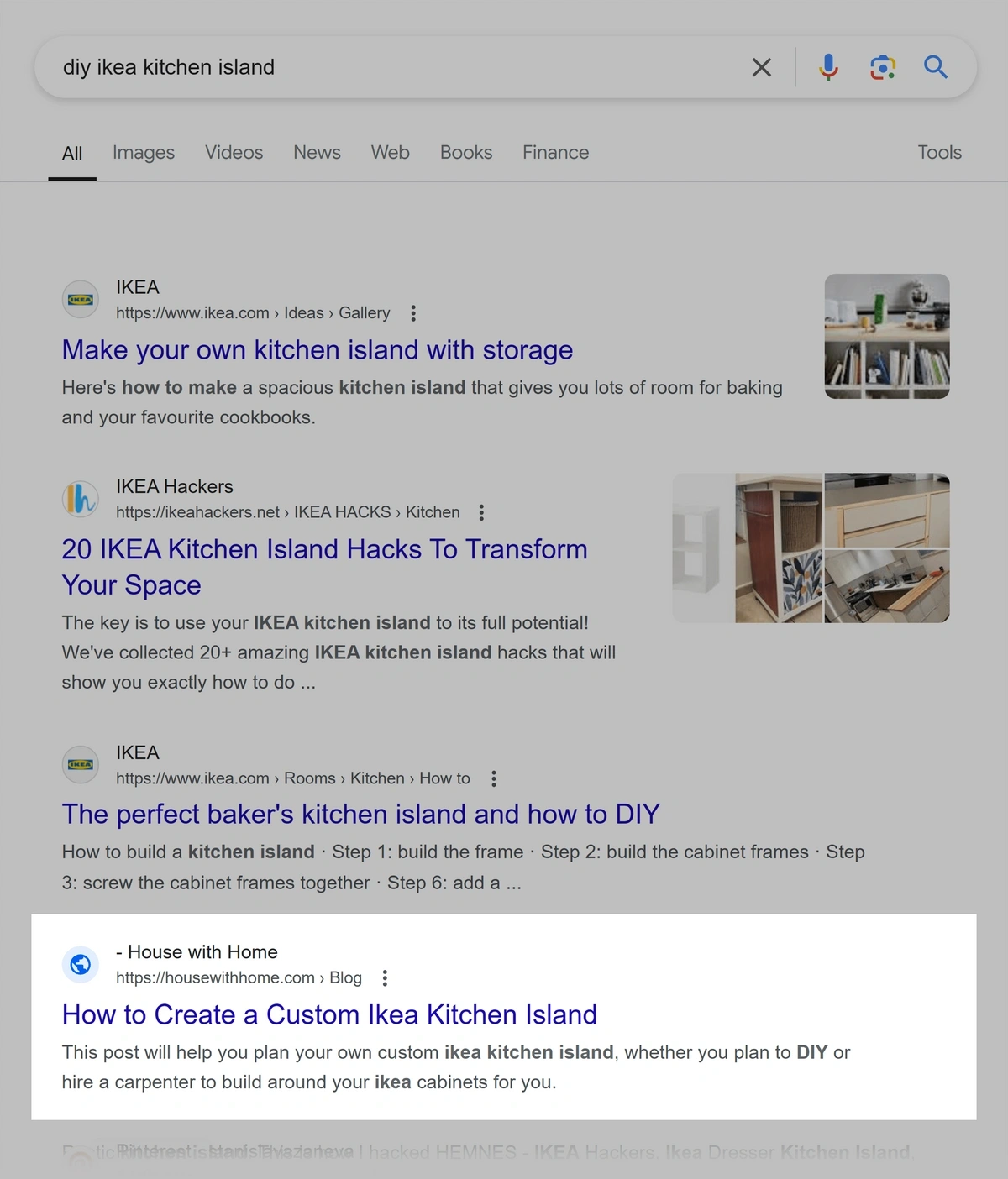
For example, this search for “diy ikea kitchen island” shows a post from a design blogger:
Improve your chances of ranking in search results by choosing the right keywords.
But how do you find the right keywords to target?
Head to the Semrush Keyword Magic Tool.
Type in a general topic idea, select the location you want to target, and click “Search.”
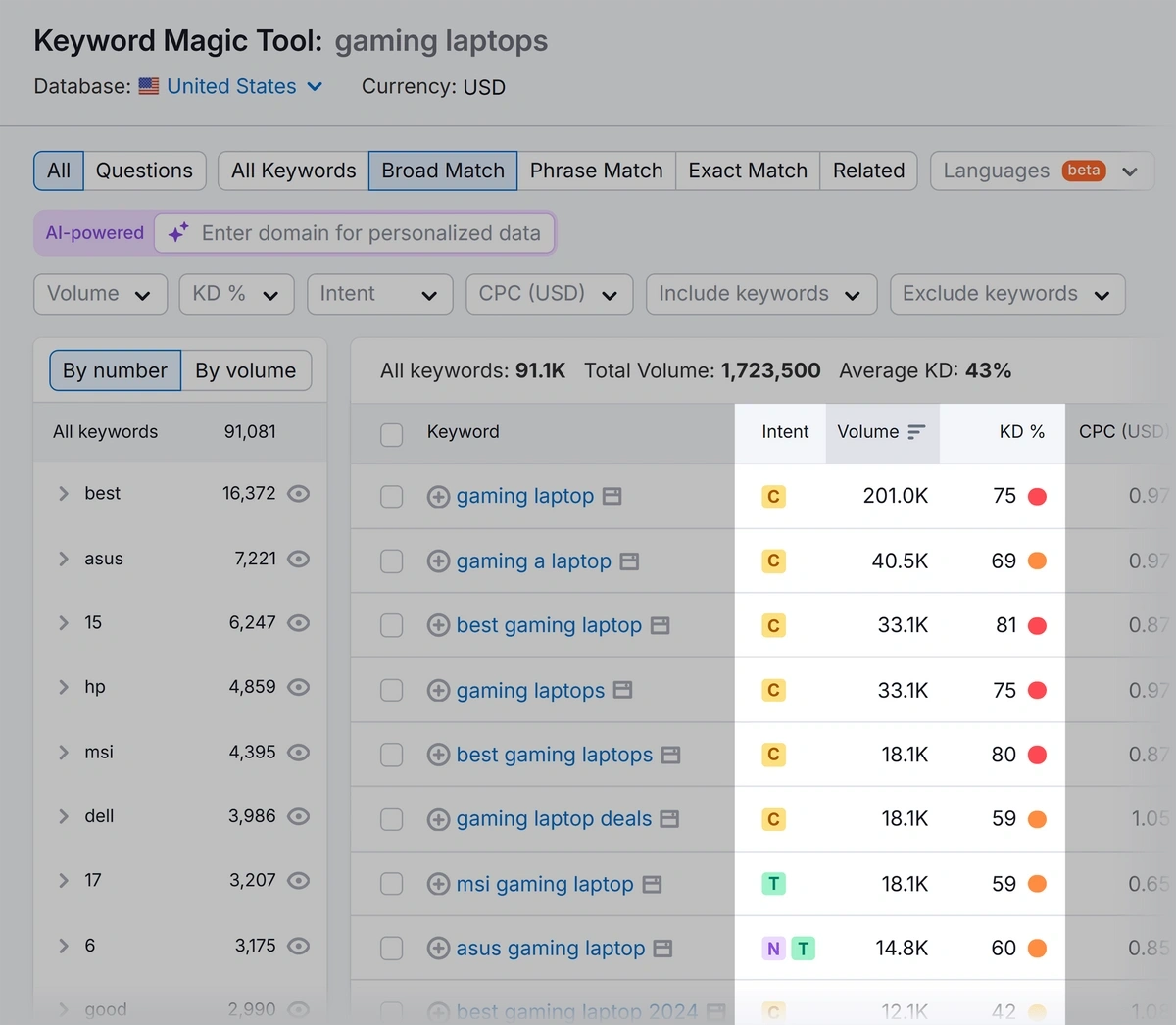
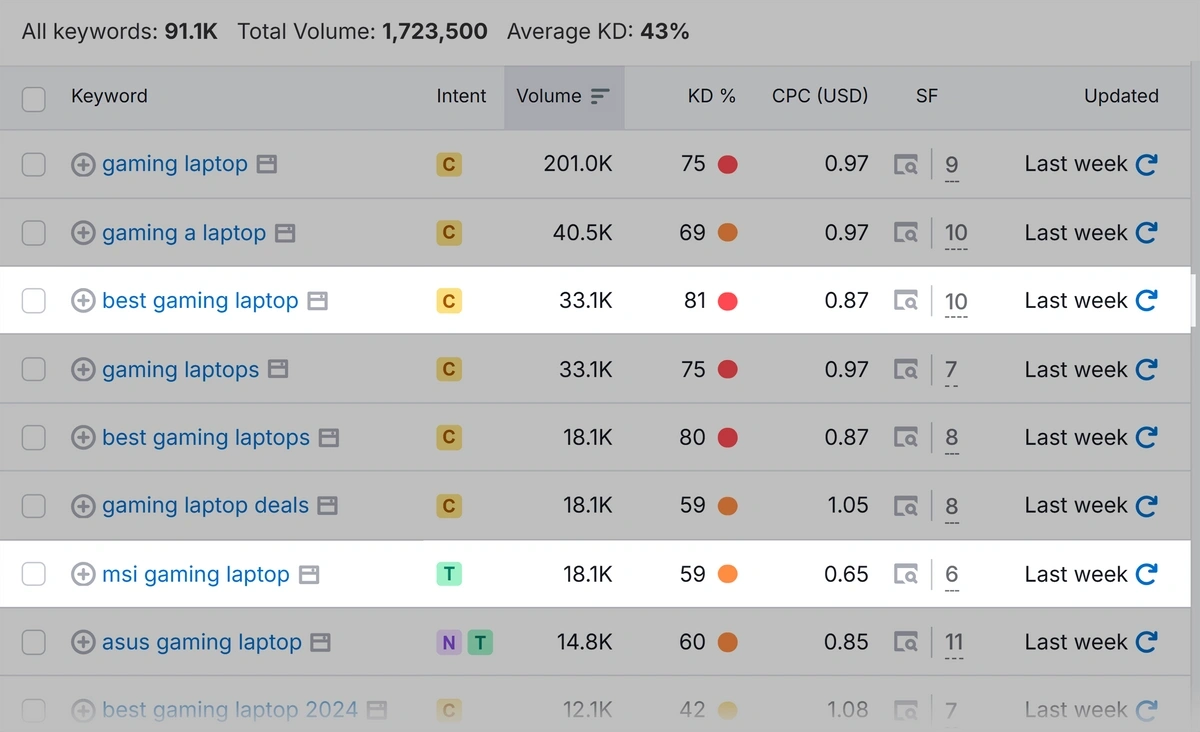
The tool will give you a list of relevant keywords with metrics like:
- Keyword difficulty (KD %): How hard it will be for you to rank for that keyword
- Volume: The average number of monthly searches for that keyword
- Intent: The goal a user has with their search
Review the list and pick keywords you’d like to rank for. Generally, it’s best to go for relevant keywords with high search volume and low keyword difficulty.
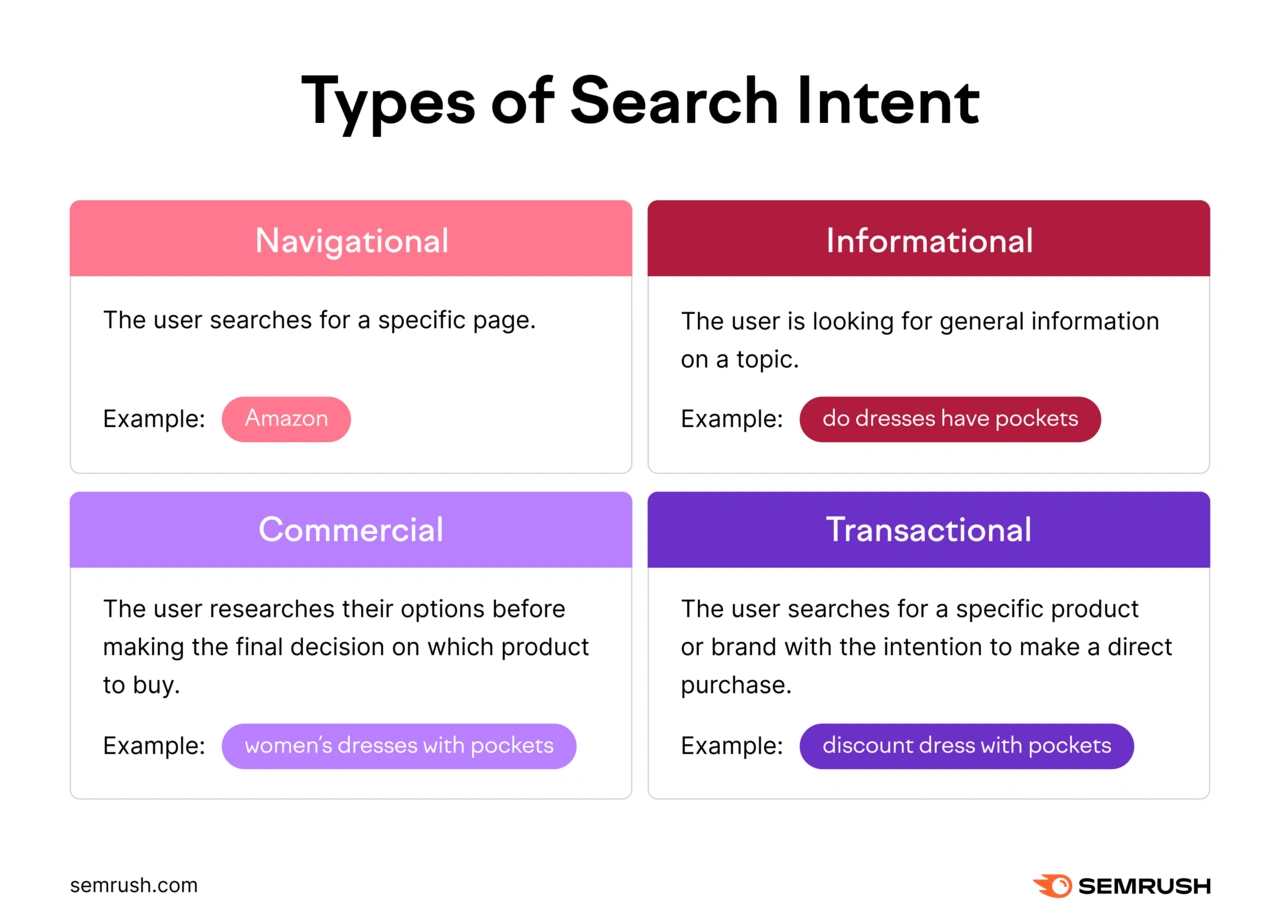
Pay attention to the “Intent” column. There are four main types of search intent: navigational, informational, commercial, and transactional.
Understanding the intent behind each keyword helps you craft content that aligns with your reader’s goals.
When you match intent to your content, your readers are more likely to find your content has value.
For example, the keyword “msi gaming laptop” has transactional intent. That means people are likely looking for a product page.
The keyword “best gaming laptop” has commercial intent. That means people might want to see a post comparing products.
