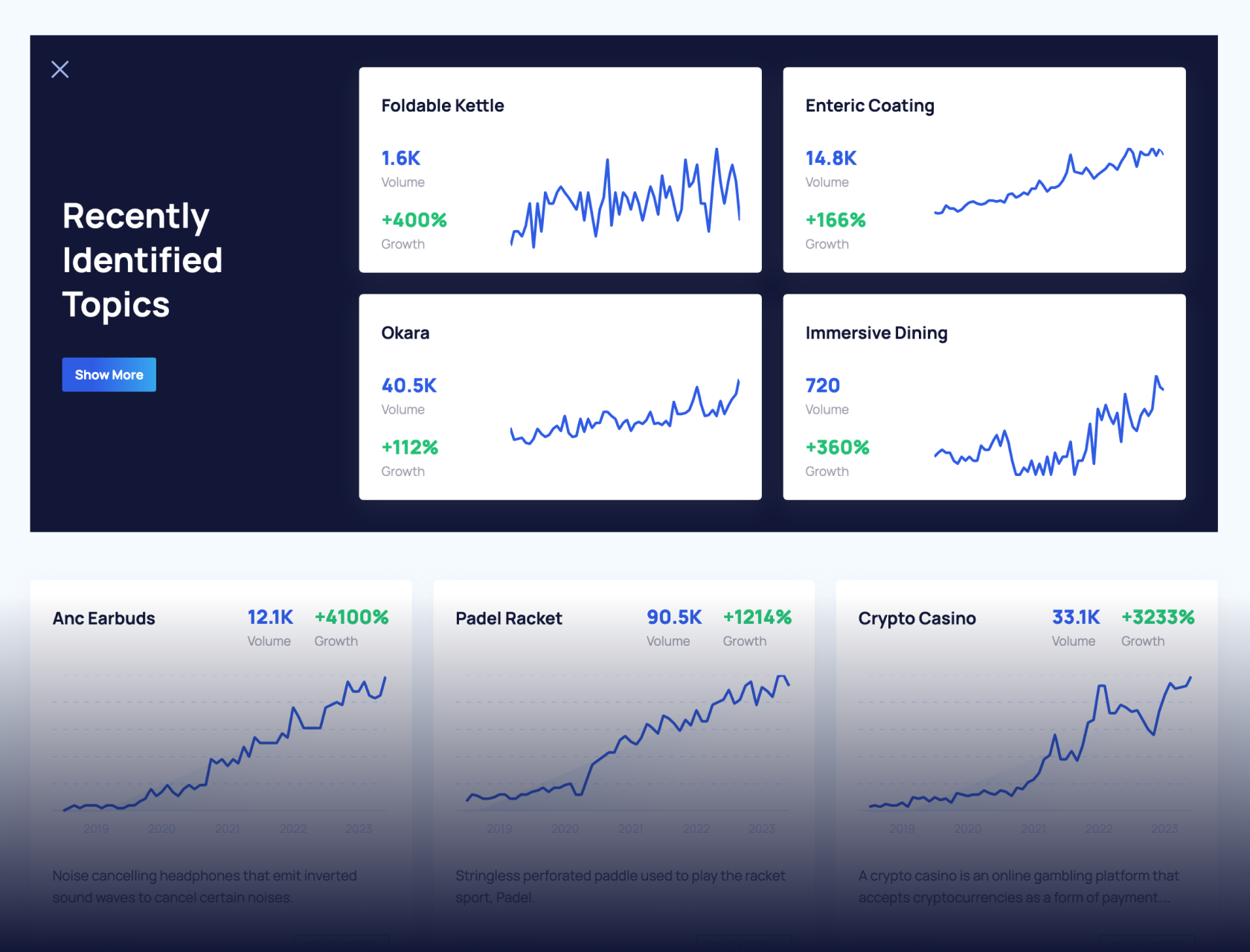
Get Advanced Insights on Any Topic
Discover Trends 12+ Months Before Everyone Else
How We Find Trends Before They Take Off
Exploding Topics’ advanced algorithm monitors millions of unstructured data points to spot trends early on.
Keyword Research
Performance Tracking
Competitor Intelligence
Fix Your Site’s SEO Issues in 30 Seconds
Find technical issues blocking search visibility. Get prioritized, actionable fixes in seconds.
Powered by data from
39+ Robotics Industry Stats & Trends (2024)
Across the globe, millions of robots are working to make our lives easier. They help make products, perform repetitive tasks, and aid in potentially life-saving medical procedures.
