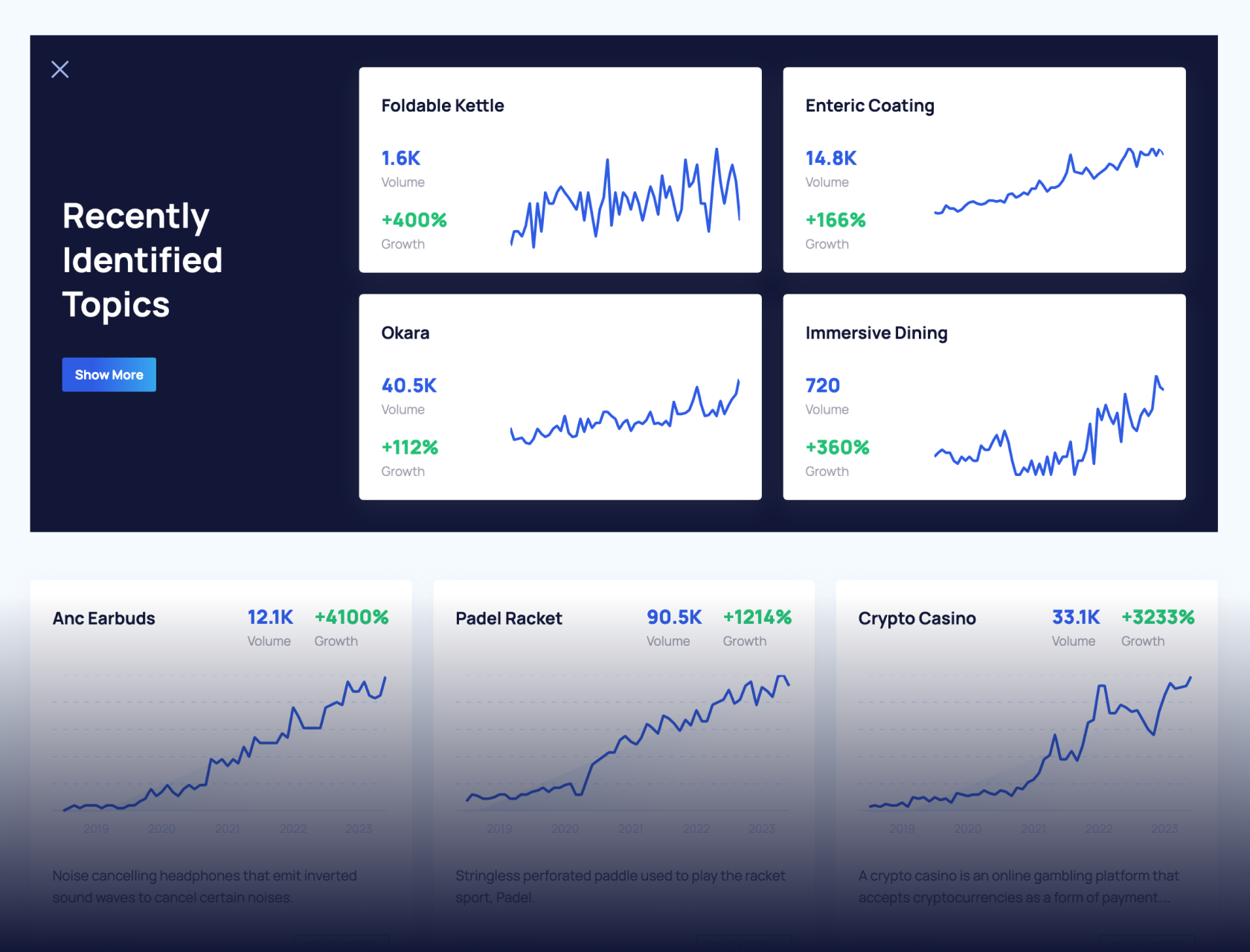
Get Advanced Insights on Any Topic
Discover Trends 12+ Months Before Everyone Else
How We Find Trends Before They Take Off
Exploding Topics’ advanced algorithm monitors millions of unstructured data points to spot trends early on.
Keyword Research
Performance Tracking
Competitor Intelligence
Fix Your Site’s SEO Issues in 30 Seconds
Find technical issues blocking search visibility. Get prioritized, actionable fixes in seconds.
Powered by data from
How to Perform a Website Content Audit (+ Free Template)
Content "freshness" is an increasingly important factor in achieving good rankings.
Google's Quality Rater Guidelines say that the best ratings should only be given to information that is "current, recent, or updated".
A content audit will help you to figure out what needs to be updated to improve (or maintain) your ranking positions.
You can use our free content audit template as you work through this guide.
Why Do a Regular Content Audit?
Whenever I work with a small business on a budget, content updates are the first thing I recommend. If your site has been publishing blog posts and landing pages for a year or more, updating that content can be more impactful than producing something new.
A content audit involves reviewing all the content on your website for accuracy, and that includes outdated information. You also need to look at performance and technical issues during the audit.
Once you know how it’s performing, you can potentially improve rankings to increase traffic.
For large sites, content audits are ongoing as part of SEO maintenance: regular tasks that need to be completed to keep your site ranking well.
Setting Goals For a Content Audit
A content audit can be a large undertaking, depending on the size of your site.
You’ll want to audit all landing pages, blogs, and product or service pages as part of the project
According to the Quality Rater's Guidelines, freshness matters most for queries related to events, news, information, and products, so it's a good idea to focus on those pages first.
When setting goals for a content audit, here are some of the other issues I think about:
- Declining rankings, traffic, or conversions. Your goal is to re-optimize and update the content to regain what you lost.
- Technical changes that had unintended consequences. For example, switching a plugin or changing the theme on your site affected the layout or page speed.
- Content that is no longer bringing in traffic or revenue. These pages can be removed and redirected.
- EEAT. Google is looking for content that oozes expertise and creates trust between the reader and the author. Often, older pages don't do this well, so it's a good idea to look for ways to improve your EEAT. The Quality Rater's Guidelines cover this in detail.
Each of these goals has a process and a set of metrics. For the purposes of this guide, we’ll use a free template to cover the most important tasks.
How to Perform a Content Audit in 3 Steps
Before you start, you'll want to gather a list of the keywords you want to rank for. If you don't have a list, check out our guide on how to choose keywords for SEO, then come back to this article.
Let’s walk through the three high-level tasks you’ll need to plan for.
1. Create an Inventory of Your Existing Content
Before you start editing content, take a step back. List everything you have in a spreadsheet.
You’ll need a complete list of:
- Blog posts
- Landing pages
- Reports
- Ebooks
- Core static pages
Remember to include pages that you don’t look at every day, like your ‘About Us’ page.
I recommend using a Google Sheet to gather all the URLs.
You can use our free content audit template.
Open the template and click “Use Template” in the top right-hand corner. This will save a copy to your Google Drive.
We’ll use this sheet to record the URL to every page that you need to analyze.
Getting the URLs to every page on your site sounds daunting. But there’s no need to worry about doing it yourself, or digging into your CMS.
I always use the Semrush Site Audit tool to get the full list. And Site Audit contains a ton of useful metrics that we can use later in the content audit.
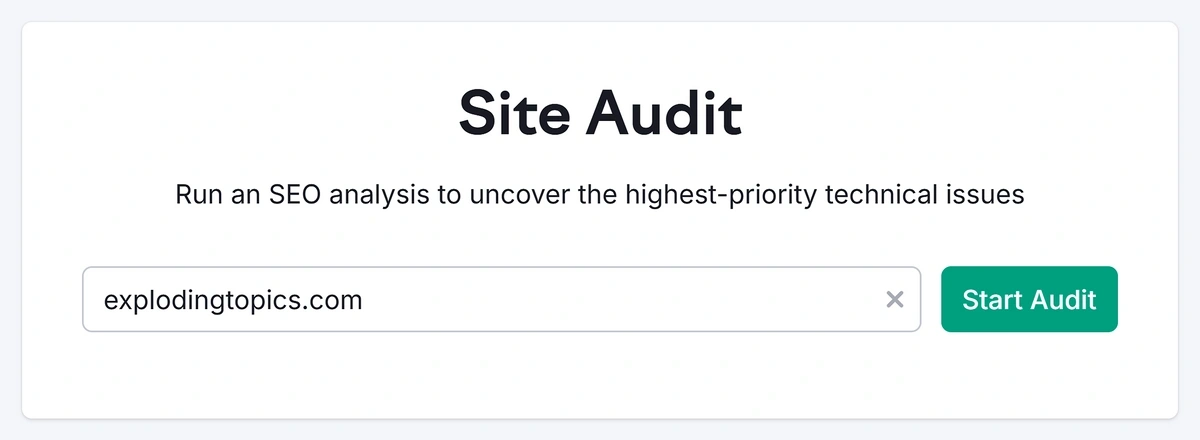
If this is your first time using Semrush, type in your URL and click “Start Audit.”