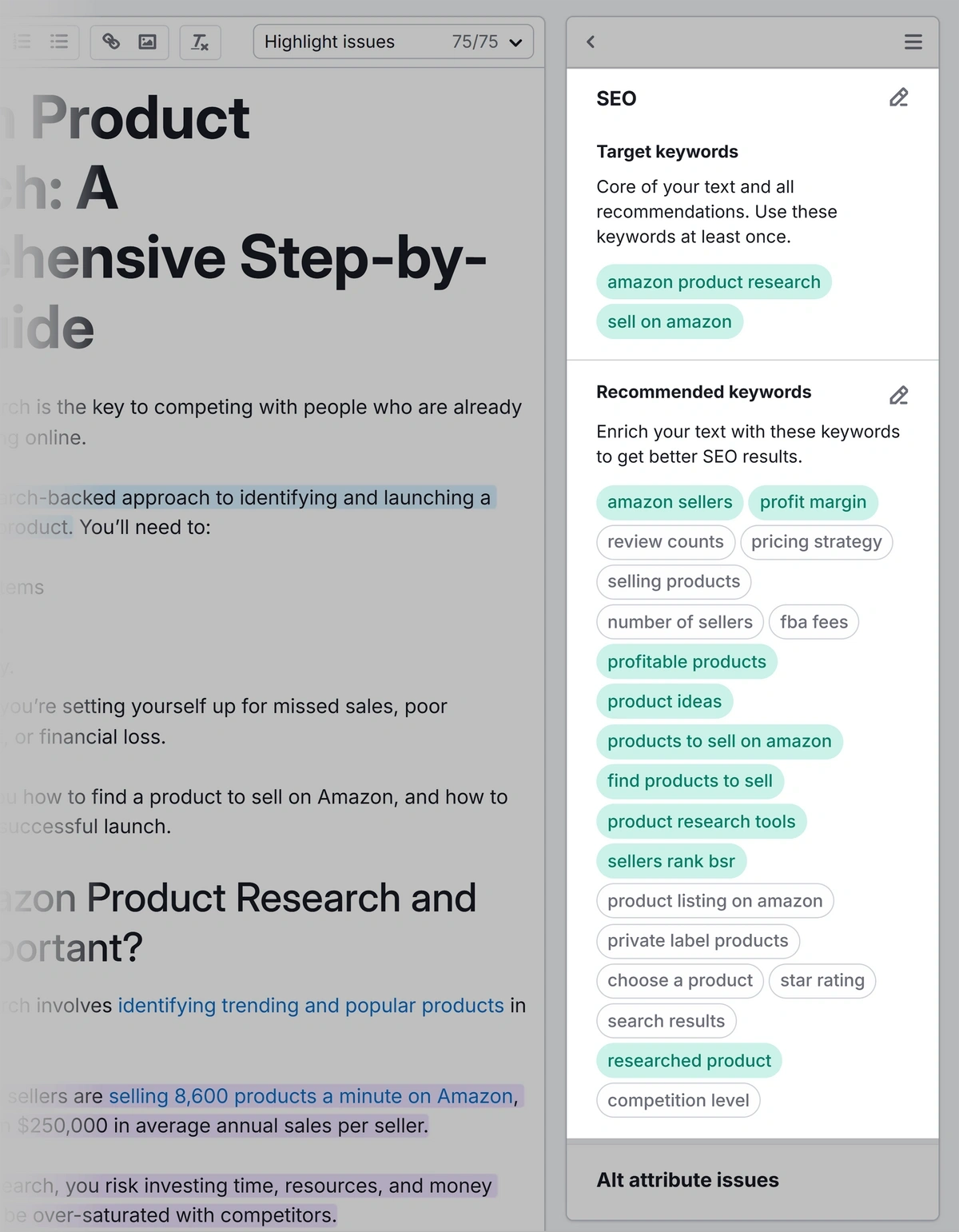
Select your keywords and note their intent. Then, use the Semrush SEO Writing Assistant to write your content.
Open the tool and click “Analyze my text.”
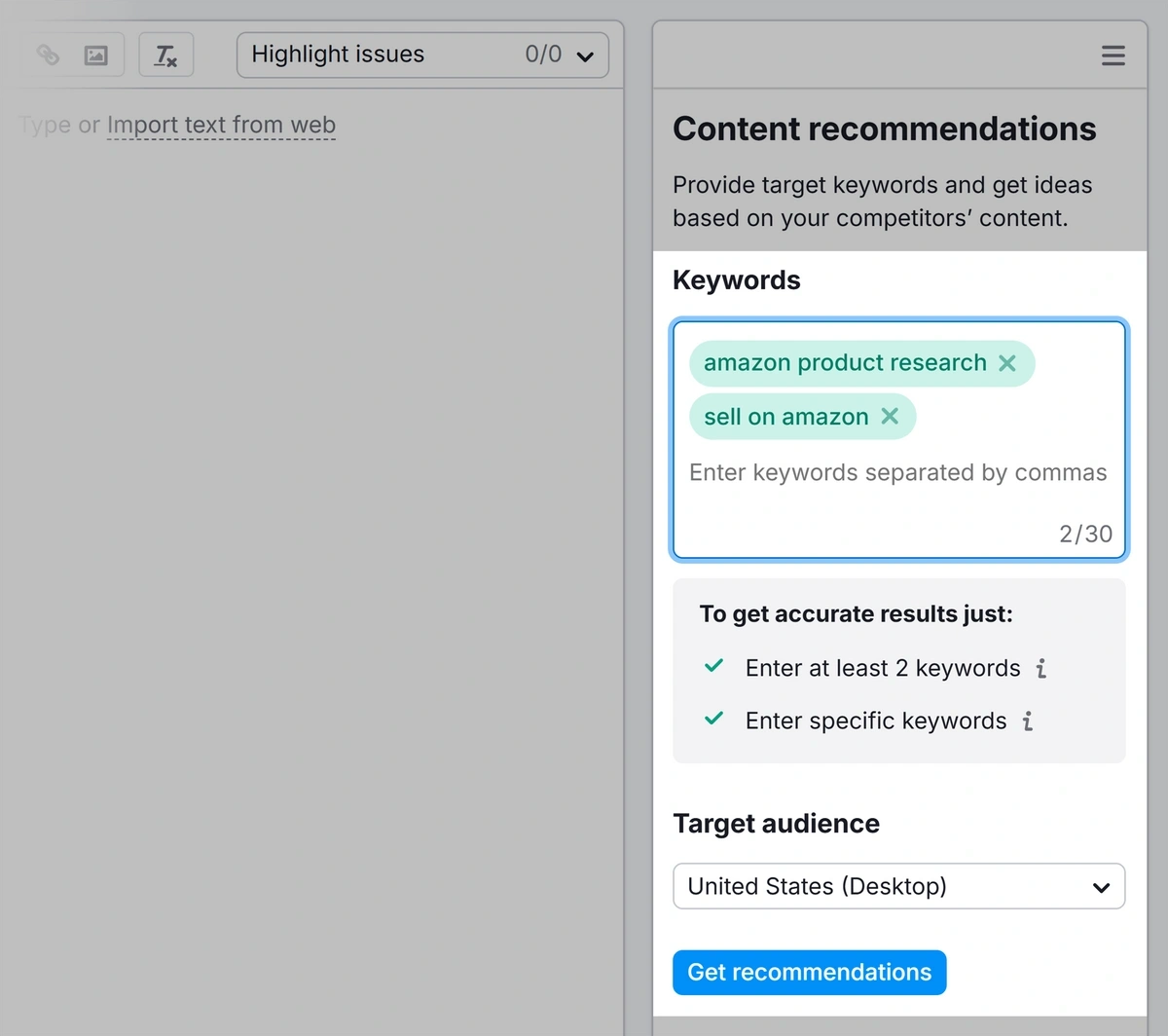
Enter your keyword(s) into the “Keywords'' input box. Then adjust your target audience and click “Get recommendations.”
I like to write content directly in the editor. If you prefer, paste it in, or import it with a URL (if you’re using the tool to update existing content—see the next section for more on that).
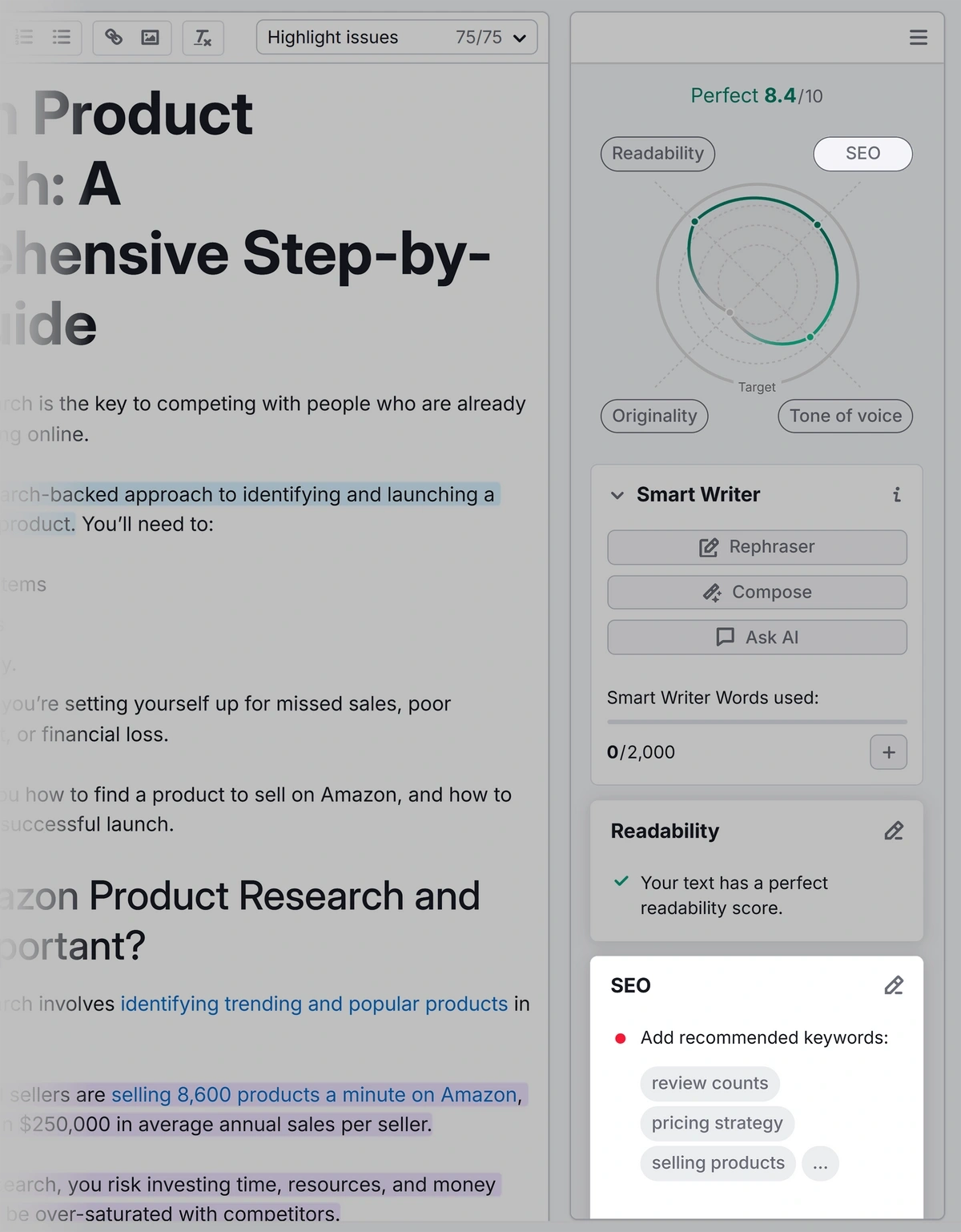
The SEO Writing Assistant will grade your content as you write and provide a tailored list of recommendations for readability, SEO, originality, and tone of voice. It'll help you write great content that has a better chance of ranking well.
Clicking “SEO” gives you on page SEO tips.
These tips include secondary keywords to add to your content.
SEO Writing Assistant also makes suggestions for images, links, and titles.
Go through and apply these tips to your content to give it a better chance of ranking well in search results.Check your ranking using our website rank tracker.
And if you're looking for more inspiration, use our free SEO Competitor Analysis Tool to see which keywords your rivals are ranking for.
7. Analyze and Improve Existing Content
Content that isn’t optimized for users and search engines likely won’t rank well in search results. Periodcially, you should look to perform a content audit to see what is and isn't working.
Along with providing ideas for optimizing your title tags, H1s, and meta descriptions, the On Page SEO Checker can also identify which pages aren’t ranking in the top 10.
It provides tips to improve each page so you can increase your chances of ranking higher and driving more traffic to your site.
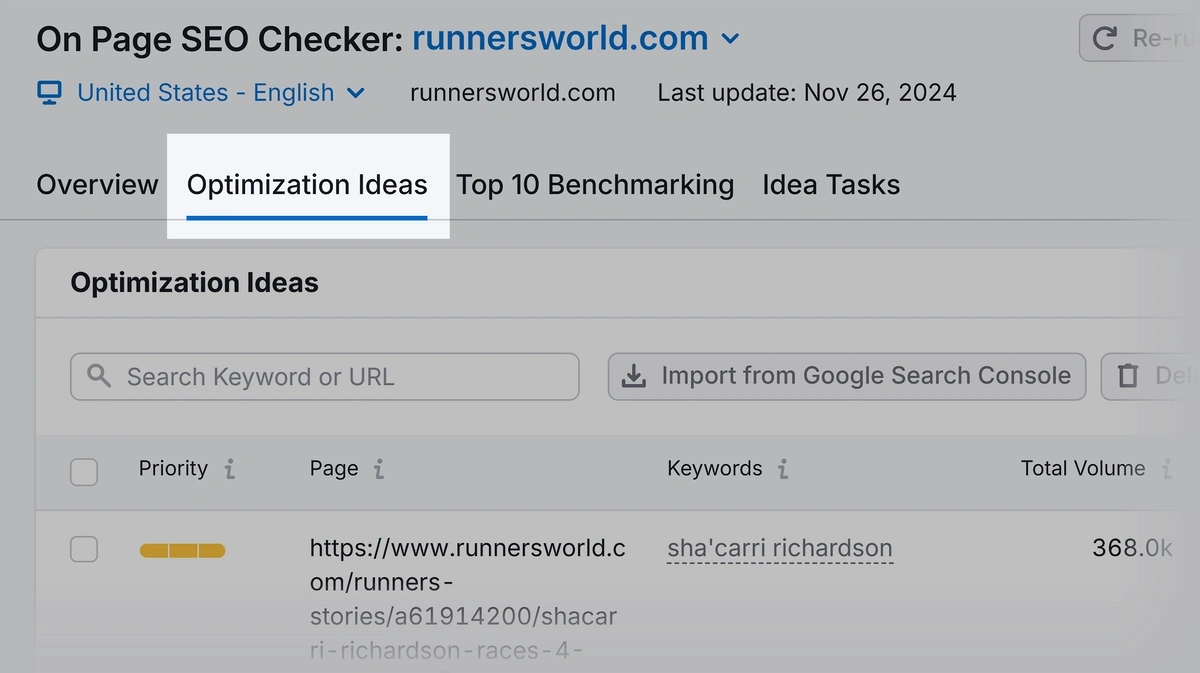
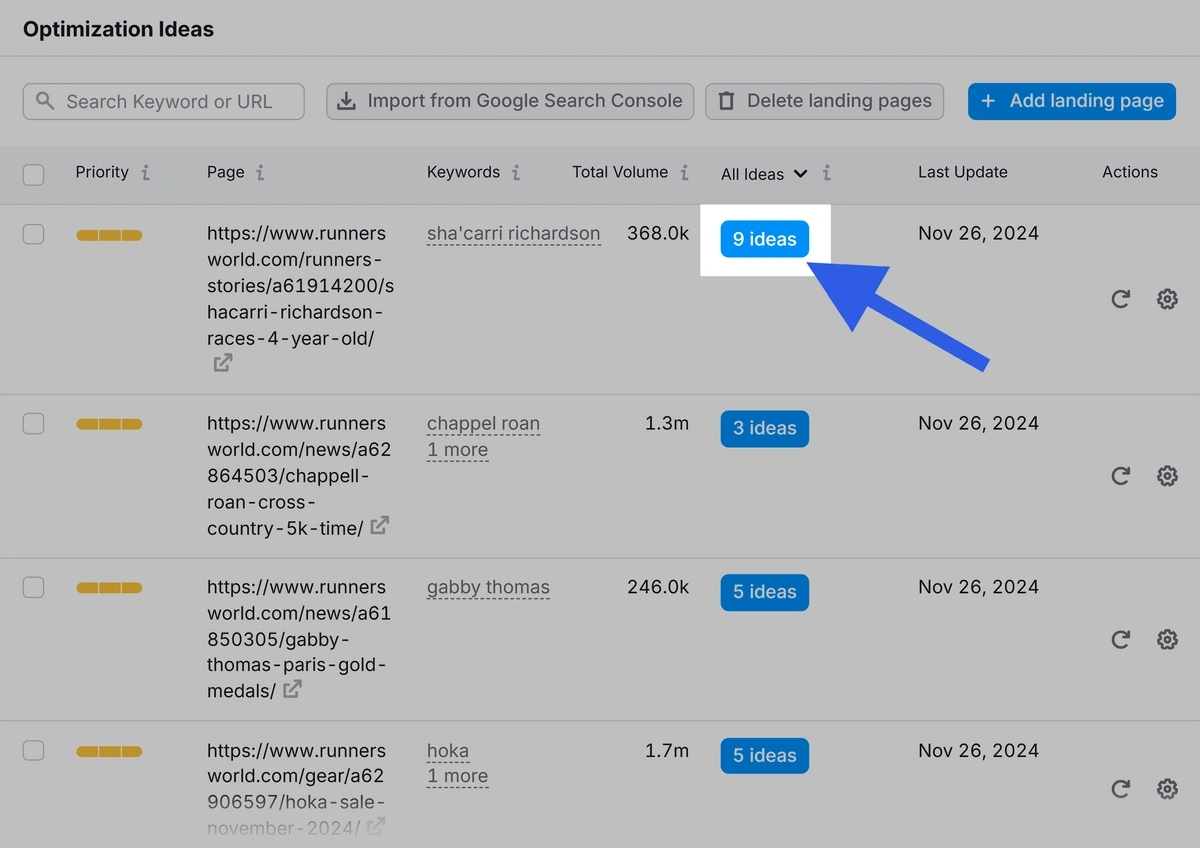
Open the On Page SEO Checker and head into your site’s project. Then click “Optimization Ideas.”
