Get Advanced Insights on Any Topic
Discover Trends 12+ Months Before Everyone Else
How We Find Trends Before They Take Off
Exploding Topics’ advanced algorithm monitors millions of unstructured data points to spot trends early on.
Keyword Research
Performance Tracking
Competitor Intelligence
Fix Your Site’s SEO Issues in 30 Seconds
Find technical issues blocking search visibility. Get prioritized, actionable fixes in seconds.
Powered by data from
8 Top Computer Science Trends (2024 & 2025)
You may also like:
Here are the 8 most important computer science trends happening right now.
And how these technologies are challenging the status quo in businesses, research and academia.
Whether you’re a fresh computer science graduate or a veteran IT executive, these are the top trends to explore.
1. Renewed focus on AI
AI has been part of the computer science world for literally decades.
However, large language models like ChatGPT have suddenly thrust AI back to the forefront.
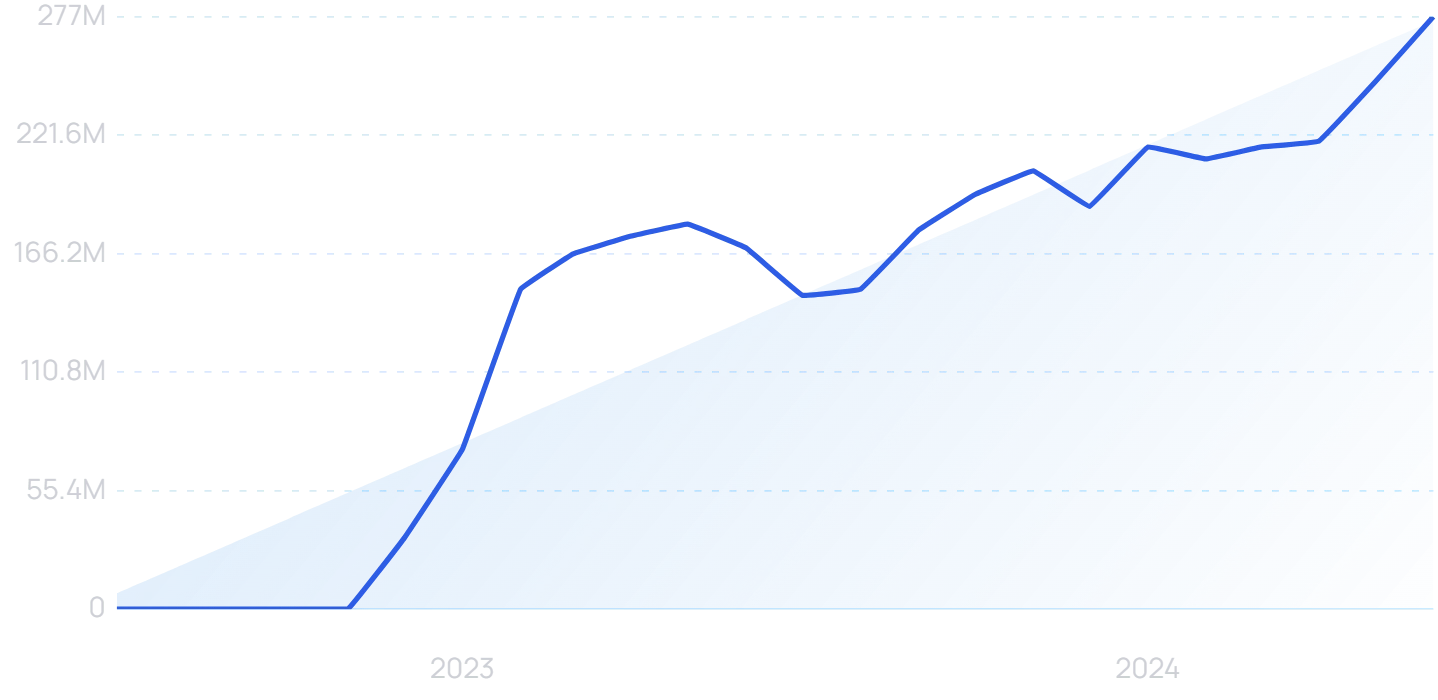
Searches for "ChatGPT" since 2022.