Semrush will guide you through the process of starting your first audit.
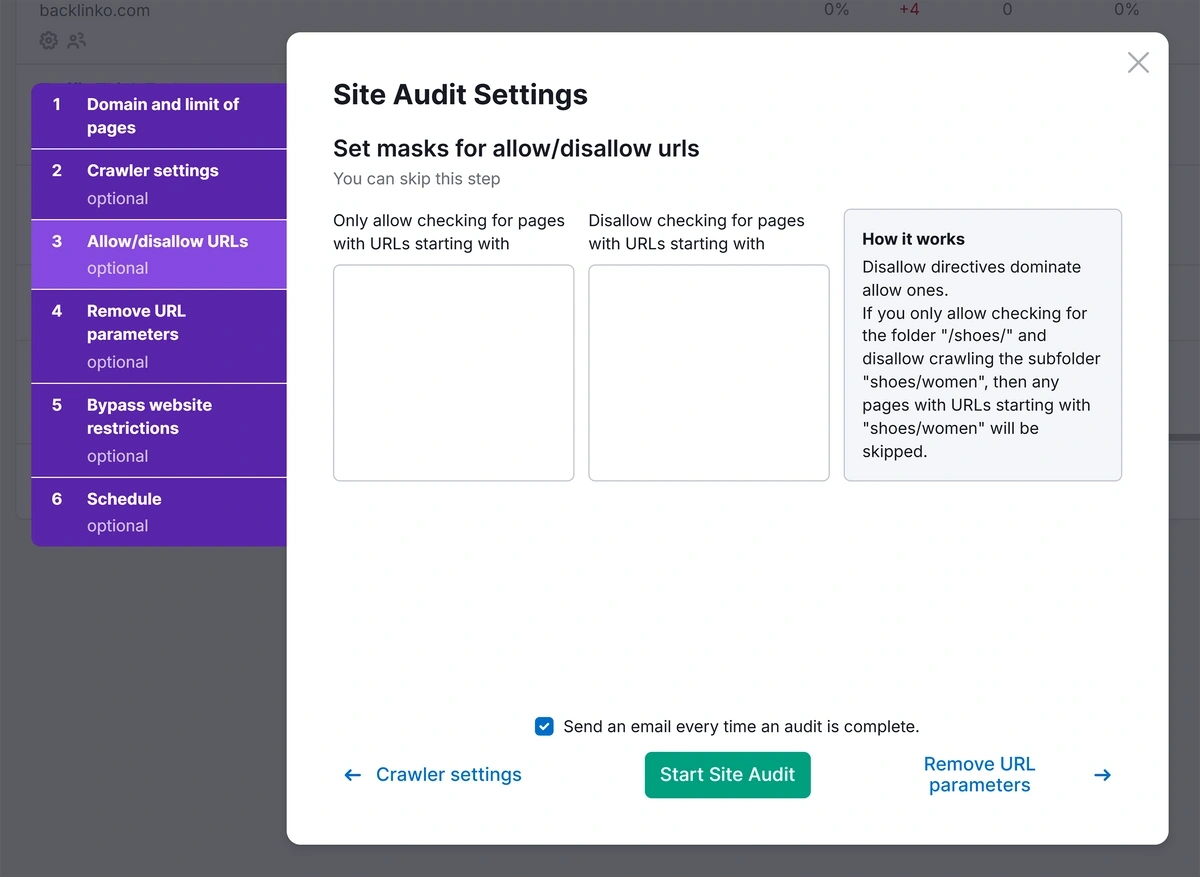
I recommend setting the page limit high enough so that it audits the entire site. But if you want to include or exclude specific sections, you can do that using the “Allow/disallow URLs” tab in the Site Audit settings.
When you’re ready, click “Start Site Audit.”
Depending on how many pages need to be crawled, a site audit can take a few minutes or up to 24 hours.
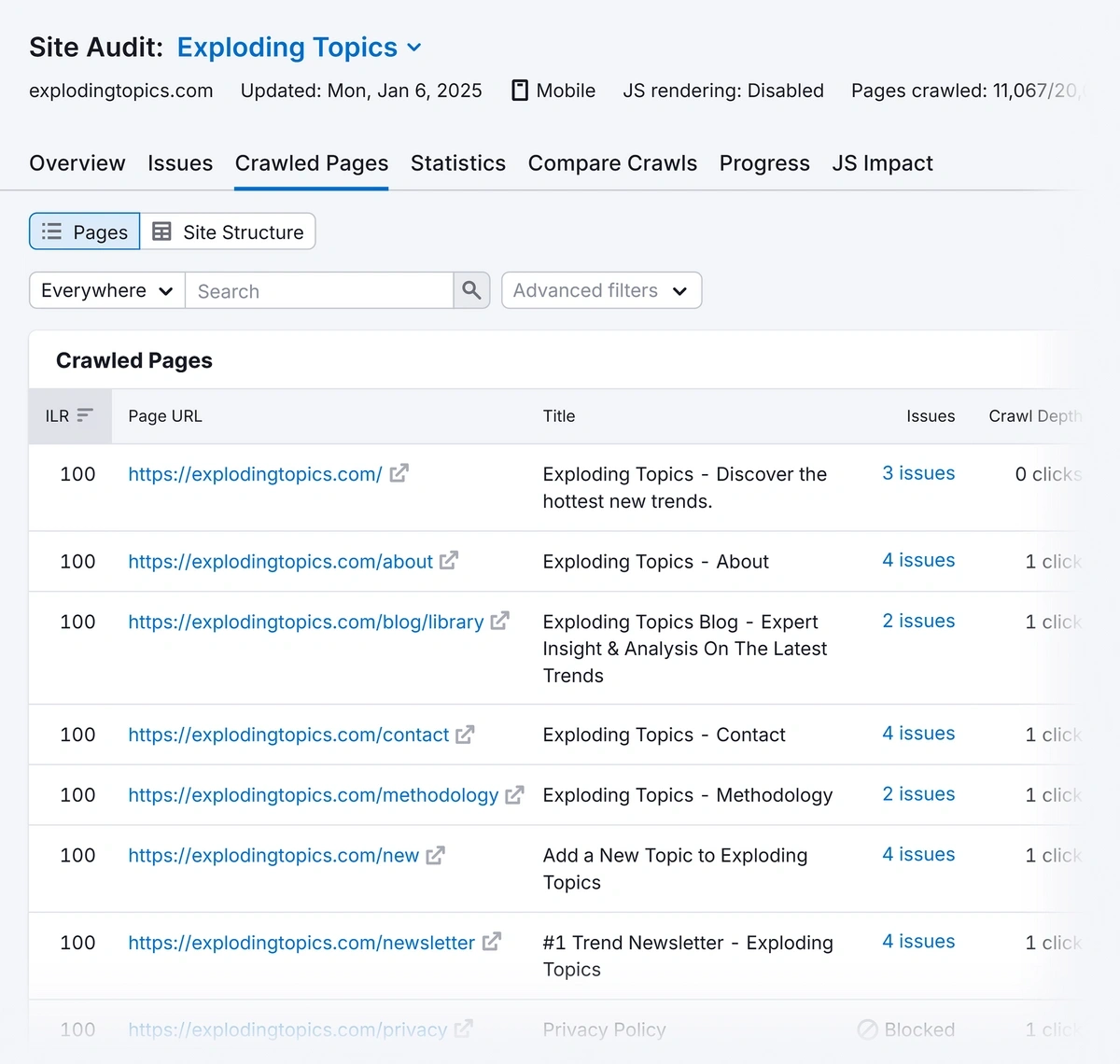
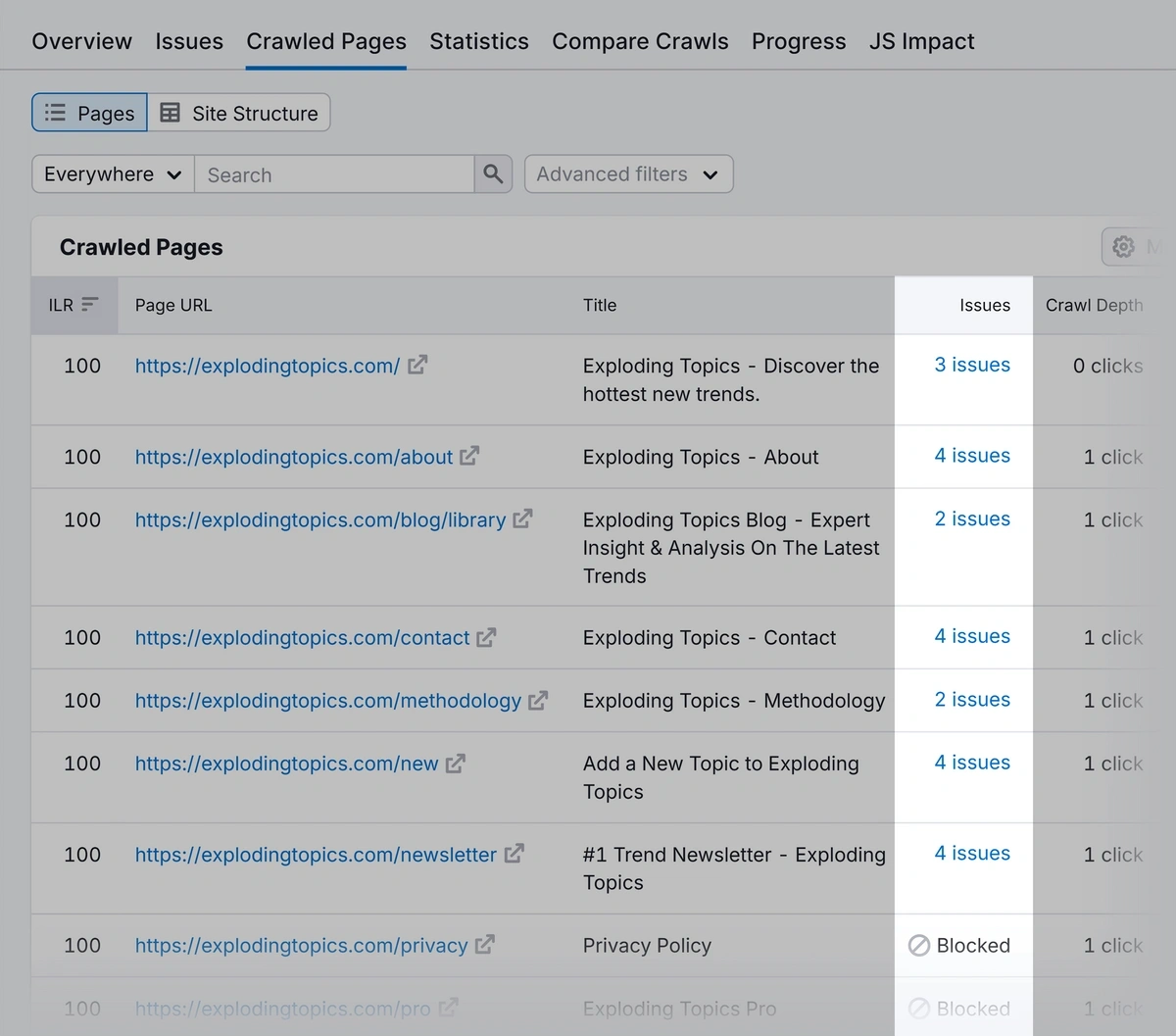
When it’s ready, open the audit report and navigate to the “Crawled Pages” tab. If you set the limit high enough, all of your URLs will be listed here.
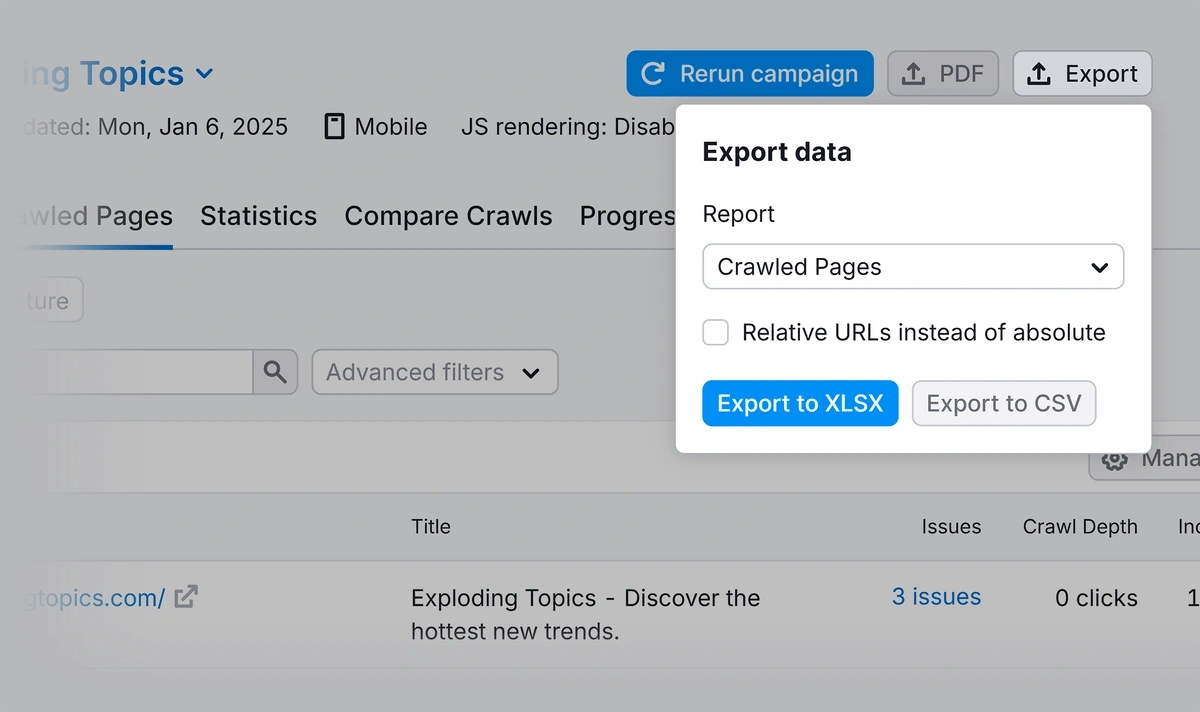
To add the entire list of pages to your audit spreadsheet, click “Export” > “Export to CSV.” You can choose to download in Excel or CSV format.