This tab lists pages you should fix. Click “# ideas” for one of the pages.
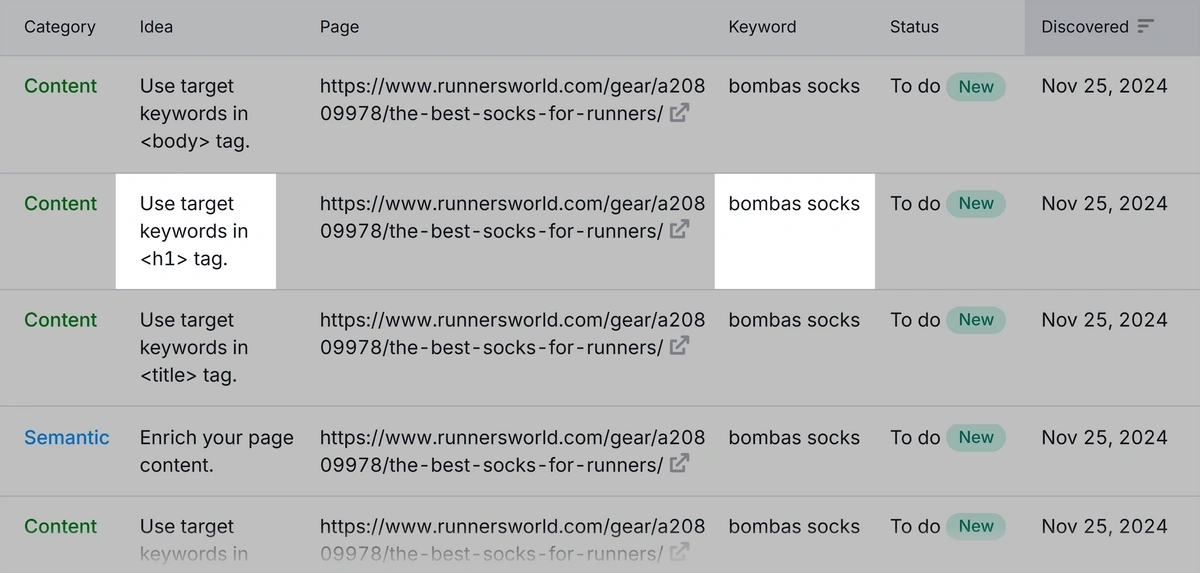
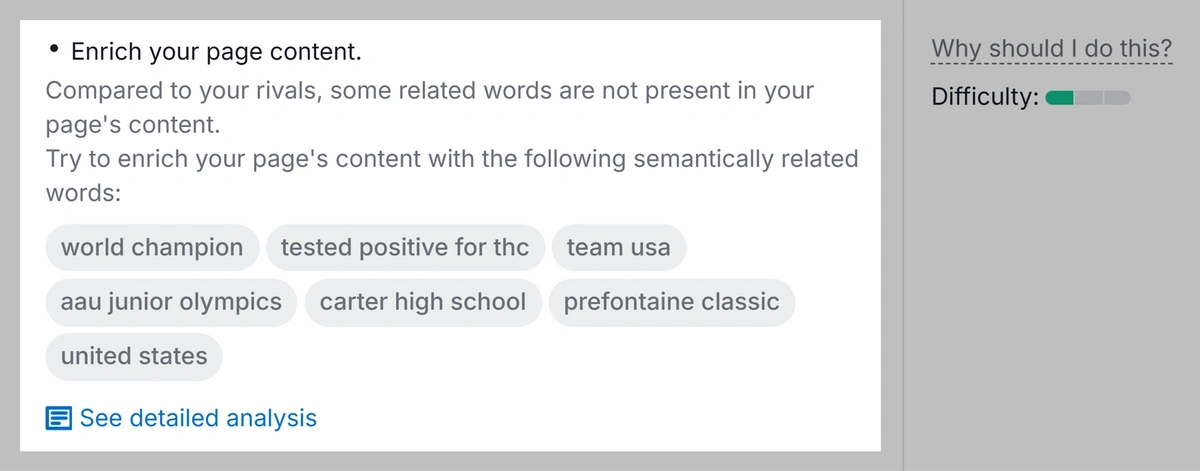
You’ll get a list of actionable ideas to improve the page. For example, this recommendation that gives you the exact related keywords to add:
You can also use SEO Writing Assistant to grade your existing content. Just paste your existing content into the editor.
Or use the SEO Writing Assistant WordPress plugin to analyze your content without leaving WordPress.
8. Add Relevant Internal Links
Internal links are links between different pages on your site. For example, a link from your homepage to a blog post is an internal link.
Internal links help search engines find your pages. And they provide a positive user experience by making it easier for readers to navigate your site.
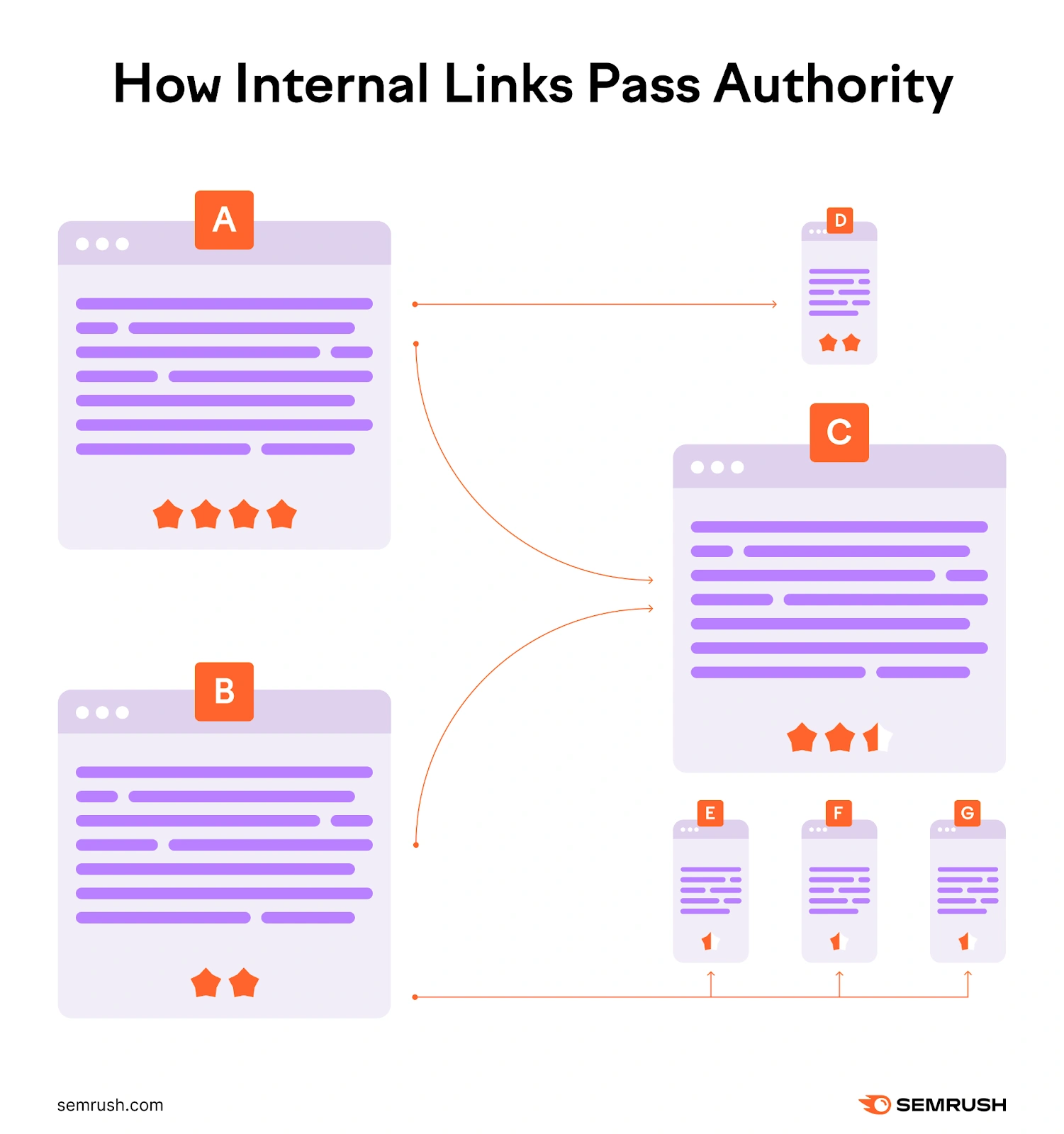
Internal links can also enhance website authority.
For example, say Page A has a number of quality backlinks. Page A may have a high level of authority. And when Page A links to Page C (and Page C to Page D), some of that authority can be passed down to each page.
This boost of authority can have a positive effect on the linked page’s rankings.
So, it’s a good idea to identify your high authority pages and link to other pages from them.
Note: This is a bit of a simplification. Authority is a complex concept, and internal linking doesn’t necessarily pass all of a page’s authority to the linked page.
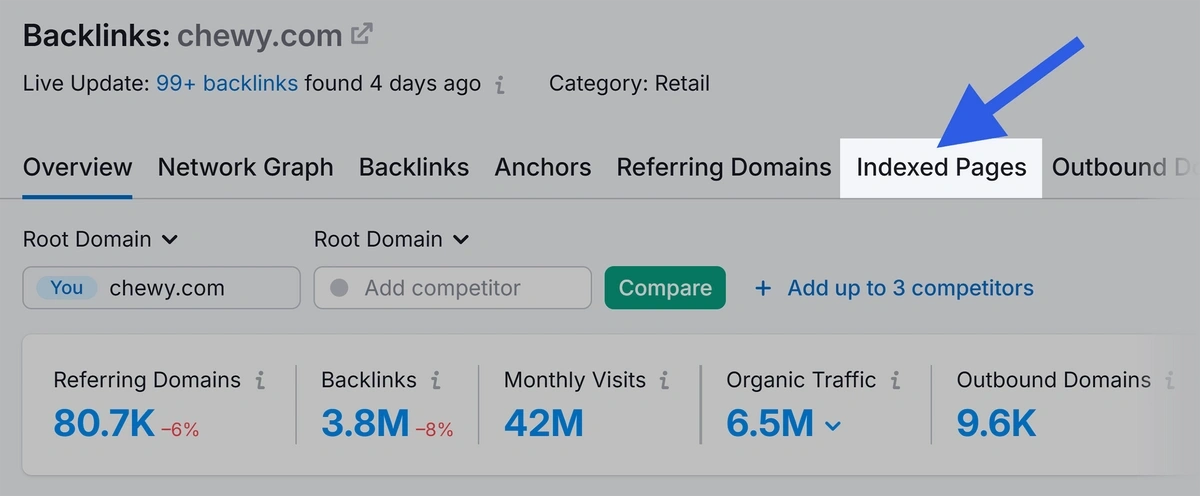
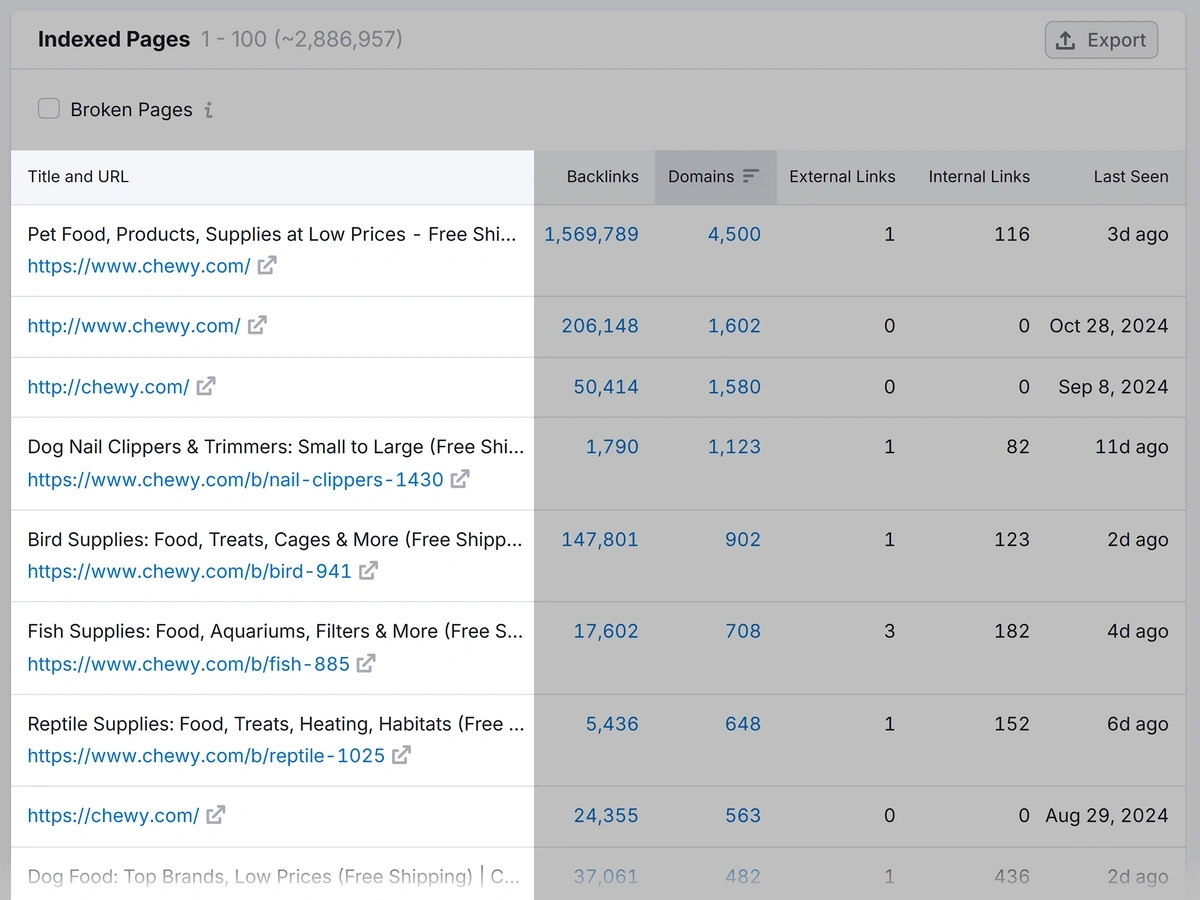
You can find high authority pages with Semrush's Backlink Analytics tool.