From optimizing LLM performance to understanding "hallucinations" to figuring out how LLMs compare to the human brain, computer scientists are putting more time and energy into AI.
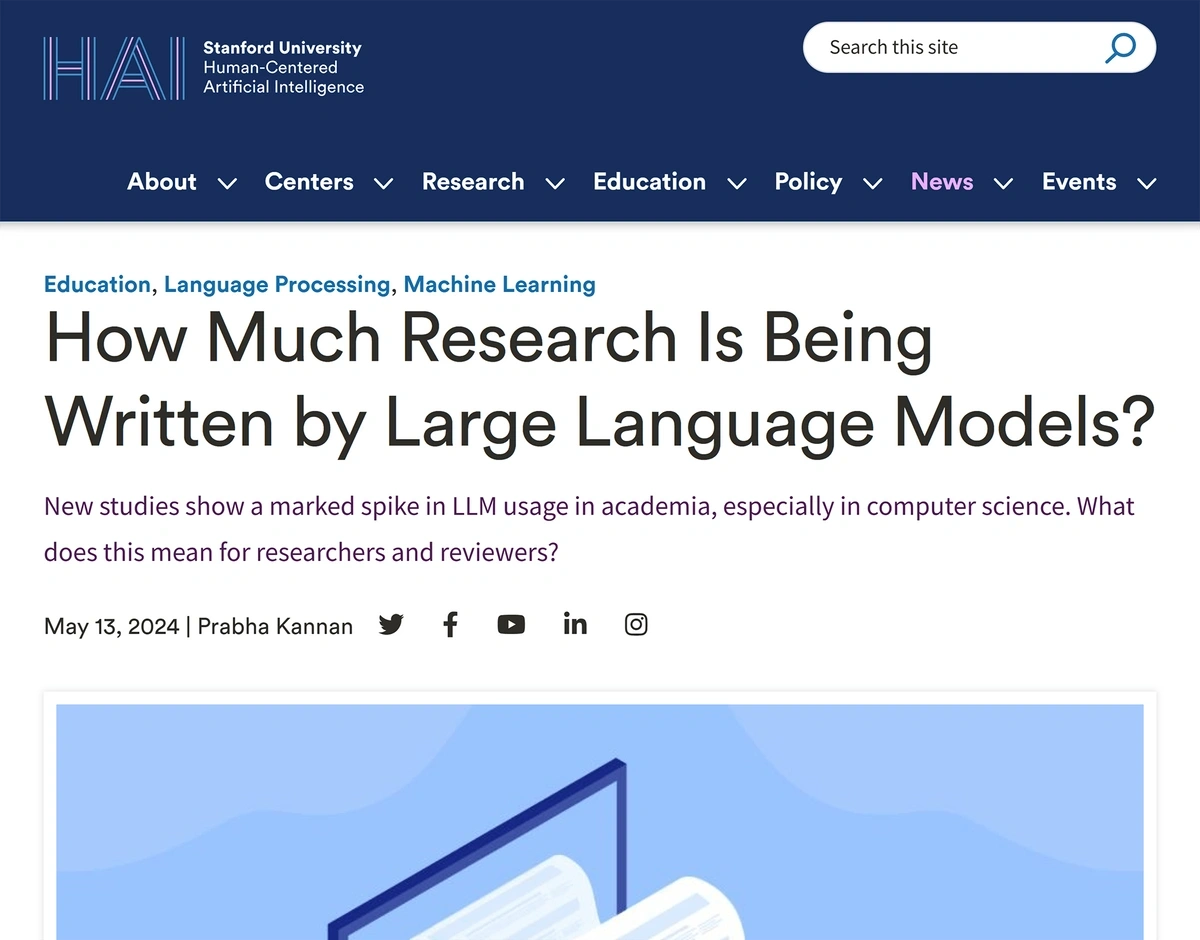
AI is even being used as part of the paper writing process.