From there, copy (or import) the list into the free content audit template.
You can also copy URLs from your sitemap, but I prefer this method because I can export an overview of issues at the same time.
Now that you have a list of all your URLs, you can start filling out the other columns.
2. Analyze Content Performance
This part of the audit is about reviewing the SEO for your entire site.
We’ll combine data from Semrush with some insights from a couple of other tools.
Organic Traffic
Organic traffic refers to website visits that come from organic search results from search engines like Google.
You’ll want to ensure you’re getting the best possible traffic to high-converting pages, like landing pages and top-performing blog posts.
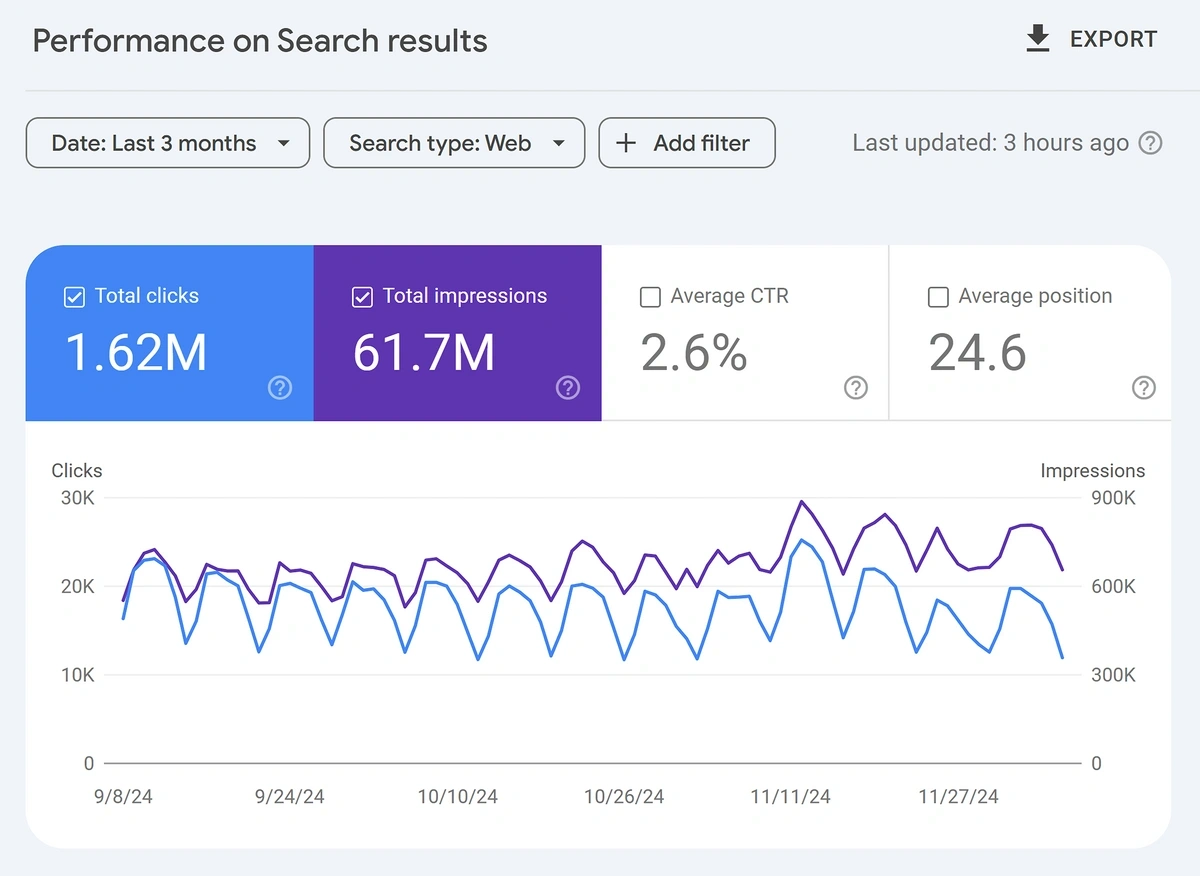
I find that I get the most accurate data from Google Search Console.