Open the tool and enter your domain. Then click “Analyze.”
Click “Indexed Pages.”
The results are sorted by the highest number of referring domains. This means pages at the top have the highest number of other websites pointing to them.
These are potentially the most authoritative on your site.
Try to insert relevant internal links in these pages to pass some of the authority down to your other pages.
9. Link to Trustworthy External Resources
External links are those that point to another domain. They can provide users with additional information and help search engines better understand your content.
Like this external link that takes users to the original research cited in the anchor text (the clickable part of the link):
External links should:
- Contain descriptive anchor text: Avoid using generic anchor text like “click here” as it doesn’t give users any useful information about where the link will take them
- Point to reputable websites: Linking to low-quality websites can cause users and search engines to stop trusting your content
- Be useful and relevant to your content: Don’t add external links just for the sake of having them
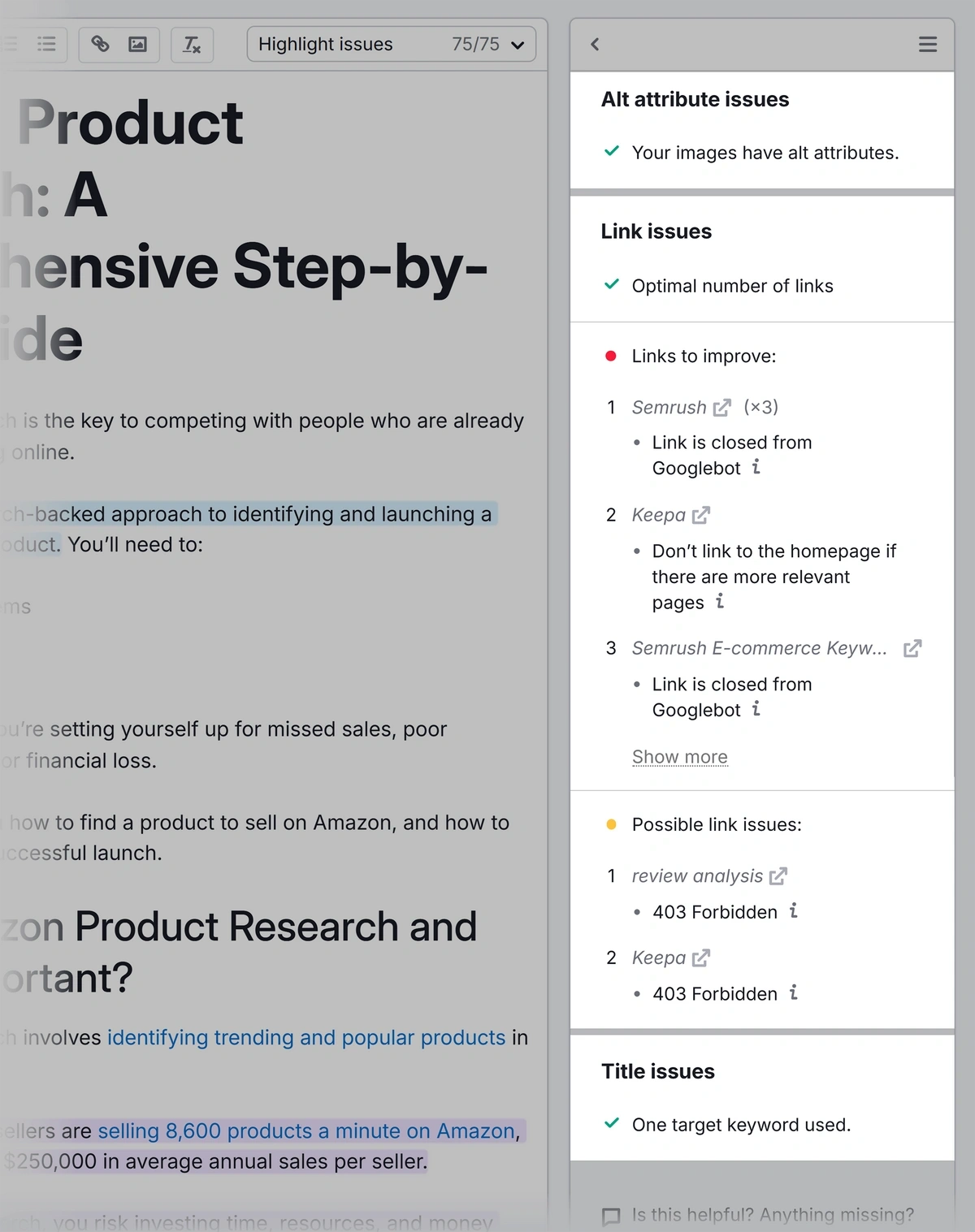
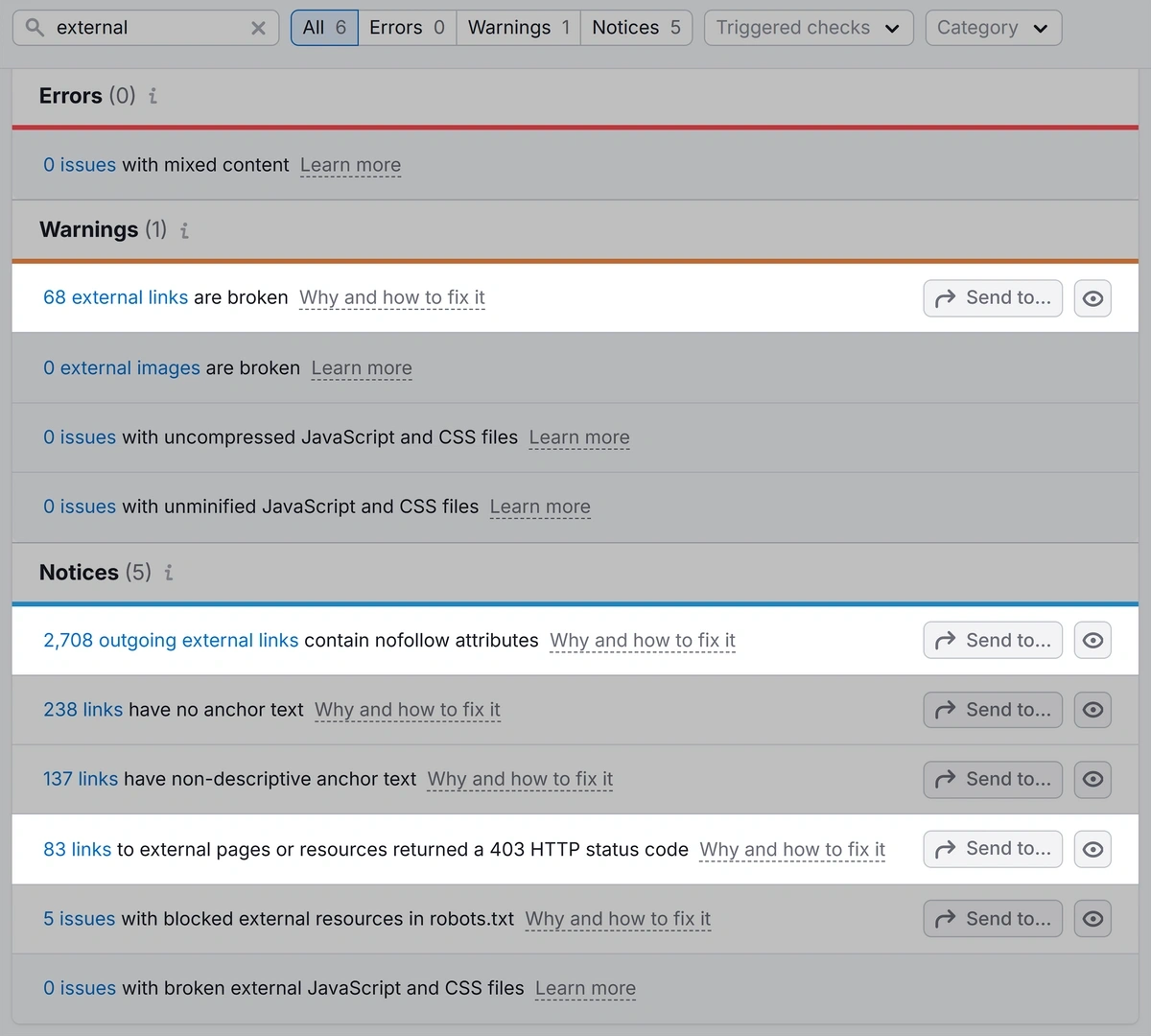
To check your site’s external links, use Site Audit.
Open your project in the tool, click “Issues,” and search for “external.”
Look for the following issues:
- Broken external links
- External links with unnecessary nofollow attributes (nofollow attributes instruct search engines not to crawl the linked page)
- Links to external resources that return errors
Click the hyperlinked text to get more information for each issue.
10. Optimize Your Images and Alt Text
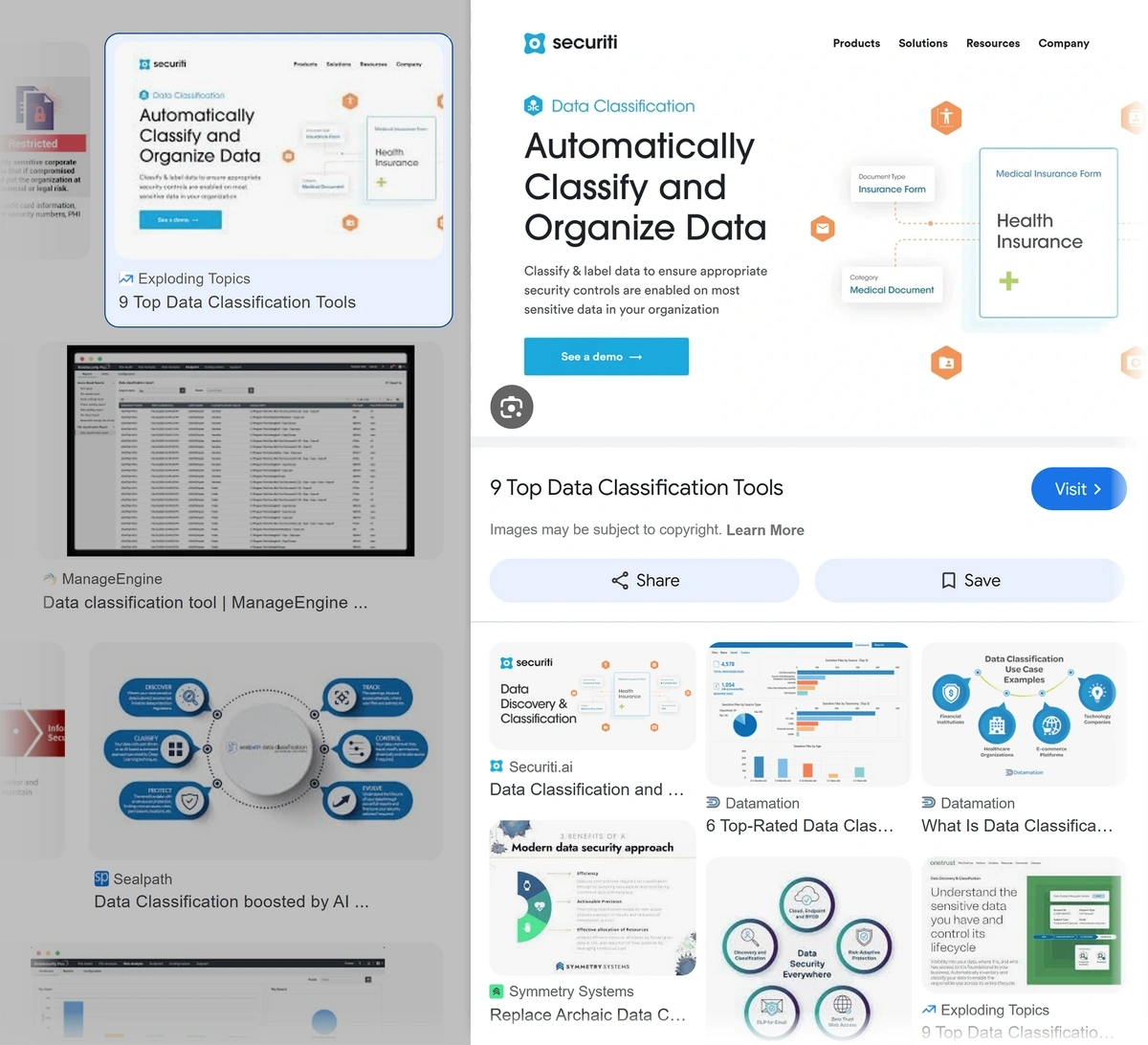
Optimized images can rank in Google’s Image Search. This can help drive more organic traffic to your site.
Here’s an Exploding Topics image ranking for the query “data classification tools”:
Optimize your images by:
- Adding descriptive alt text: Alt text describes your image for screen readers and search engines, and can display if your image doesn’t load
- Use keyword-rich image names: Avoid giving your images names like “IMG_768.jpg” and opt for something descriptive instead, like “homemade-pecan-pie.jpg”
- Create an image sitemap: This may increase the chance of your images ranking in search results
- Reduce display dimensions: Large images can decrease page speed, which can hurt user experience and potentially impact your rankings
- Compress your images: Reduce your image file sizes (without significantly reducing their quality) to potentially improve load times
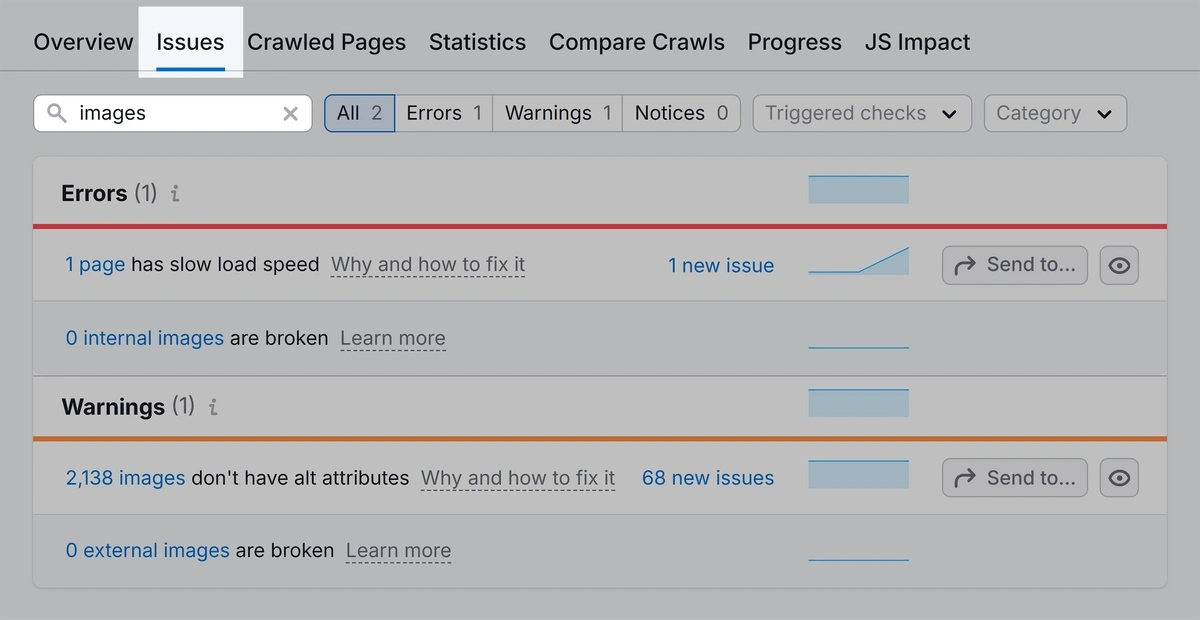
Check your images for any issues by heading back into the Semrush Site Audit tool and clicking the “Issues” tab. Then, search for “images.”