While industrial robots have been around for decades, recent breakthroughs in AI, machine learning, and engineering have made them exponentially more effective at their jobs. Today’s robots are present in virtually every industry. In fact, thanks to smart robots, they’re even working in our homes.
In this report, you’ll see the numbers and trends behind this multi-billion dollar industry.
Top Robotics Industry Statistics
Before getting into the whole report, let’s take a look at the top robotics industry statistics:
- The global robotics industry is projected to hit $43.32 billion in revenue by 2027
- Asia controls over one-third of the global robotics industry’s revenue
- There are over 3.4 million industrial robots in the world today
- The global robot-to-human ratio in the manufacturing industry is 1 to 71
- Industrial companies plan to invest 25% of their capital in industrial automation over the next five years
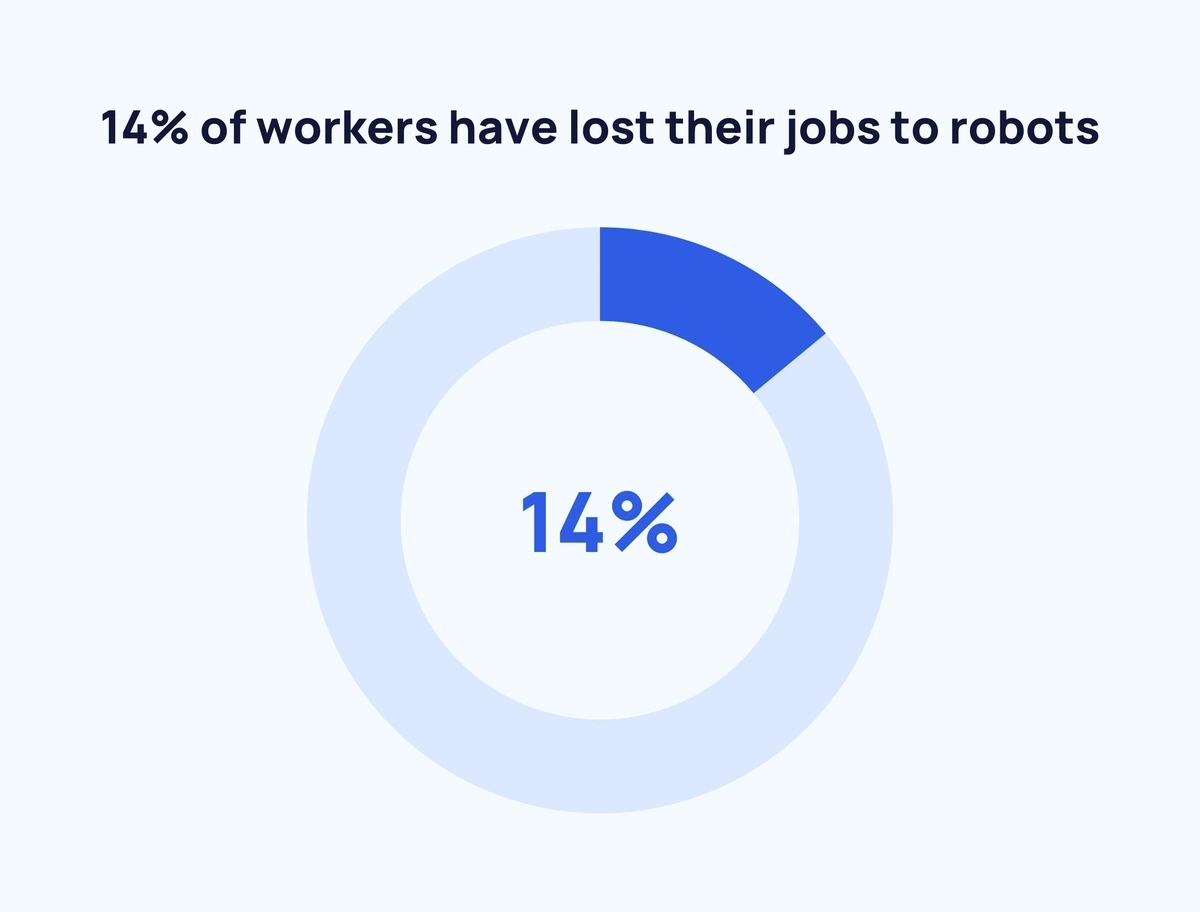
- 14% of workers have lost their jobs to robots
Robotics Industry Market Sizes and Projections
Robotics generates billions of dollars in revenue worldwide each year. Demand for automation has created multiple sub-categories of robots, from large industrial robots to smaller cobots and domestic robots.