Select your site from the dropdown at the top-left. Then click “Performance” from the navigation menu.
The number we’re interested in is “Total clicks”, which tells you how many people clicked on a page in Google search results.
Scrolling down, you’ll find a table with information on:
- Queries (keywords)
- Pages
- Countries
- Devices
- Search appearance
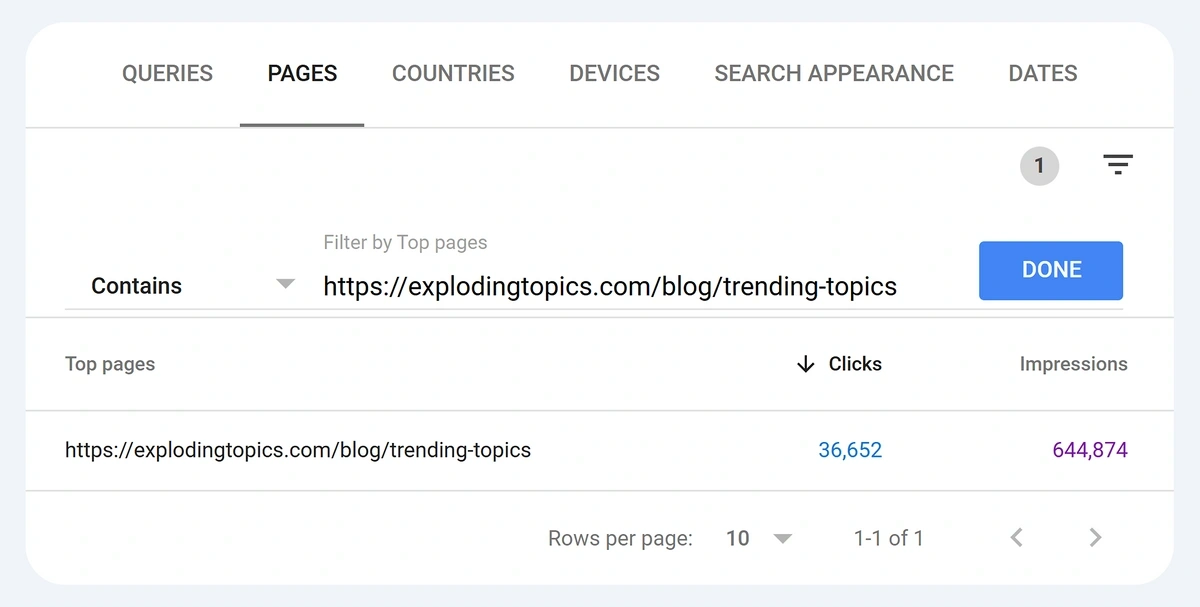
Click the “Pages” tab to display the data by page.
For a small site, you can then click the filter icon to search for individual URLs and see the number of clicks they got.
Record the clicks in the “Organic Traffic” column in your content audit Google Sheet.
On large sites, extracting this data page-by-page is likely to take a long time. Instead of manually searching for URLs, you can export the data.
Upload it into a blank tab in your sheet. You can then use a VLOOKUP statement to bring the click data into your main sheet, which will save time compared to manually copying it over.
Keyword Rankings
Keyword rankings are important because they tell you where your page appears in the search engine results page (SERP).
(For this step, you'll need a list of keywords that you already know you want to rank for.)
We can use Semrush to export the ranking data for each page. This will allow you to see which pages likely need optimization.
Create a new column in your content audit spreadsheet titled “Keywords” and make a note of each primary keyword next to the page URL.
You can easily search your website for keywords if you’re not sure which keywords you targeted on each page.
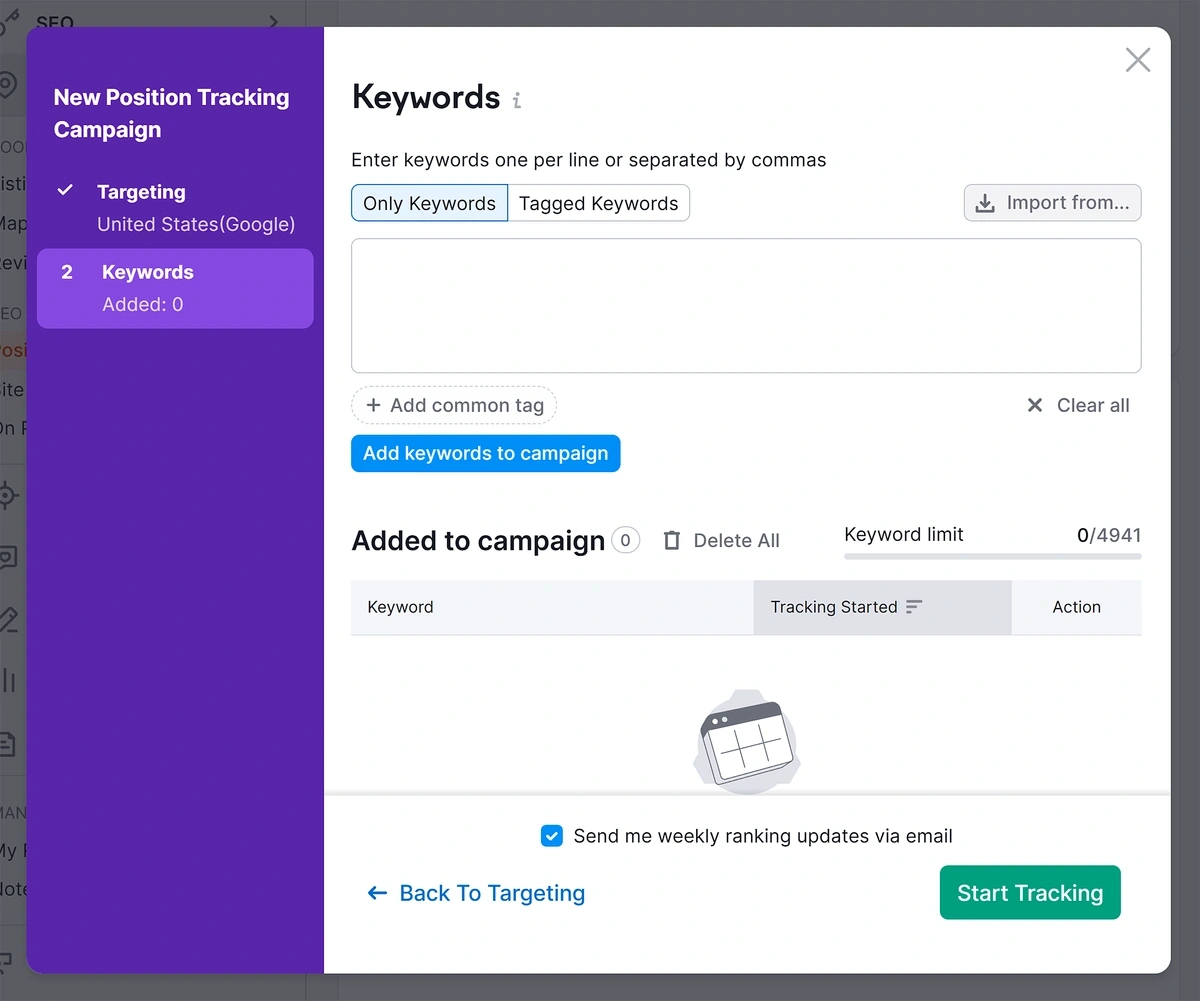
Next, open up the Semrush Position Tracking tool.