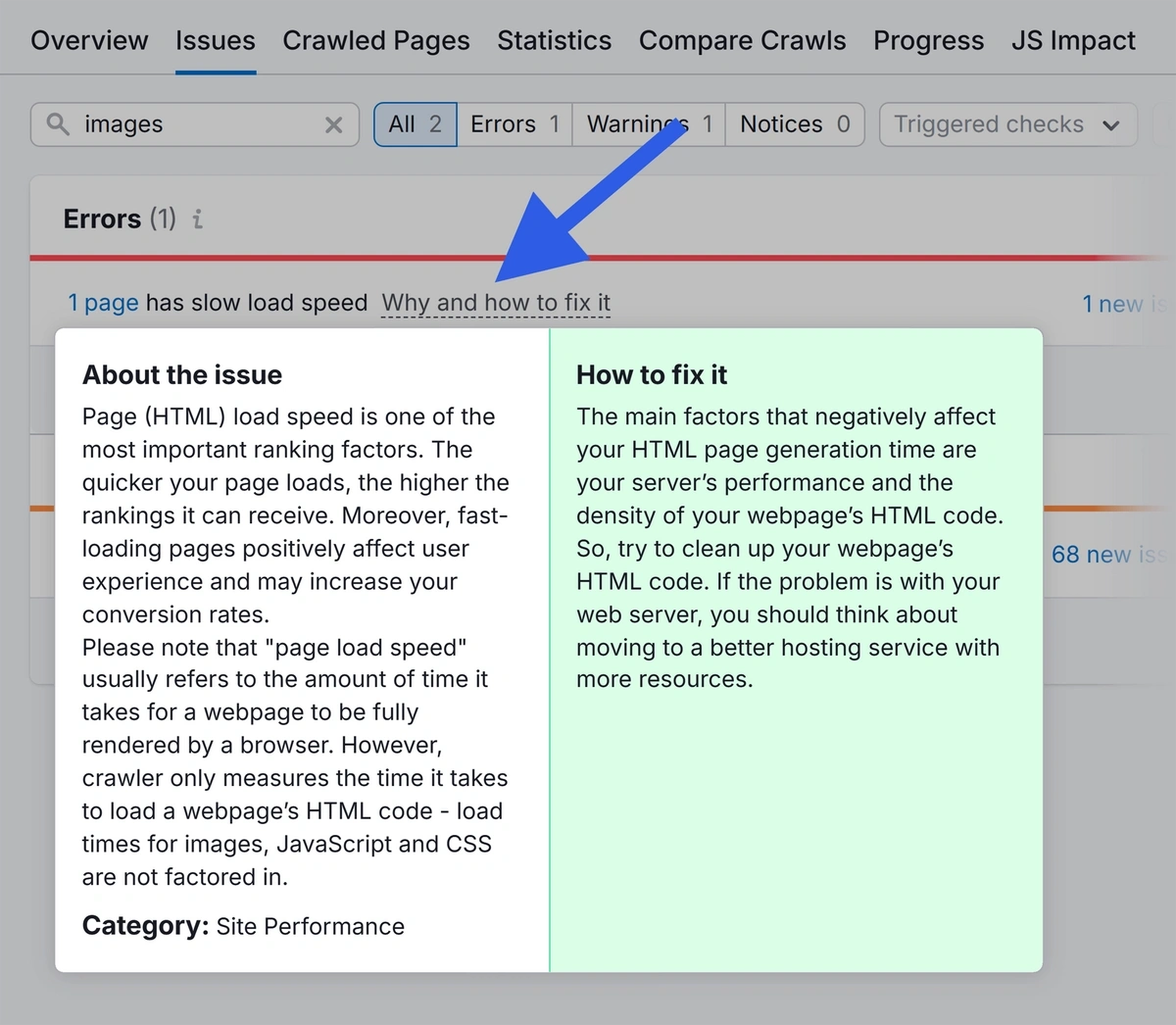
Click into each issue to see what you should fix. Or, click “Why and how to fix it” or “Learn more” for more information.
11. Review Your Site’s UX
User experience (UX) is the overall experience someone has on a website. Aspects like page load time, mobile-friendliness, and the functionality of your site can influence user experience.
And user experience and SEO go hand-in-hand.
For example, a website that has numerous broken links and takes a long time to load provides a poor user experience.
This bad UX can turn users away and reduce your conversion rate. But it can also hurt your rankings.
Reviewing UX elements on your site is another task you can perform with the Semrush On Page SEO Checker.
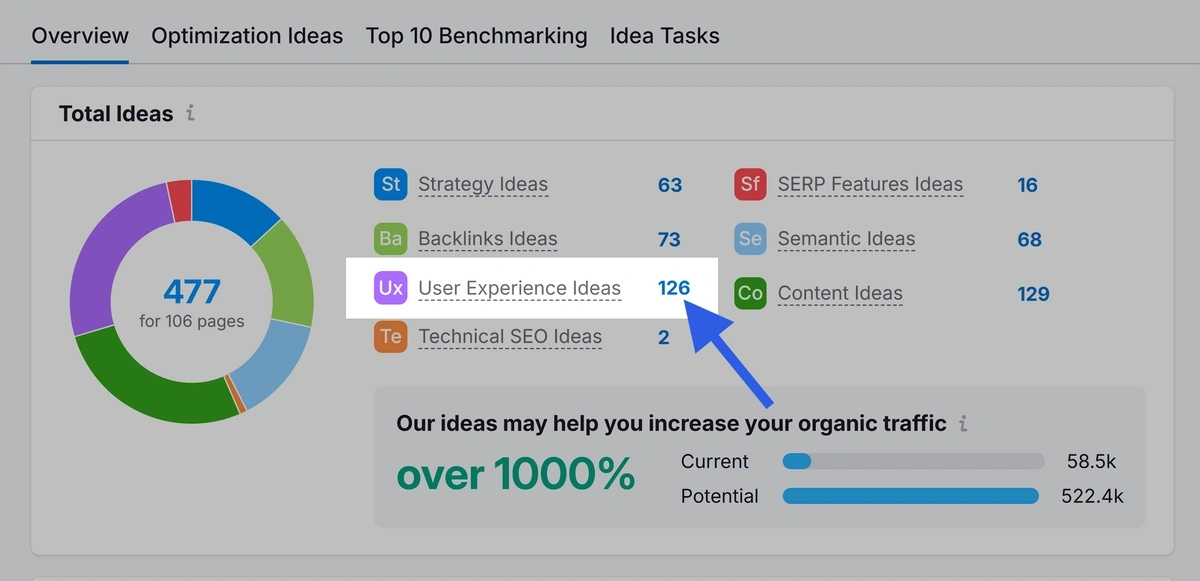
Open the tool and head into your project. Click “Connect” and follow the prompts to connect your Google account.
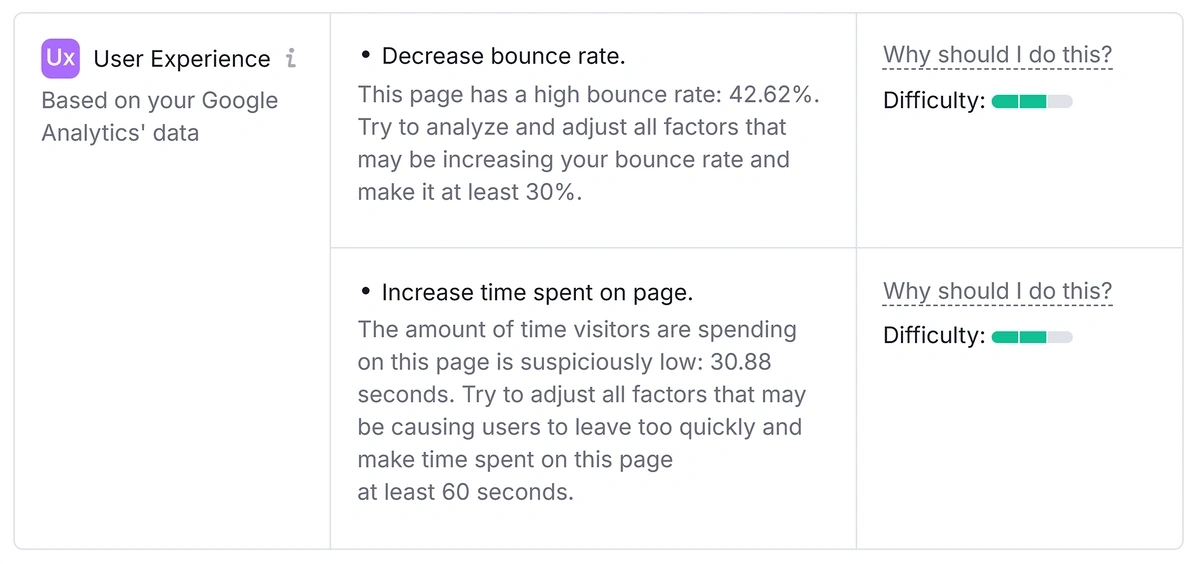
Once connected, the tool will review your site’s Google Analytics data. Click the “#” beside “User Experience Ideas” to get tailored UX suggestions.
Like suggestions for reducing bounce rate and increasing the time users spend on the page.
Work through these suggestions to improve the UX on your site.
12. Optimize for Featured Snippets
Featured snippets have the highest click-through rate (42.9%) of all positions in the search results (if they appear). So, ranking for featured snippets can increase clicks to your site. And give your site more visibility.
For a breakdown of how much featured snippets can boost traffic for specific keywords, use our SEO traffic estimator.
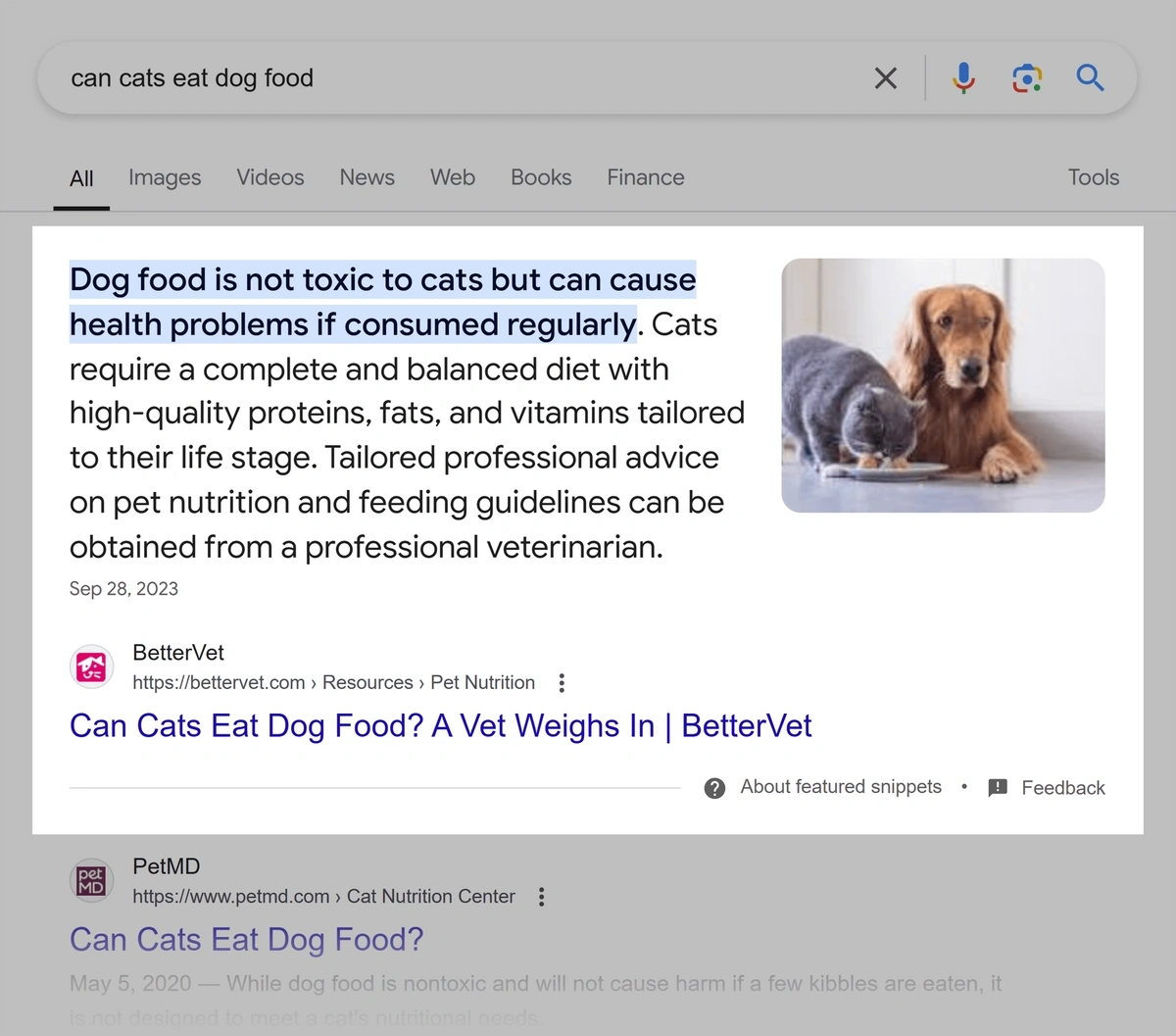
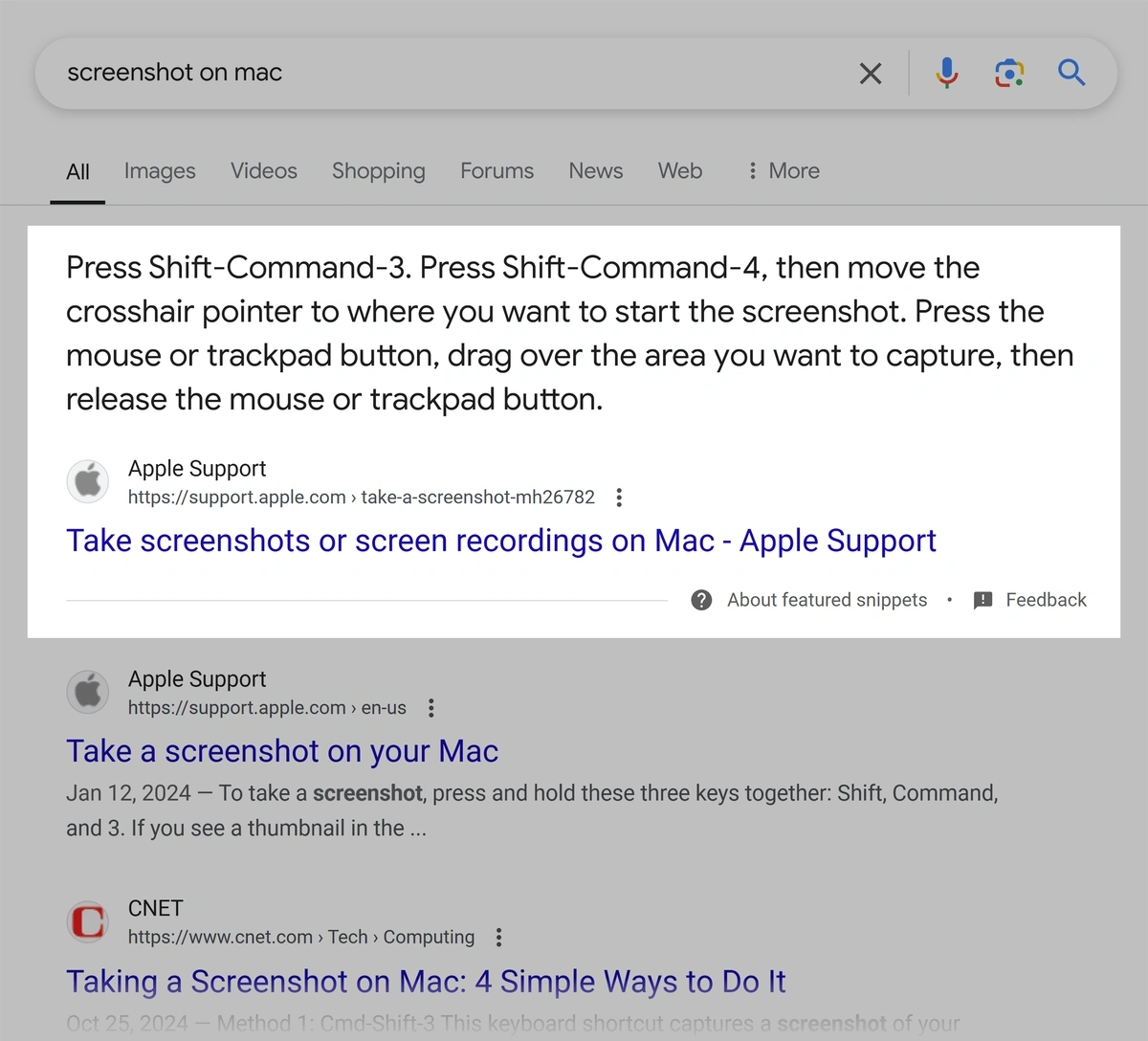
Featured snippets are website excerpts that answer a user’s query. They’re often at the top of the search results.