One study by Stanford University found that nearly 18% of computer science papers were written with the help of LLMs.
Researchers discovered that computer scientists are increasingly using AI to write research papers.
For context, this number was closer to 2% before ChatGPT launched and quickly took off in late 2022.
2. Practical use cases for quantum computing emerge
Quantum computing is the use of quantum mechanics, such as entanglement and superposition, to perform computations.
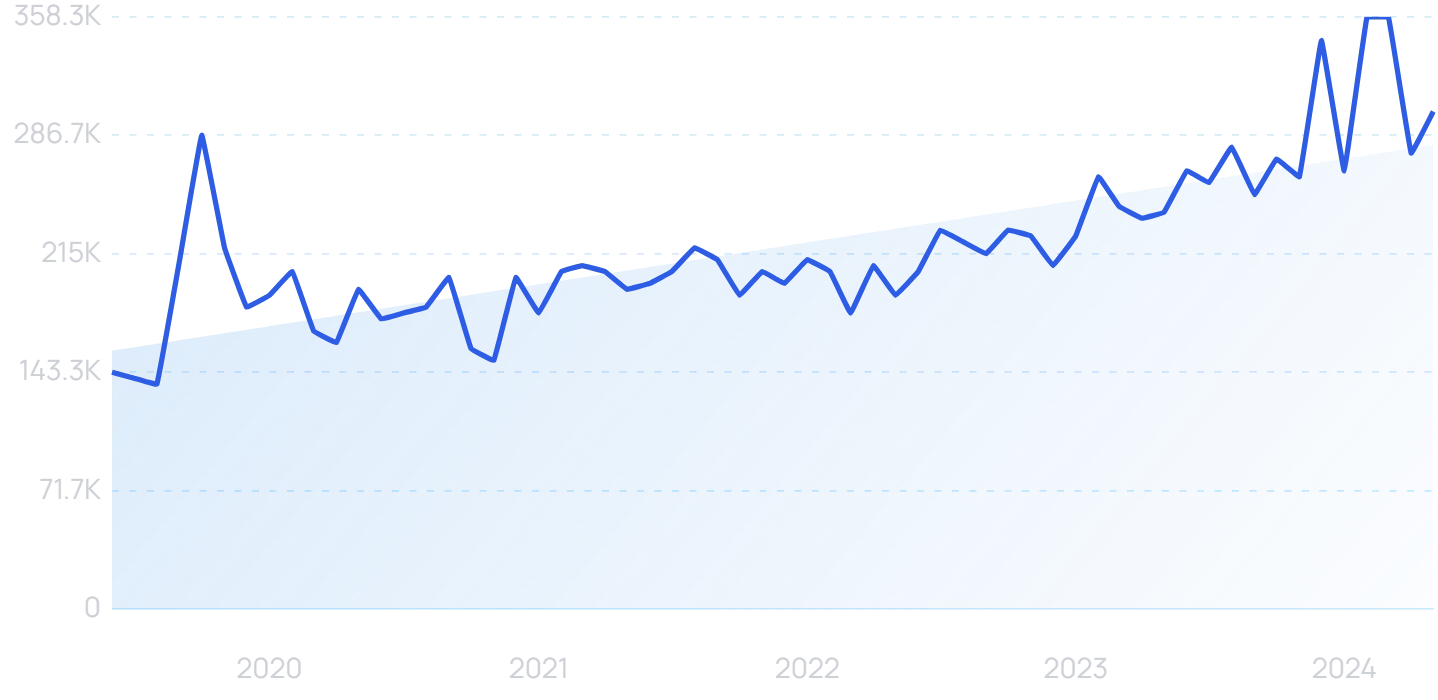
“Quantum computing” searches are up 110% over 10 years. Interest spiked in late 2019 when Google announced it had achieved quantum supremacy.
It uses quantum bits (qubits) in a similar way that regular computers use bits.
Quantum computers have the potential to solve problems that would take the world's most powerful supercomputers millions of years.