If you’ve used the tool before, select your site from the list. If you haven’t, create a new campaign. Paste in your list of important keywords in the second step.
If you don’t have a keyword list, you can click the “Import From…” button to pull queries directly from Google Analytics or Google Search Console. This will give you a baseline measurement of what you already rank for.
When you click Start Tracking, Semrush will gather ranking data for the keywords you provided.
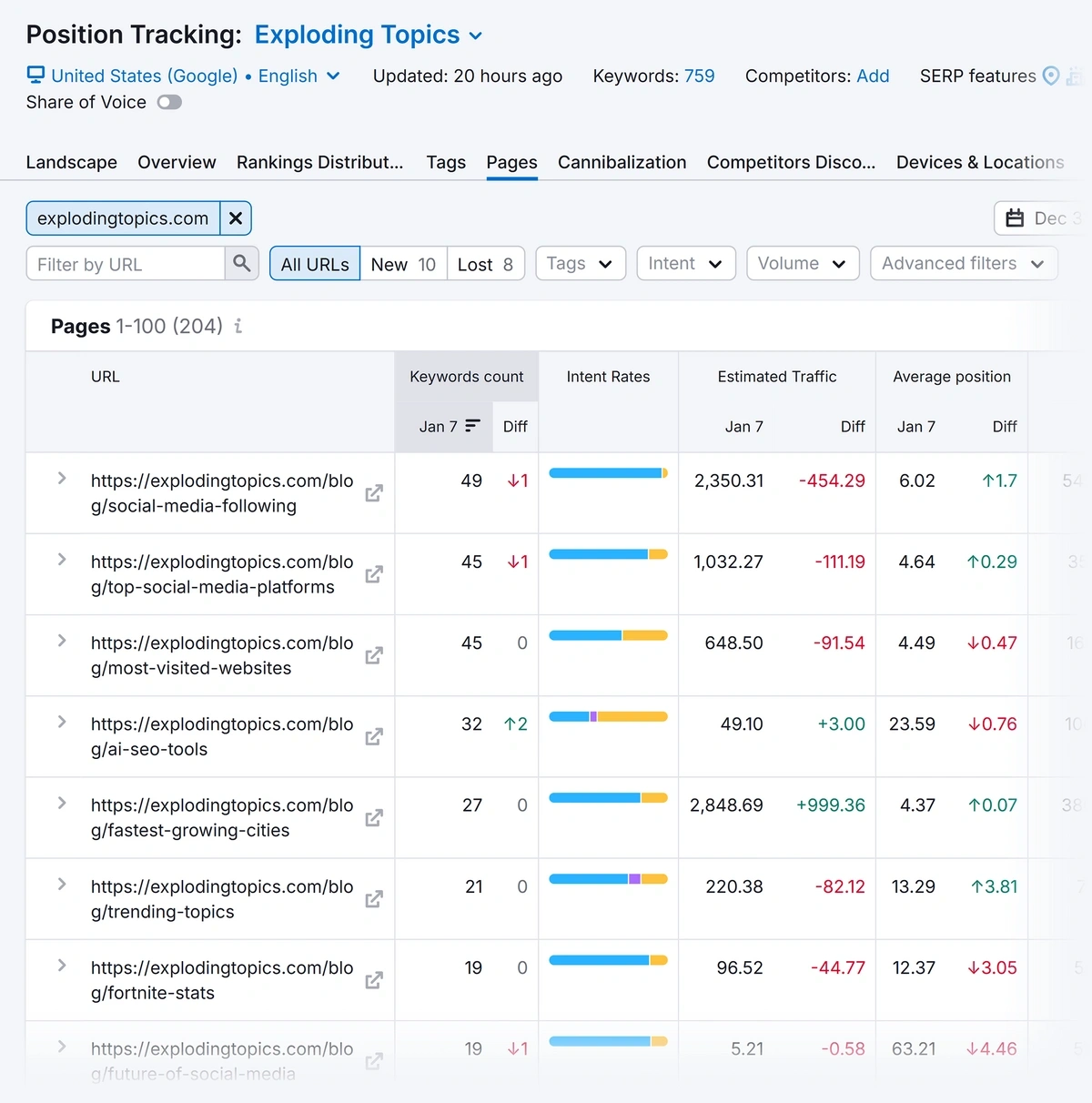
Once it’s done, click the “Pages” tab to find keyword positions for individual pages.
Again, you can “Filter by URL” to find each page’s average position and any recent movement up or down. Use the date filter above the table to compare over a longer period.
Enter the ranking position next to each page in the content audit template.
For large sites, export the data and merge it into your “Current Ranking” column using a VLOOKUP equation.
Once you’ve recorded the current position, you should also review the changes over time. The Semrush Position Tracking tool will do this for you.
For example, if your search engine position is trending down, it’s a sign that the content has decayed, lacks freshness, or may no longer be delivering value to your target audience. In that case, you know that the content needs to be optimized or updated.
Content optimization is a complex topic that deserves a deeper dive. We produced a separate guide on improving search engine positioning to help you understand how to adjust content to improve rankings.
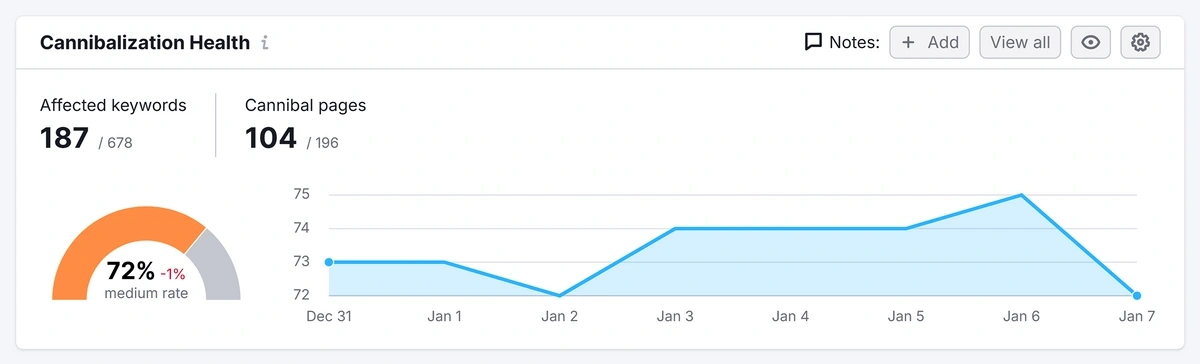
Reviewing Cannibalization
Cannibalization means you have more than one page ranking for the same keywords.
This can be a problem because your visibility for that keyword is split between multiple pages on your site.
So it can harm your rankings, and reduce organic traffic to the page you really want people to visit.
Cannibalization is often accidental. It can be difficult to avoid if the content is closely related. However, if it’s impacting your revenue, you need to track down and fix the problem as part of reviewing keyword rankings.
You can find cannibal pages in the Semrush Position Tracking report. Click your project, then click the “Cannibalization” tab to review the affected pages.
If any of your pages are losing keyword positions and appear to be cannibalizing each other, it’s a sign that you need to clarify the purpose of each page by optimizing the content.
You can make a note of this in your sheet next to the URLs that are cannibalizing each other.
Backlinks
Backlinks are links from other websites that point to pages on your site.
These links signal to search engines (and users) that your content has value.
In general, links from sites with high domain authority are most valuable. Having these kinds of links can help your content to rank well.
So it’s important to know how many backlinks each of your pages has.