Like this:
There are four main types of featured snippets:
- Paragraph snippets (pictured above)
- List snippets
- Table snippets
- Video snippets
Try to rank for featured snippets by optimizing your content for them.
Here’s how:
Open Semrush’s Organic Research tool and enter your domain. Choose a target location and click “Search.”
Click the “Positions” tab.
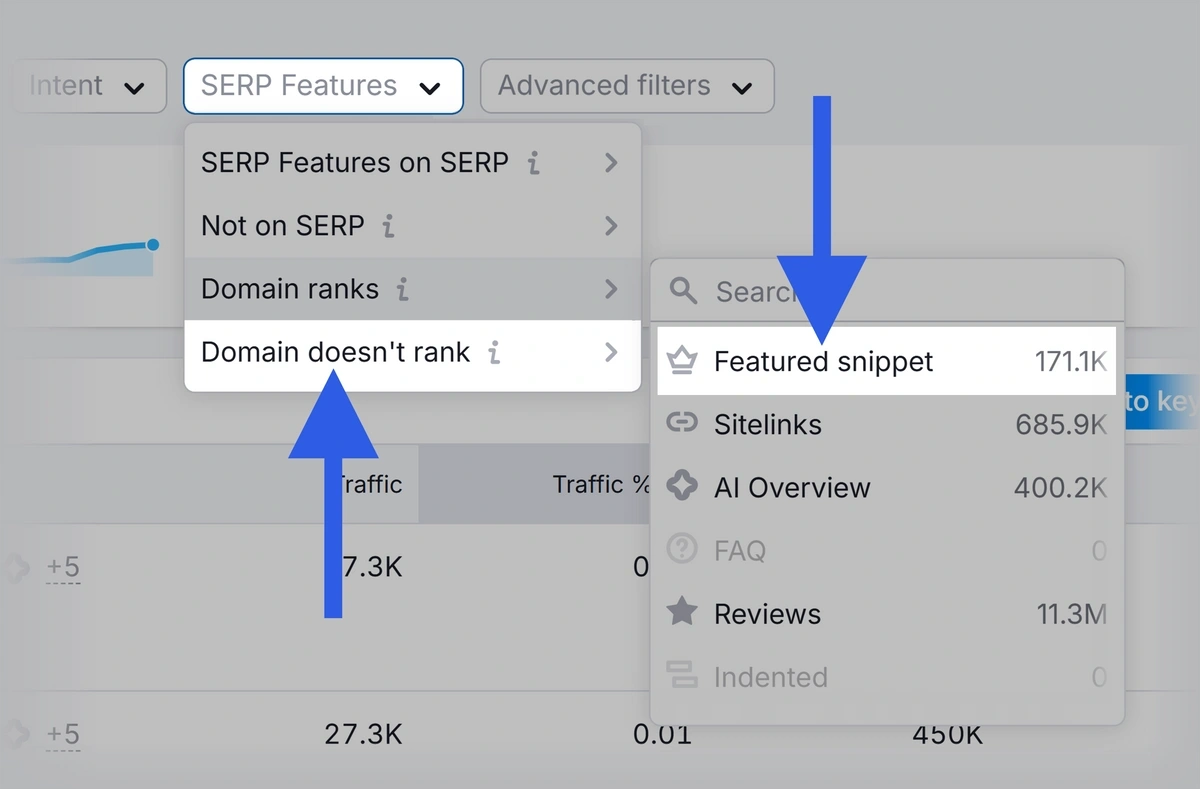
Then, use the “SERP Features” dropdown to select “Domain doesn’t rank” and “Featured snippet.”
This shows you which featured snippets you don’t have for the keywords you already rank for.
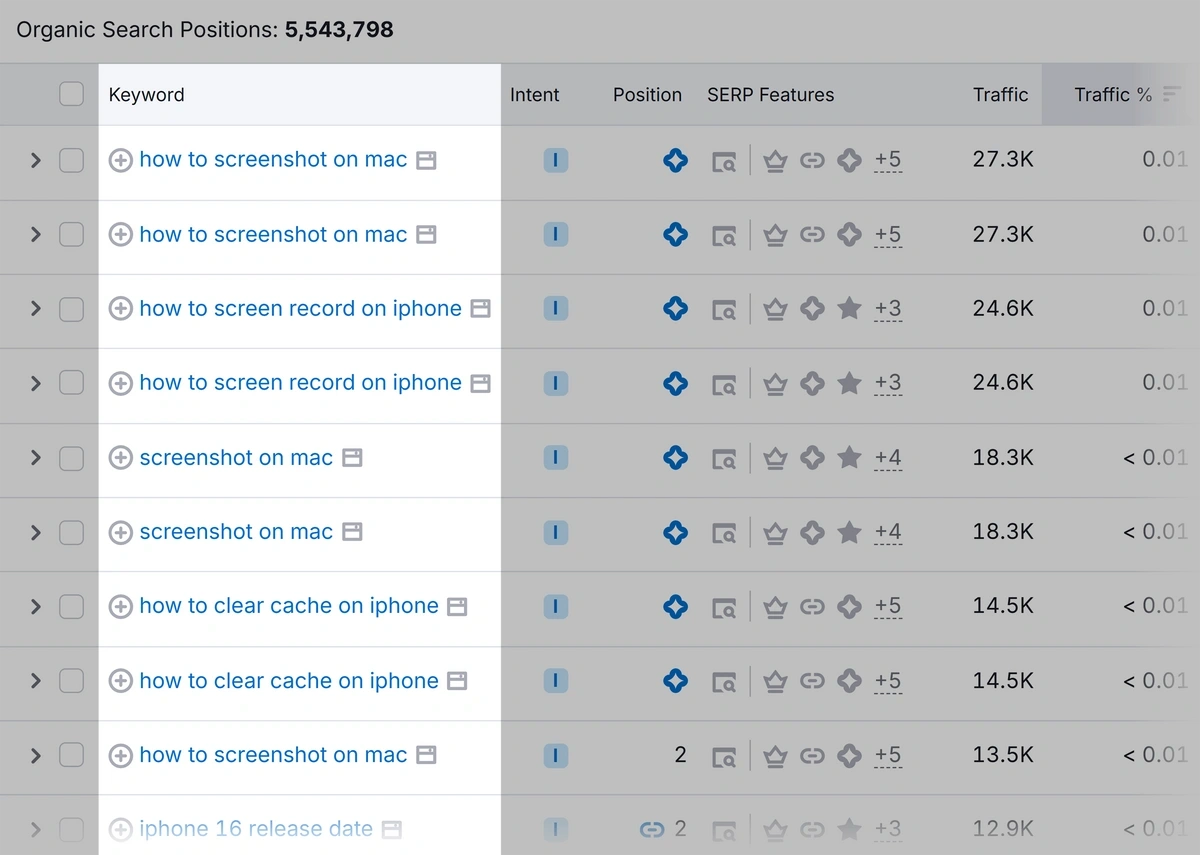
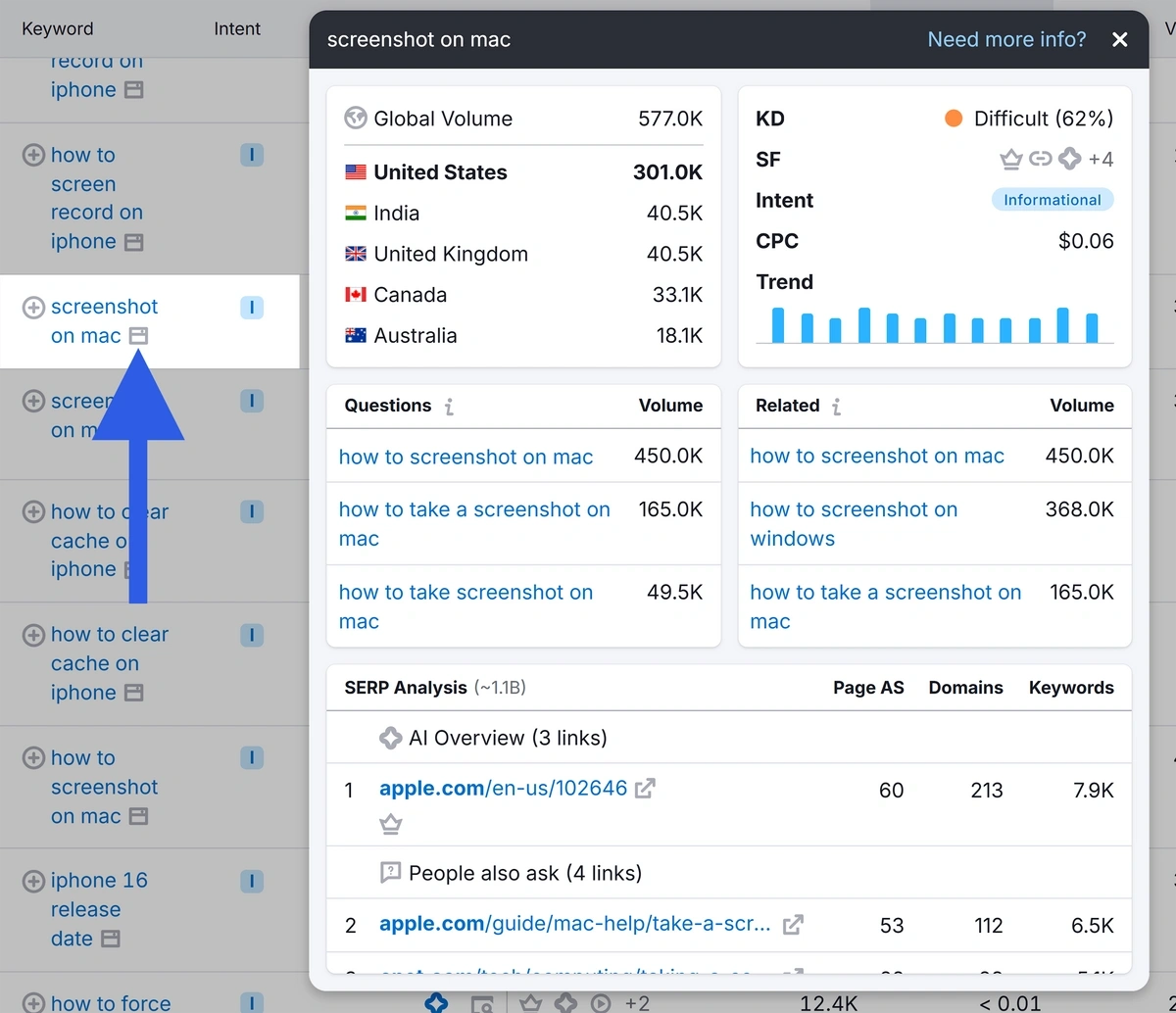
If you click the icon beside the keyword, you can get a quick view of the keyword’s data.
For example, you can see which site is ranking for the featured snippet.
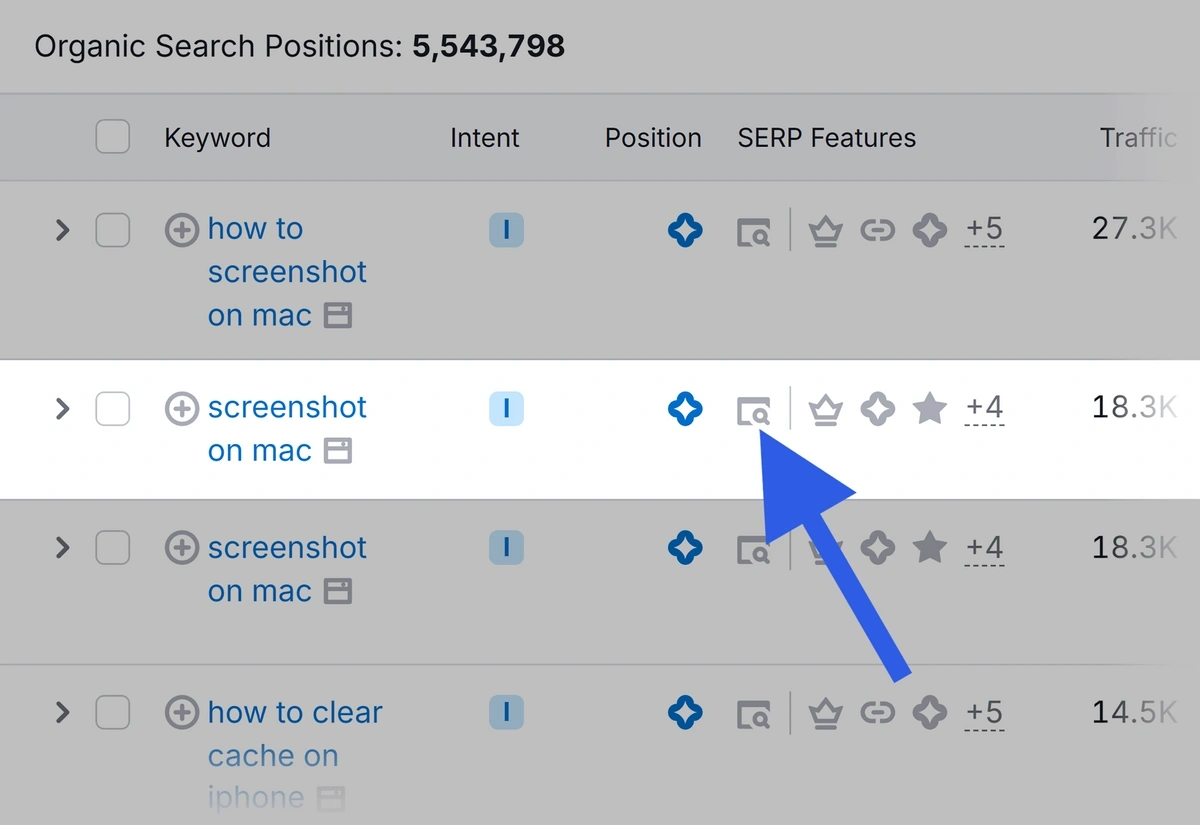
Then, click the icon in the “SERP” column to see a snapshot of the search results for that term.