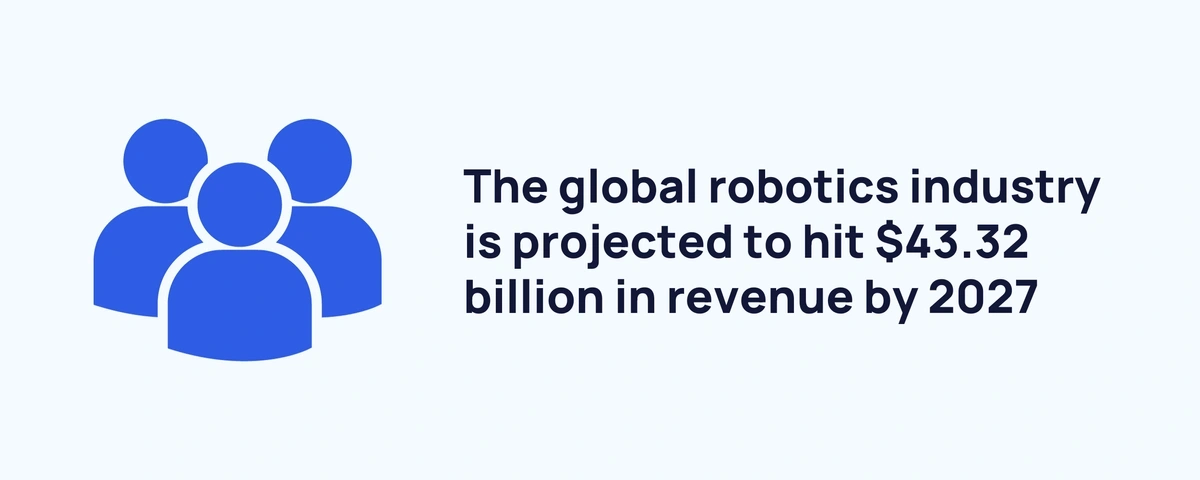
The global robotics industry is projected to hit $43.32 billion in revenue by 2027 (Statista)
In 2023, the robotics industry generated $37.37 billion in revenue — up from $18.47 billion in 2016. During that time, revenue from service robotics increased by over $16 billion. Experts predict demand for service robotics will continue to surge in the coming years.
Asia controls over one-third of the global robotics industry’s revenue (Statista)
Asian companies generated $13.51 billion in robotics revenue in 2023, making it the top robot-producing region by a large margin. North American companies generated $9.39 billion in revenue while Central and Western European companies generated $9.02 billion.
Europe leads the world in commercial service robot revenue (Statista)
European companies posted $6.82 billion in revenue from service robots in 2023. The next best regions were North America at $5.78 billion and Asia at $3.57 billion.
Notable European service robotics startups include UK-based TouchLab and Estonia-based Starship Technologies.
Researchers predict the vision-guided robotics market will be worth $20.1 billion by 2030 (NextMSC)
NextMSC valued the global vision-guided robots (VGR) market at $6.12 billion in 2021 and predicts a 12.7% CAGR between now and 2030.
VGRs use 2D or 3D cameras to capture images, allowing robots to perform tasks with more precision. The food and beverage packaging industry is a top sector fueling growth in the VGR market.
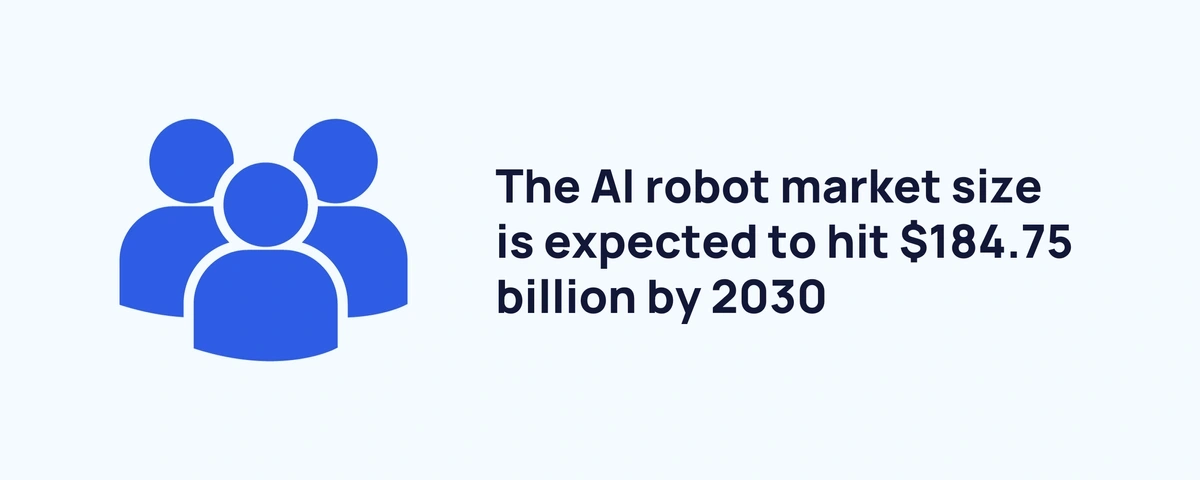
By 2023, the AI robot market size is expected to reach $184.75 billion (NextMSC)
AI robotics is set to grow at a 32.9% CAGR throughout the 2020s, up from its $95.6 billion valuation in 2021.