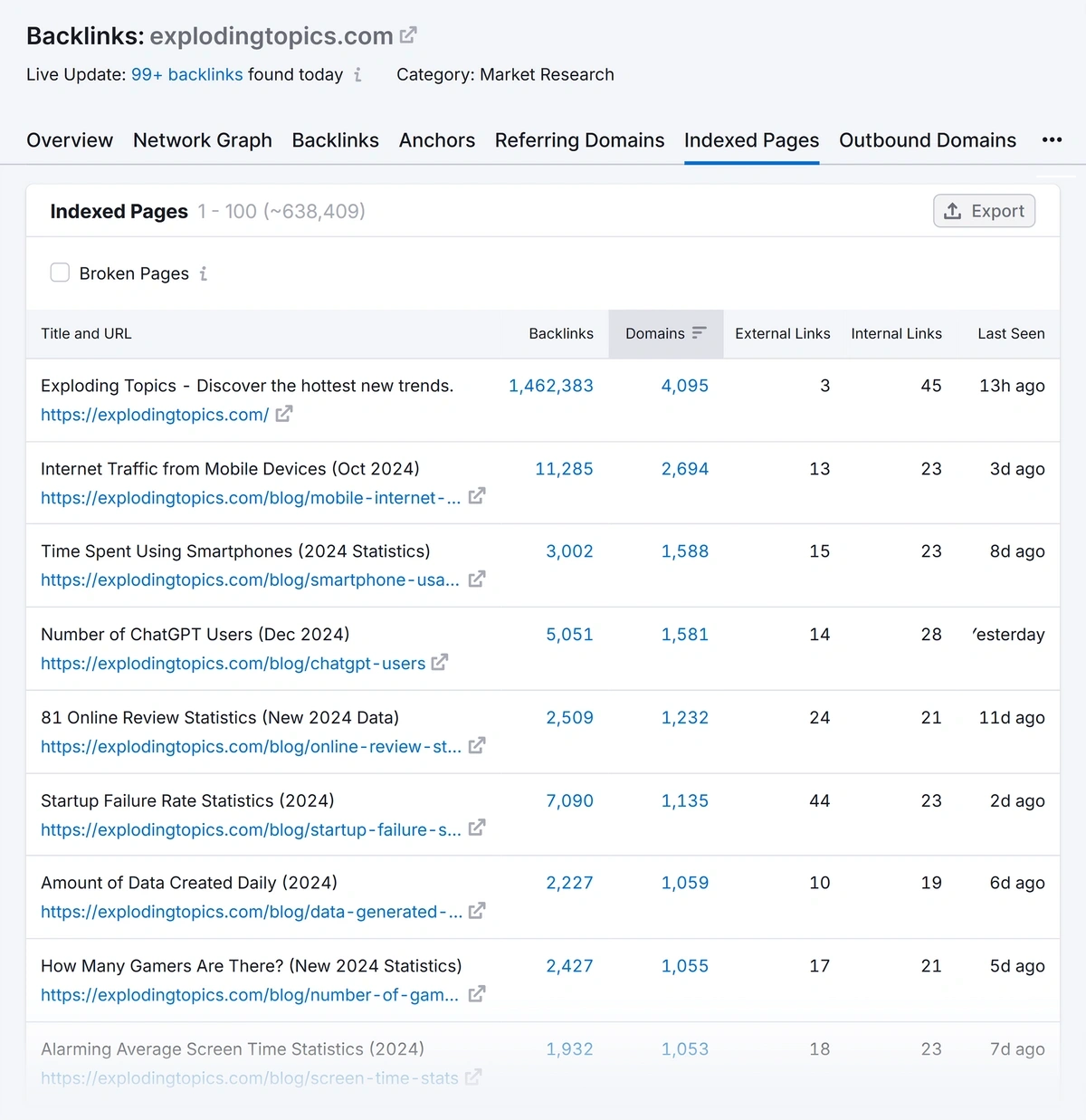
To get this data, use the Semrush Backlink Analytics tool.
Enter your domain name, and click “Analyze.”
Click the “Indexed pages” tab to see how many backlinks and domains link to each page.
Add the numbers from the “Backlinks” column to the corresponding cells in your content audit spreadsheet.
If your pages need more links to give them a ranking boost, the Semrush Link Building Tool makes it easy to find opportunities to get more backlinks.
On Page SEO
On page SEO refers to the optimization of an individual web page.
You can see our guide to on page SEO to learn more about what this includes.
During a content audit, you’ll want to look at:
- Keyword usage and placement
- Content structure
- URL structure
- Readability
- Content quality
- Internal linking
- Content freshness
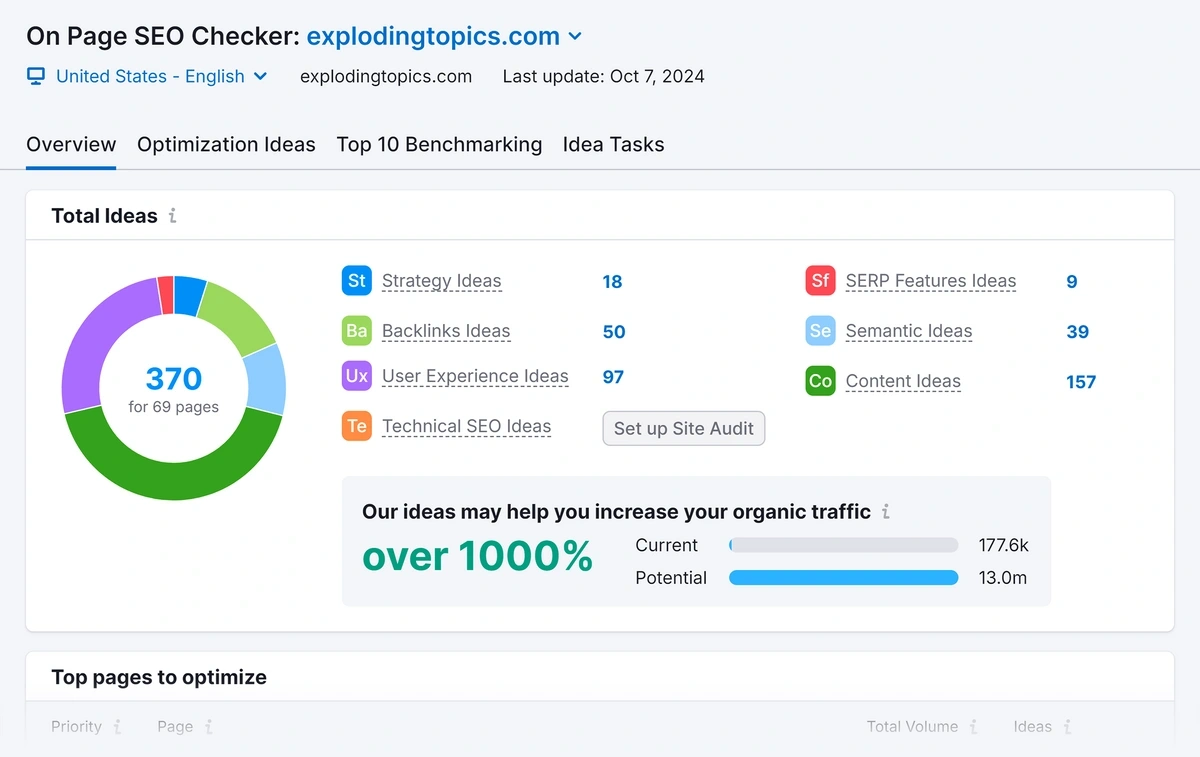
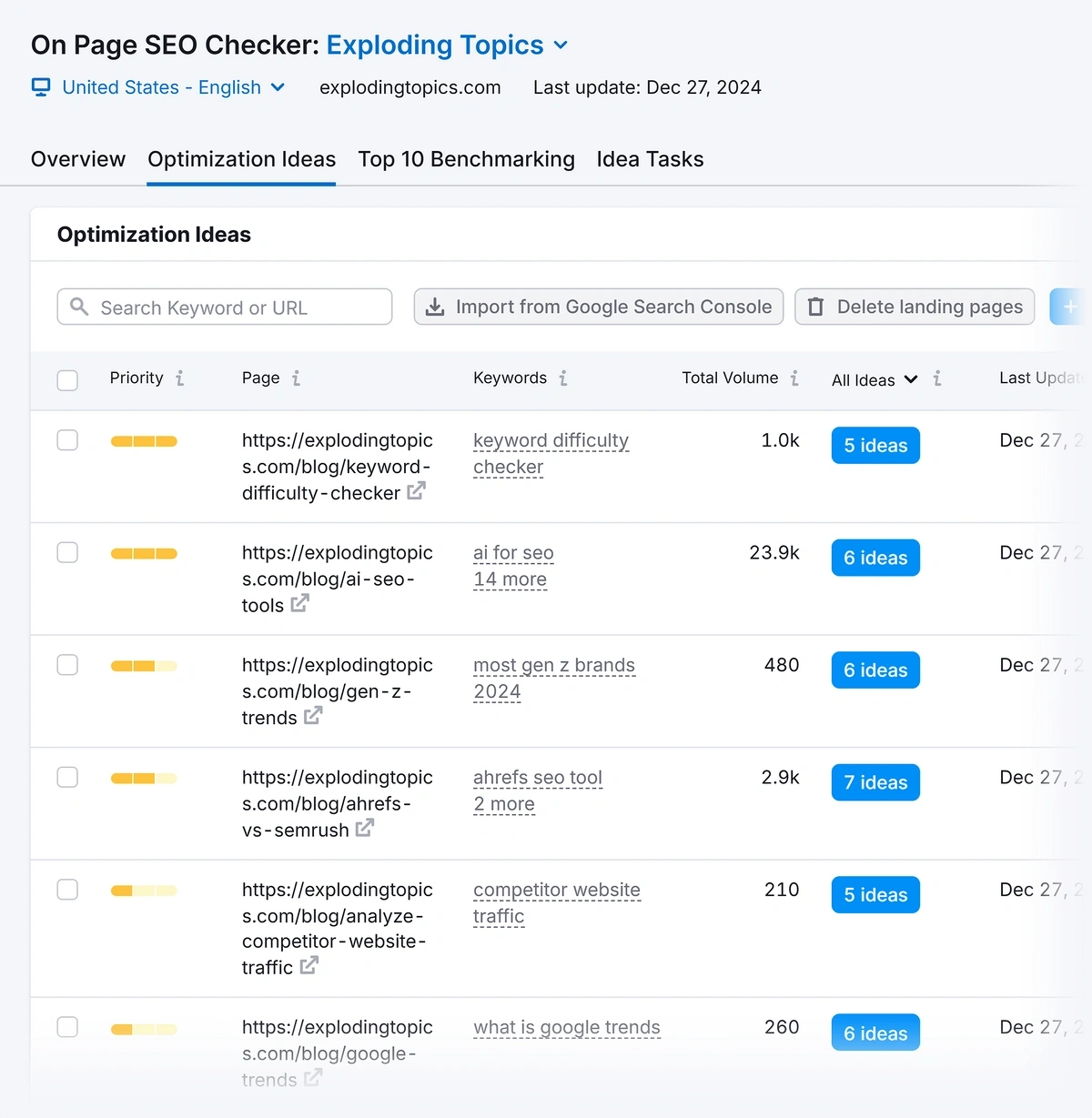
The Semrush On Page SEO Checker is perfect for this step in your content audit. It helps you to improve content performance by providing actionable optimization ideas for each page.