Note which type of featured snippet is ranking (i.e., paragraph, list, table, or video).
Then, optimize your content to try and capture the featured snippet position.
Here are a few ways to optimize for the different types of featured snippets:
- Paragraphs: Write an accurate and succinct answer to the user’s query that’s, ideally, fewer than 300 characters
- List: Include useful bulleted or numbered lists within your body content
- Table: Include a table (with a heading) within your content
- Video: Upload videos with clear audio and marked timestamps to YouTube
13. Include Relevant Schema Markup
Schema markup, also called structured data, is code you add to your site to help search engines better understand your content.
This code can also help search engines display certain content in a rich format within the search results (known as rich snippets). Rich snippets can help your site stand out in the SERPs.
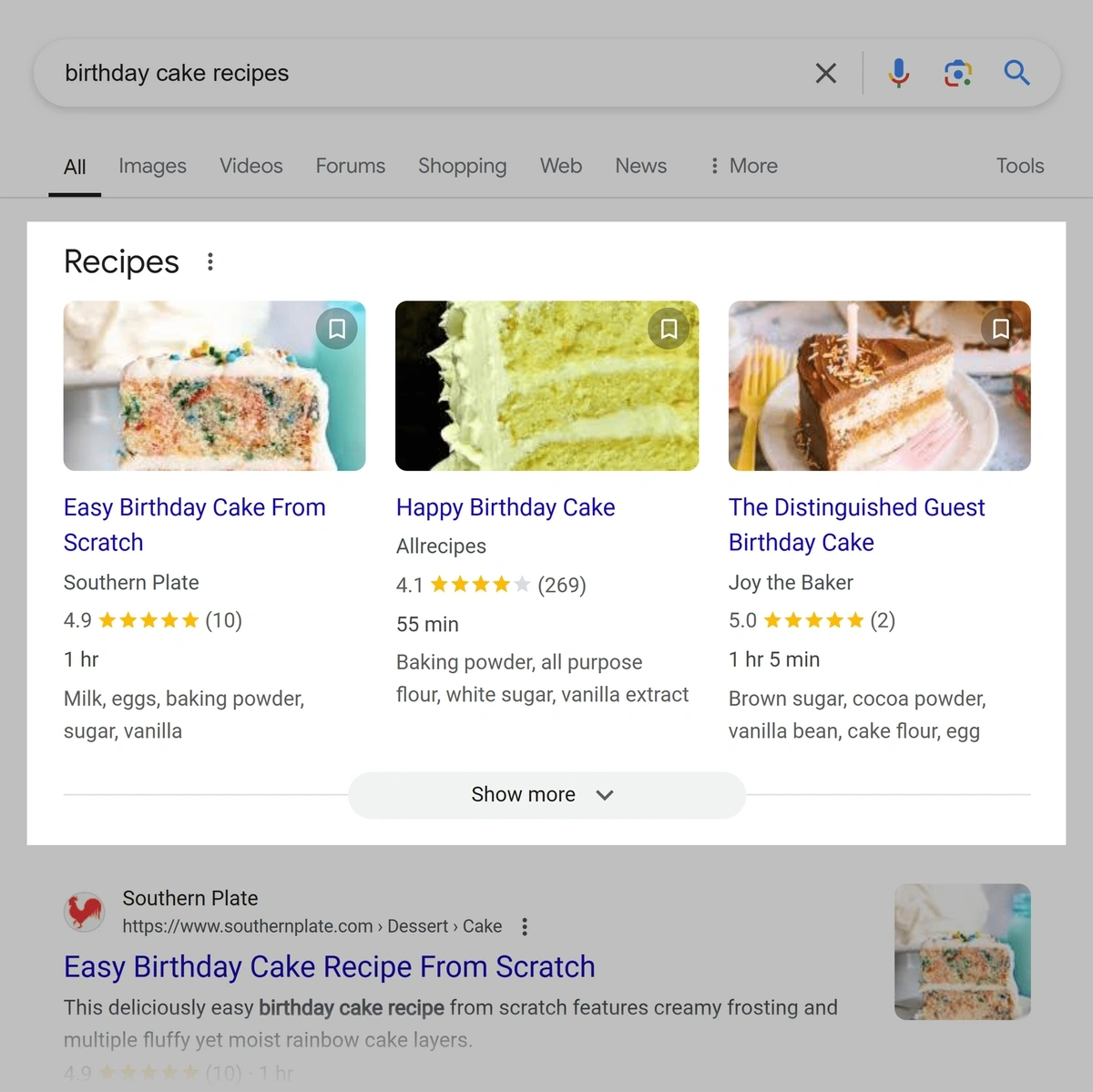
This example includes star ratings, review counts, cooking times, and recipe ingredients:
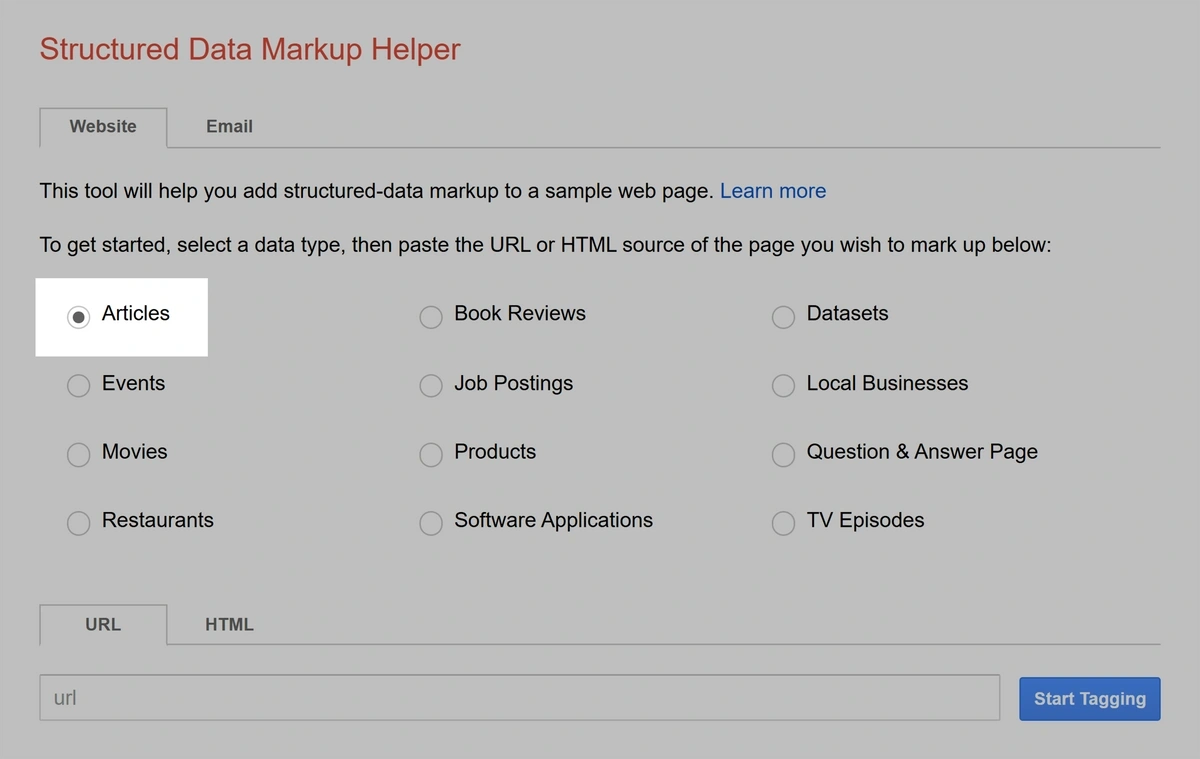
Google’s Structured Data Markup Helper can help you generate the markup for your web page.
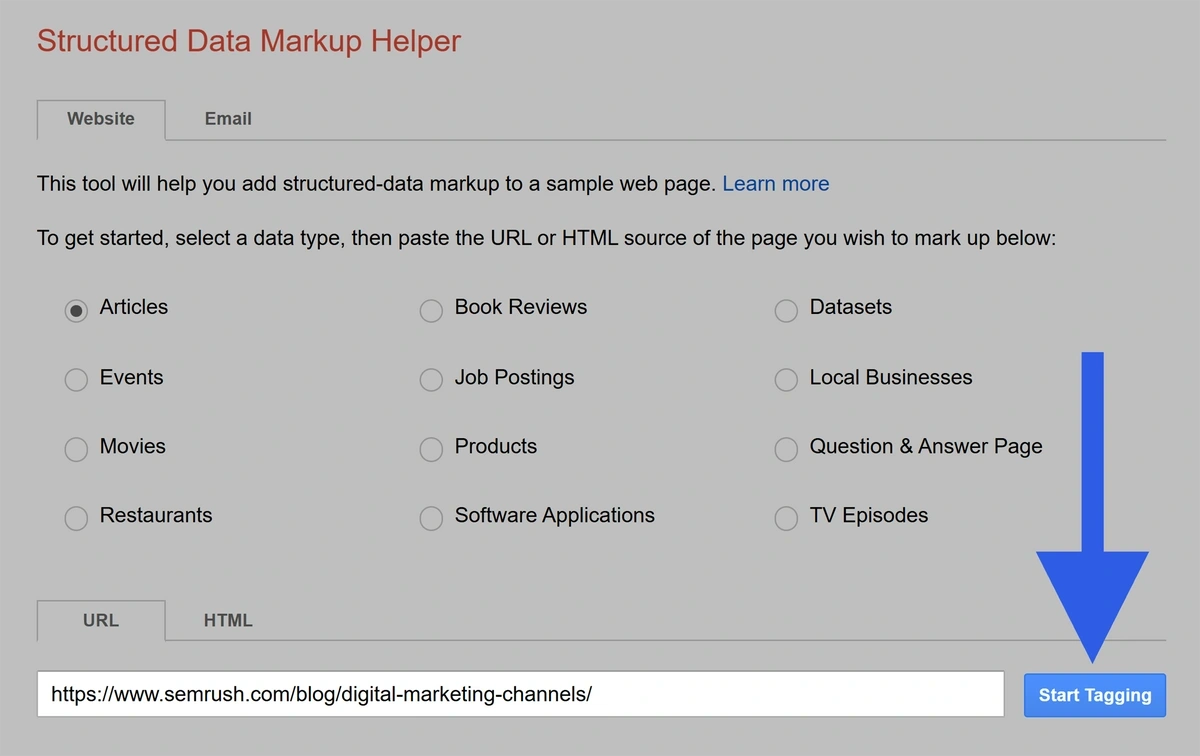
Head to the tool and choose the data type that reflects the page you’re adding the markup to. We’ll use “Articles” for this example.
Paste in the URL of the page and click “Start Tagging.”
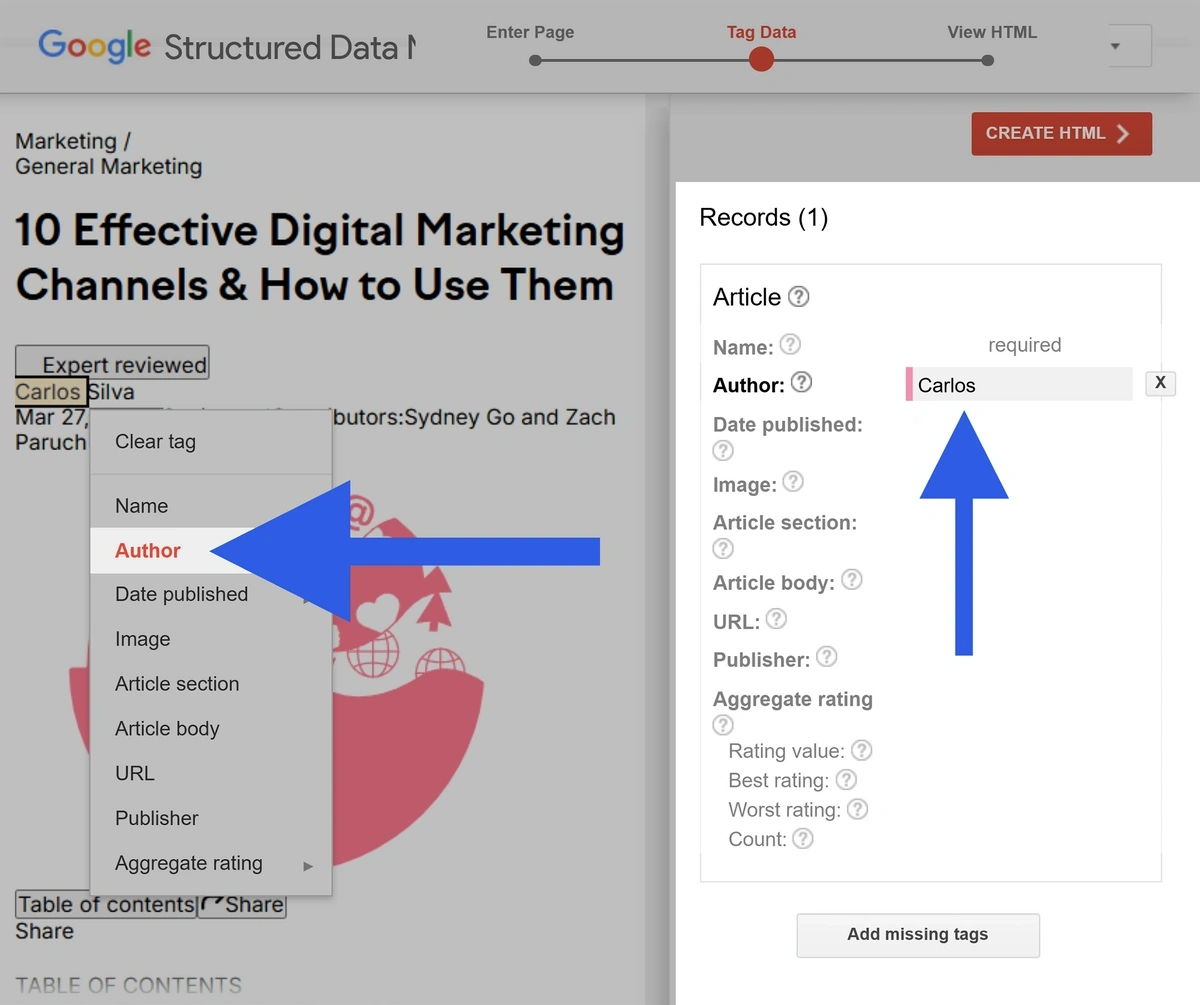
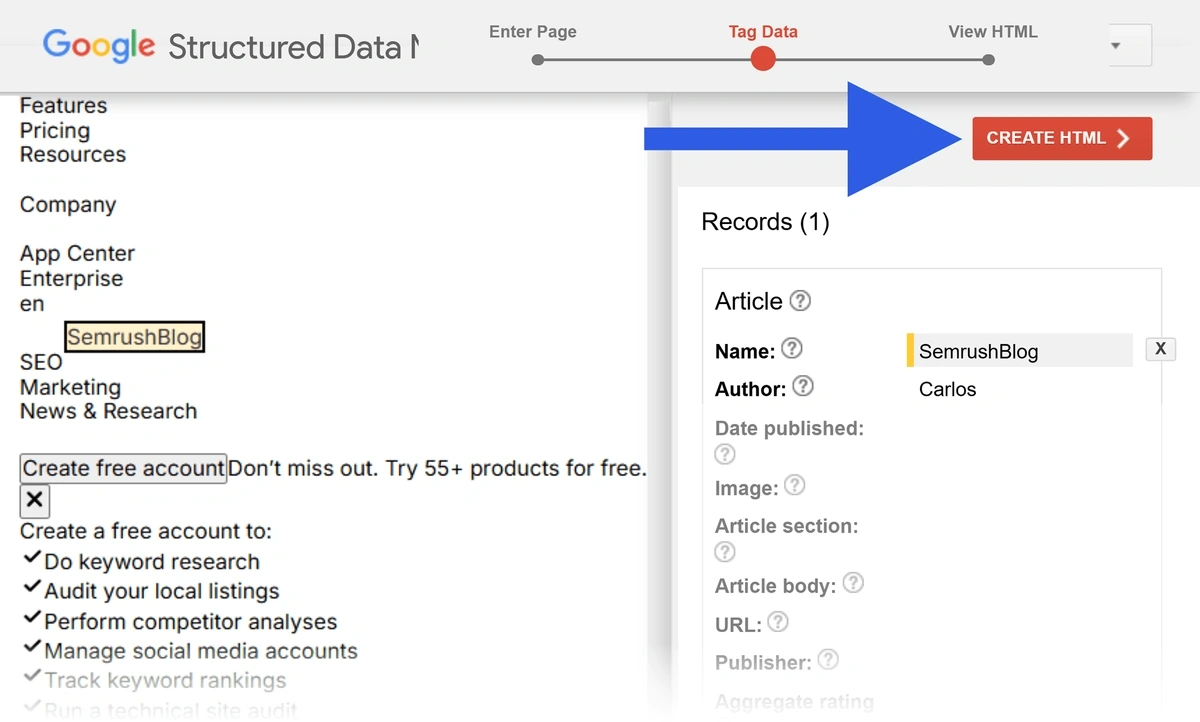
Next, highlight the data you’d like to mark up. For example, we can highlight the author’s name and select “Author” to apply author schema markup.