AI-powered robots can be used as service robots and industrial robots. Service uses include smart home devices like iRobot’s Roomba and Braava. Industrial AI robots use machine learning to detect defects in products and ensure greater quality control.
The mobile cobots market is predicted to reach $7.66 billion by 2030 (NextMSC)
Mobile cobots — or collaborative robots — are one of the fastest-growing segments of the robotics industry. Cobots work alongside humans, functioning as extra sets of hands or feet to complete manufacturing tasks.
The market was worth just $656.1 million in 2021, but is projected to grow at a 30.7% CAGR between 2022 and 2030.
How Many Robots Are There?
As the robotics industry grows year over year, so does the number of robots operating around the world. This section reveals how many robots—both industrial and service—are active today.
It is estimated that there are approximately 3.4 million industrial robots in use worldwide (Stanford)
Since 2011, the number of industrial robots in operation has nearly tripled. 517,000 new industrial robots were installed in 2021 alone. Of those new installations, 39,000—or 7.5%—were collaborative robots.
China leads the world in new industrial robot installations (Stanford)
China installed over 268,000 new industrial robots in 2021, more than any other nation in the world combined. Japan had the second-highest number of new installations with 47,200, followed by the United States (35,000), South Korea (31,100), and Germany (23,800).
Professional service robot installations are on the rise (Stanford)
Unlike industrial robots, professional service robots perform non-manufacturing jobs across all kinds of industries. Their use has increased at astonishing rates in certain segments.
There were 50,000 new service robots installed in the transportation and logistics industry in 2021 compared to 34,000 in 2020. In the hospitality industry, installations almost doubled between 2020 and 2021—from 11,000 to 20,000. Service robots also saw increased use in the medical and professional cleaning industries.
The United States is the global leader in professional service robot production, with 225 manufacturers as of 2021. China (104), Germany (91), Japan (66), and France (54) round out the top 5 service robot manufacturing nations.
In the manufacturing industry, the global robot-to-human ratio is 1 to 71 (Robotiq)
The latest World Robotics Report found that there are 141 robots for every 10,000 manufacturing employees across all global markets. South Korea is the global leader in robot density, with 766 robots per 10,000 employees. That’s one robot for every 13 human employees.
Industrial Automation Statistics
Industrial robots have countless functions, but they all serve the same objective: to make manufacturing more efficient and profitable. These stats examine how today’s manufacturers are using robots and the opportunities and challenges they face.
Industrial companies plan to invest 25% of their capital in industrial automation over the next five years (McKinsey)
Logistics, automotive, healthcare, and pharmaceutical companies plan to invest even more than 25% of their total capital on automation over the next five years.
As for the dollar amount companies plan to invest, 23% of retail and consumer goods manufacturers report that they plan to invest $500 million or more in automation. 15% of food and beverage manufacturers also plan on committing at least $500 million to improving automation.
Palletization and packaging is the top use case for industrial automation (McKinsey)
83% of manufacturers are either planning on or are currently implementing automation for palletization and packaging. 82% use automation for material handling and ground movement, 80% for goods receiving and storage, 77% for material handling and forklifts, and 75% for sorting.
The top perceived positive impact of industrial automation is quality (McKinsey)
When asked about the positive impacts of industrial automation, 97% of manufacturing leaders pointed to the quality of products. That’s not the only near-unanimous benefit of automation. Speed of production (95%) and production capacity (92%) are also major benefits of automation.
High costs are among the top challenges for manufacturers looking to implement automation (McKinsey)
39% of automotive and 36% of food and beverage manufacturers say high costs are a bottleneck to automation adoption. For logistics and fulfillment companies, technology readiness is a top automation challenge.
Challenges for healthcare and pharmaceutical manufacturers include the reliability of existing systems and policies & regulations.
Robotics and Employment Statistics
Are robots coming for our jobs? While automation has certainly made some jobs redundant, there’s a gap between reality and perception when it comes to robots in the workplace. At the same time, increased demand for robots has led to more opportunities for robotics engineers.