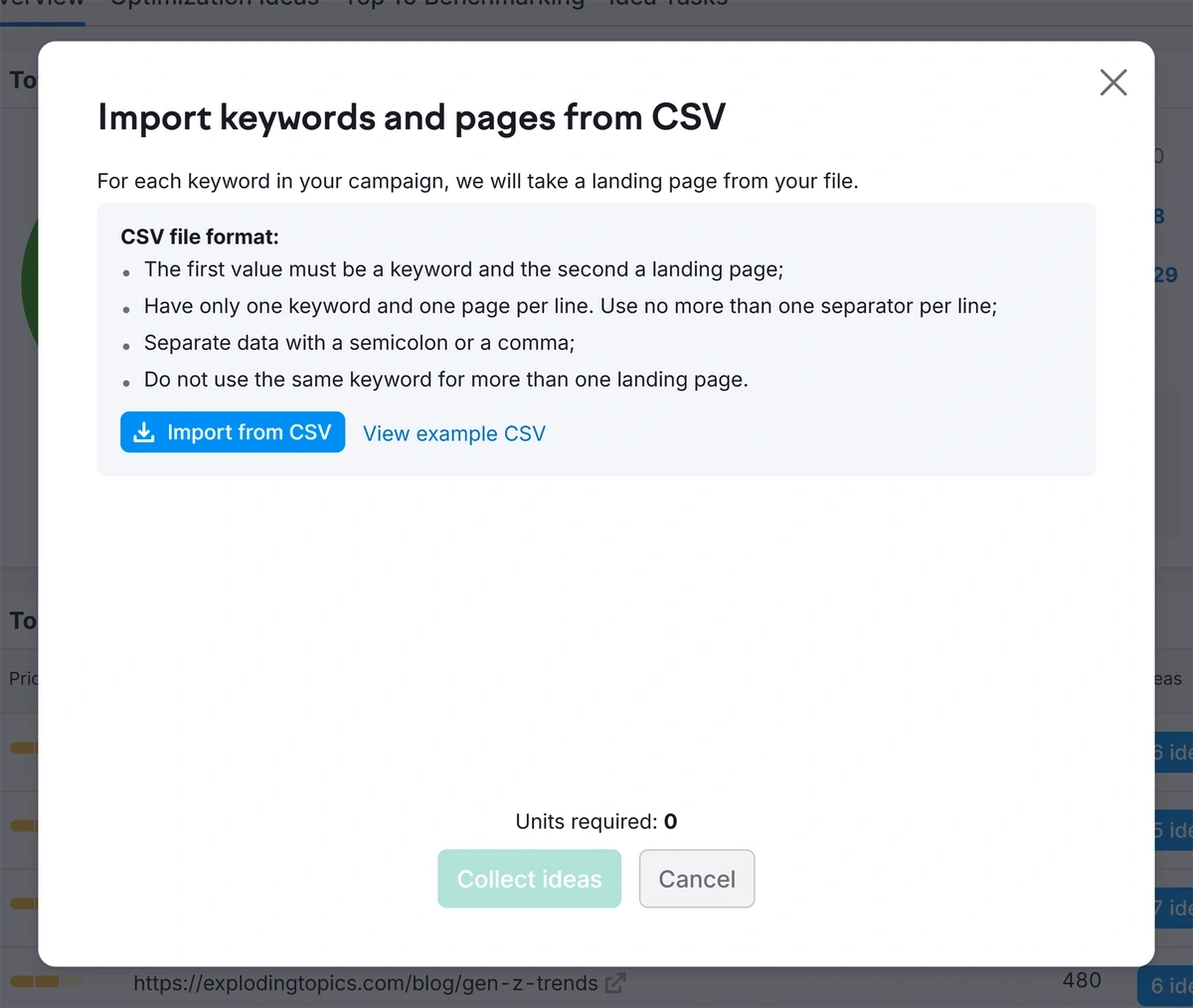
Go back to your content audit sheet in Google Drive. We’re going to duplicate it to create a file we can upload to the On Page SEO Checker.
First, duplicate the data to a new tab in your spreadsheet. Delete all columns except “Keywords” and “URLs”. Make sure they are in that order, then export this tab as a CSV file.
Back in Semrush, open the On Page SEO Checker.
After setting your location, click “Import keywords and Pages” at the top and upload your CSV file here.
Click “Collect ideas” at the bottom of the page to start the on page SEO check.
All the recommendations are listed in the “Optimization Ideas” tab.
For now, I recommend making a note of pages that you could optimize. You can pass this back to your content team to action.
In your content audit sheet, mark pages with on page SEO suggestions as “Yes” and pages with no optimization suggestions as “No.”
Technical SEO
Technical SEO issues can include:
- Sitemap problems
- Problems with crawling the site
- Pages that aren’t indexed, but should be
- Broken internal links
- Slow load speeds
These issues can be a headache for people who visit your site, which is why they sometimes impact rankings.