You can also mark up other items like images and the article’s publication date. Go through and highlight each markup property.
When you’re done, click “Create HTML.”
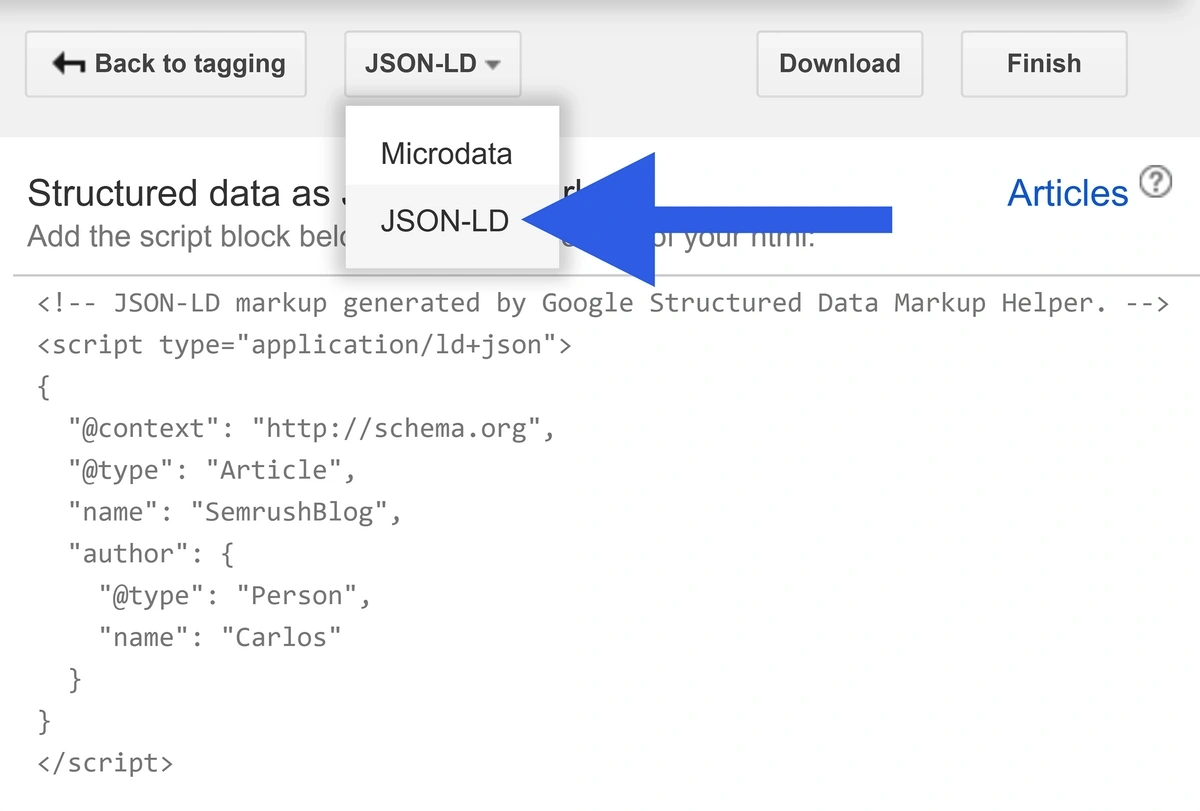
The tool will give you two types of schema markup code: JSON-LD and microdata. Google recommends using JSON-LD if possible.
Copy and paste the code into your page’s <head> section.
After implementing schema markup, use Semrush’s Site Audit to monitor and ensure you’ve set it up correctly.
Here’s how:
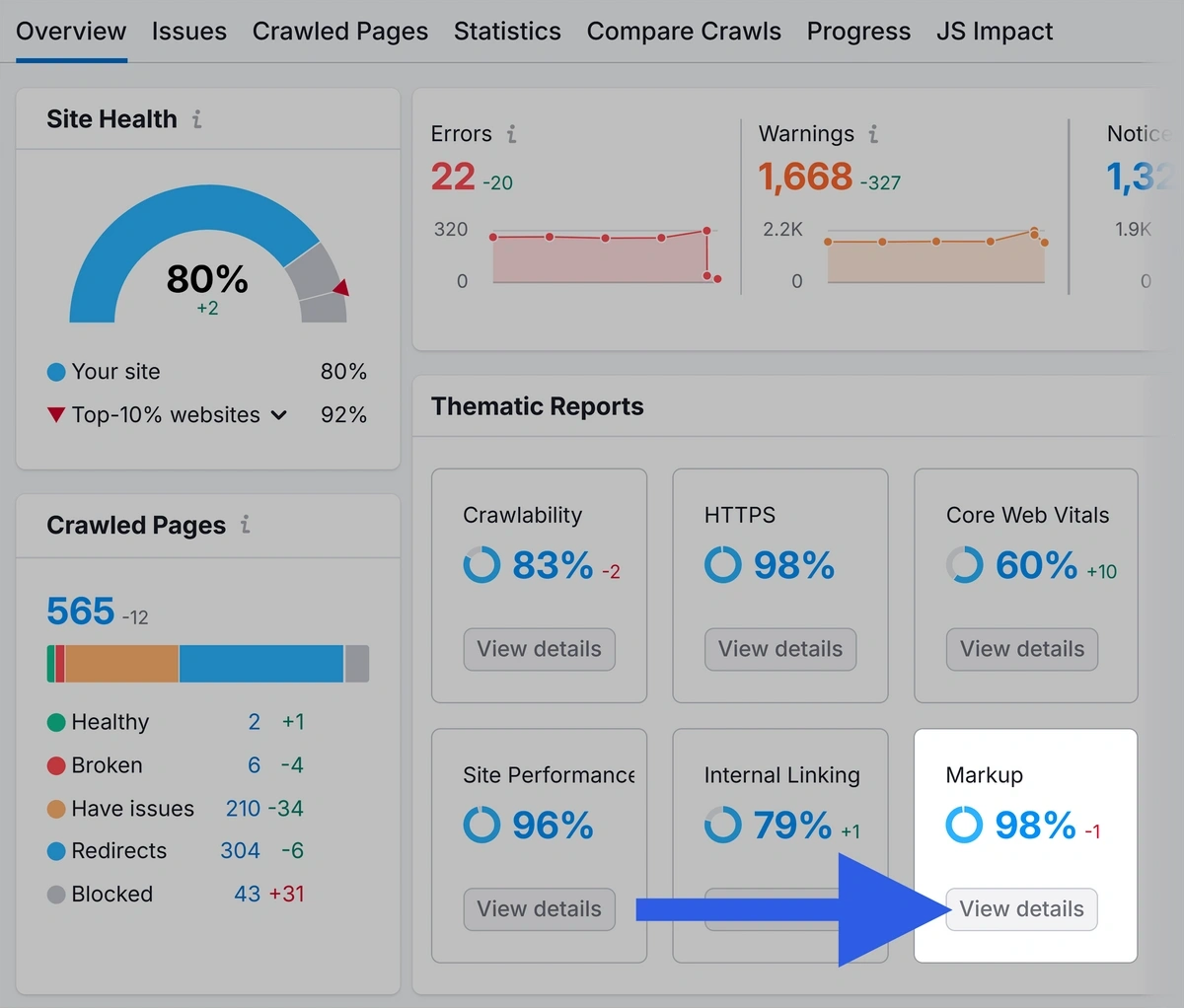
Open the Site Audit tool and head into your project from earlier. Under “Markup” click “View details.”
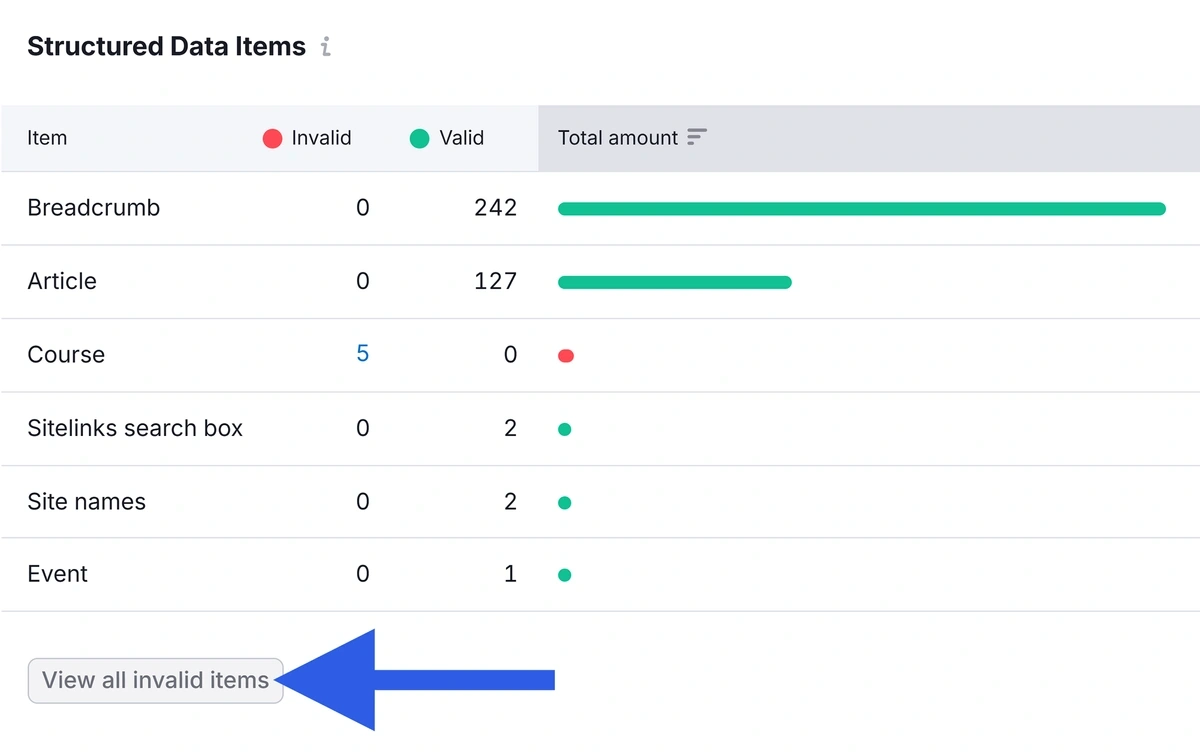
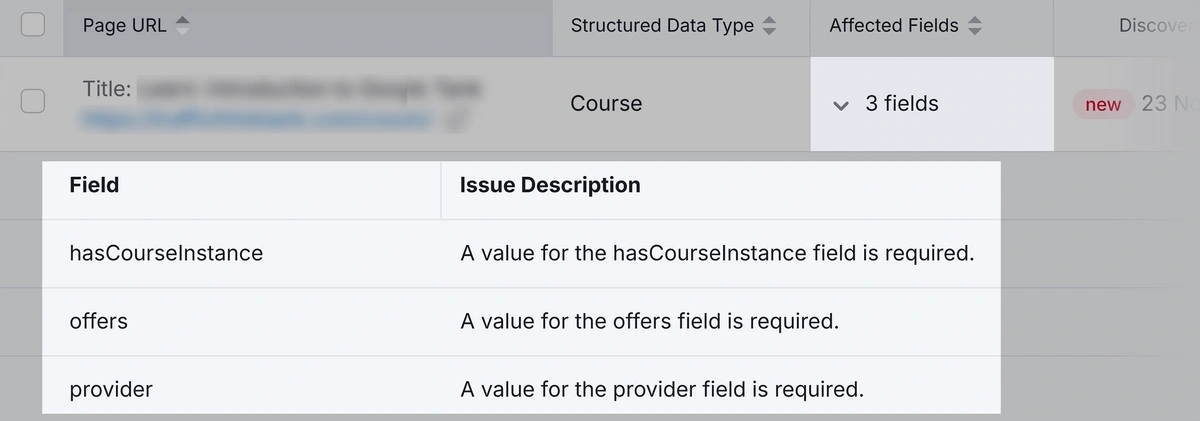
Scroll down to “Structured Data Items” and click “View all invalid items” to view errors with your schema implementation.
Click the “# fields” in the “Affected Fields” column to view specific errors.
Fix these errors to ensure search engines can properly understand your page’s content.
Apply On Page SEO to Improve Your Site’s Performance
Improving your on page SEO can help provide a great experience for your users. And it will make it easier for search engines to find and understand your content.
Save our free on page SEO checklist and use it for each page you want to optimize.
It reminds you to use the On Page SEO Checker and Site Audit for each relevant step. Try these tools and more with a Semrush free trial.
Stop Guessing, Start Growing 🚀
Use real-time topic data to create content that resonates and brings results.
Exploding Topics is owned by Semrush. Our mission is to provide accurate data and expert insights on emerging trends. Unless otherwise noted, this page’s content was written by either an employee or a paid contractor of Semrush Inc.
Share
Newsletter Signup
By clicking “Subscribe” you agree to Semrush Privacy Policy and consent to Semrush using your contact data for newsletter purposes
Written By


Keri Lynn Engel is the Manager at Exploding Topics, where she focuses on building high-traffic SEO strategies and organic growth e... Read more