Around 3 in 20 workers have lost their jobs to robots (BYU)
For decades, the fear of automation reducing the manufacturing workforce has been widely publicized. And while some jobs have undoubtedly been replaced, the perception is far worse than reality.
Individuals who have lost their jobs to robots estimate that 47% of all jobs have been replaced by automation. People who still have their jobs estimate that number to be 29%. In reality, 14% of workers have been replaced by robots.
65% of robotics engineers hold a bachelor’s degree (Zippia)
Most robotics engineers have a four-year degree, but some have broken into the industry with even less education. 15% have an associate’s degree, while 3% have a high school diploma.
Higher education correlates to higher salaries in the field. The average robotics engineer salary is $99,309 with a bachelor’s degree, $112,368 with a master’s degree, and $124,995 with a doctorate degree.
Over half of robotics engineers work at companies with 500 or less employees (Zippia)
28% of robotics engineers work at companies with 100-500 employees. 66% of robotics engineers work for private companies while 25% work for public companies.
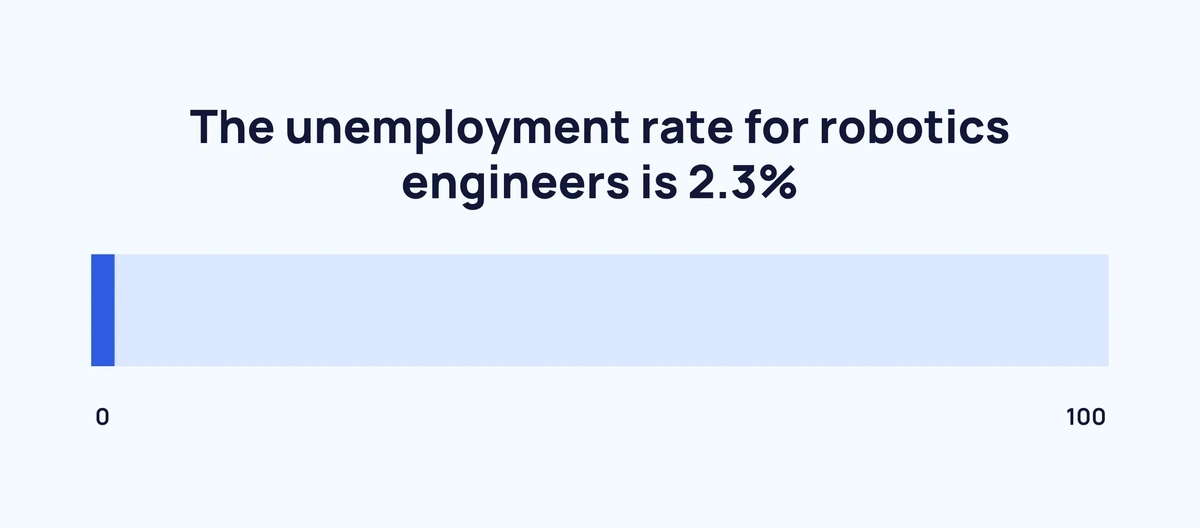
Currently, the unemployment rate for robotics engineers stands at 2.3% (Zippia)
The unemployment rate for robotics engineers was less than half the national average in 2021: 2.3% vs. 4.83%. The field has seen less unemployment than the national average every year going back to 2010.
Robotics engineers tend to change jobs frequently. 61% stay at their jobs for two years or less. Only 6% of robotics engineers have been in their positions for 11 years or more.
Wrap Up
The first robots were confined to the factory floor, but today they can be found in hospitals, homes, restaurants, and more. The robotics industry is growing at a breakneck pace, and with AI, machine learning, and cloud technology the room for innovation is virtually limitless.
As much as humans fear that robots will replace them, the future is looking more and more like a place where robots and humans work together.
Robotics is just one aspect of humanity’s push toward automation. If you want to learn more, read up on our list of fast-growing machine learning startups and emerging AI trends.
Stop Guessing, Start Growing 🚀
Use real-time topic data to create content that resonates and brings results.
Exploding Topics is owned by Semrush. Our mission is to provide accurate data and expert insights on emerging trends. Unless otherwise noted, this page’s content was written by either an employee or a paid contractor of Semrush Inc.
Share
Newsletter Signup
By clicking “Subscribe” you agree to Semrush Privacy Policy and consent to Semrush using your contact data for newsletter purposes
Written By


Josh is the Co-Founder and CTO of Exploding Topics. Josh has led Exploding Topics product development from the first line of co... Read more