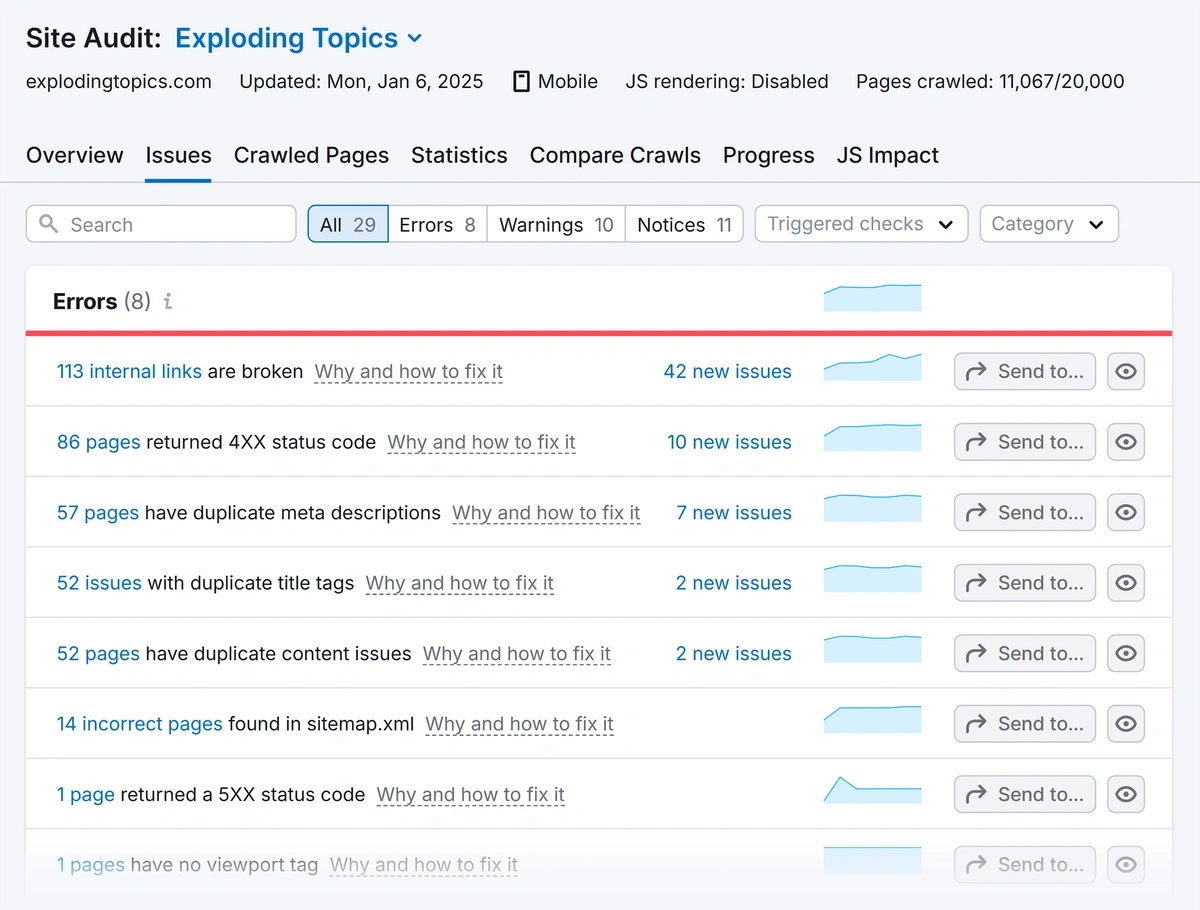
We can go back to the Site Audit tool in Semrush to find these technical issues. And if you already crawled your entire site, the information is already recorded for you. Just click the “Issues” tab.
Issues are categorized into:
- Errors: These items need immediate attention
- Warnings: You should address these after you’ve resolved all errors
- Notices: You can address these later, or deal with them while resolving other, more important issues
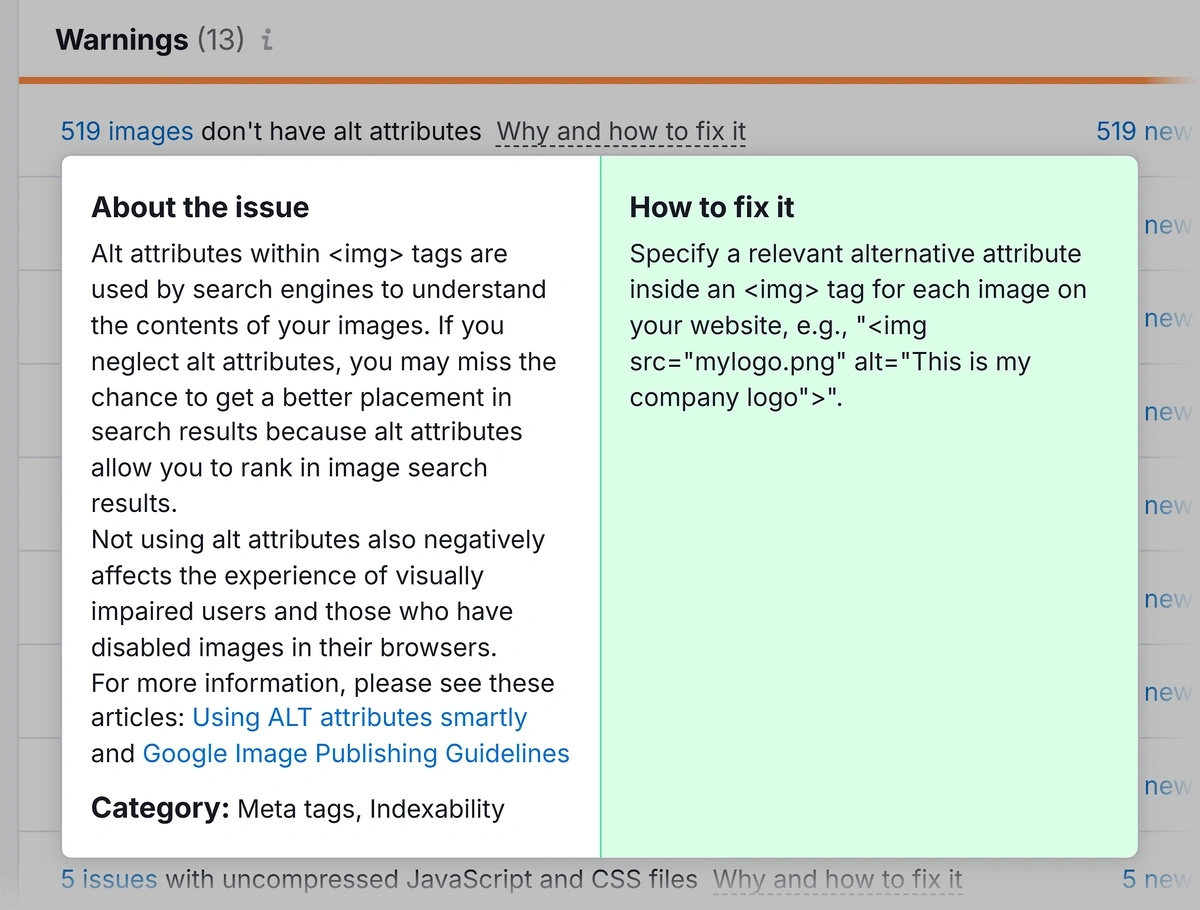
Click on “Why and how to fix it” for more details about a problem.
Next, go to the “Crawled Pages” report and go through the list to see whether there are issues specifically affecting the important pages you’re auditing.
You can do this using the search feature.
Add the number of issues listed for each page to the "Technical SEO" column in your content audit sheet.
Freshness
Content freshness is a measure of how old your content is.
You can get some idea of this by looking at the date each post or page was updated.
If a post hasn't been updated for a while, and you're seeing declining rankings or traffic, you should consider that for an update.
I also recommend using the free Freshness Distance Calculator tool. It looks at the search engine results for any query and provides an estimate of how often you should update your article to be considered "fresh".
As you can see from this example, any topic related to the news needs to be updated very frequently. For the search term "tiktok ban", you'd need to update your content every few weeks to compete:
3. Create an Action Plan
Now that you’ve gathered key information about each of your important pages, assign an action to each based on your audit’s findings.
Here are some options:
- Keep as is: For high-quality, up-to-date content that performs well in terms of traffic and/or keyword rankings
- Update: For content that’s underperforming, low-quality, contains outdated information, has SEO issues, or needs more backlinks; consider whether the content of the article needs to be "fresh" in order to rank well
- Consolidate and redirect: For duplicate content or content competing for the same keywords (cannibalization)
- Delete: For content that’s not relevant to your target audience or brand
These options are included in the content audit template, but you can add your own actions based on your needs.
As you evaluate each page, select the appropriate action in the “Action” column of your audit spreadsheet.
From here, it’s time to action the items in the sheet.
Here are some tips:
- If you decide to delete content, always review the backlinks; avoid deleting anything that large sites are linking to
- Follow our SEO copywriting checklist when optimizing content to avoid keyword stuffing
- For large sites, follow the 80/20 rule and focus on the pages that are most important (usually the ones that bring in the most revenue)
- Run the Site Audit again if you make any major changes
Improve Your SEO Results with a Content Audit
Publishing content is a great way to bring in organic traffic.
But if your content audit is overdue, spending time on content updates and optimizations could be a better use of your resources.
That’s why a content audit should be a part of your monthly SEO tasks.
Before you start your first audit, sign up for a free Semrush trial. You’ll immediately get access to 55+ marketing tools, including Site Audit and Position Tracking, so you can get the best possible data about your site’s performance.
Stop Guessing, Start Growing 🚀
Use real-time topic data to create content that resonates and brings results.
Exploding Topics is owned by Semrush. Our mission is to provide accurate data and expert insights on emerging trends. Unless otherwise noted, this page’s content was written by either an employee or a paid contractor of Semrush Inc.
Share
Newsletter Signup
By clicking “Subscribe” you agree to Semrush Privacy Policy and consent to Semrush using your contact data for newsletter purposes
Written By


Claire Broadley is the Lead Editor and AI Content Strategist at Exploding Topics, where she oversees editorial workflows, AI SEO s... Read more