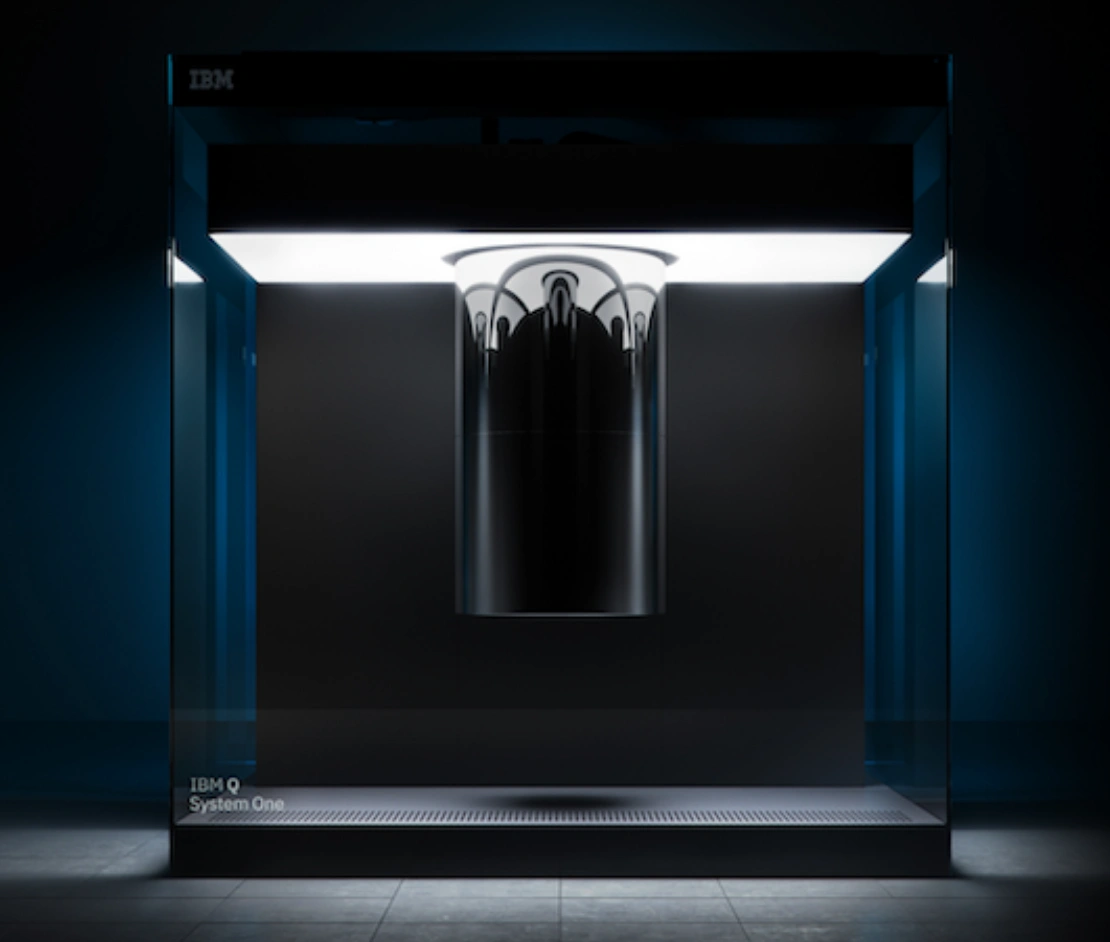
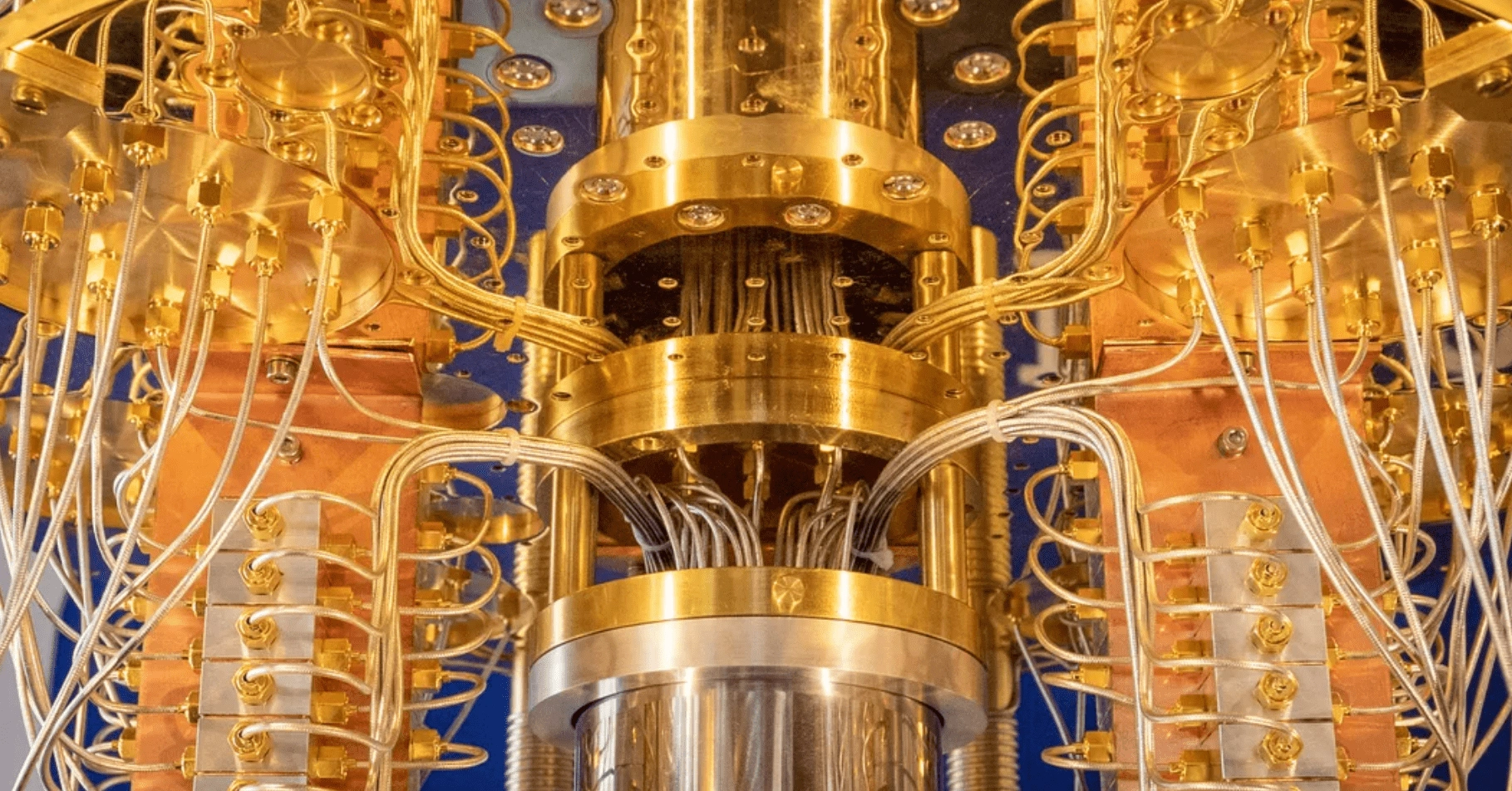
IBM’s System One - the first-ever circuit-based commercial quantum computer.
Companies including IBM, Microsoft and Google are all in competition to build reliable quantum computers.
In fact, Google AI and NASA published a joint paper that claimed to have achieved "quantum supremacy".
This is when a quantum computer outperforms a traditional one at a particular task.
Quantum computers have the potential to completely transform data science.
They also have the potential to accelerate the development of artificial intelligence, virtual reality, big data, deep learning, encryption, medicine and more.
The downside is that quantum computers are currently incredibly difficult to build and sensitive to interference.
Quantum computers have enormous upside. But are also expensive and unstable.
Despite current limitations, it's fair to expect further advances from Google and others that will help make quantum computers practical to use.
Which would position quantum computing as one of the most important computer science trends in the coming years.
3. Zero Trust becomes the norm
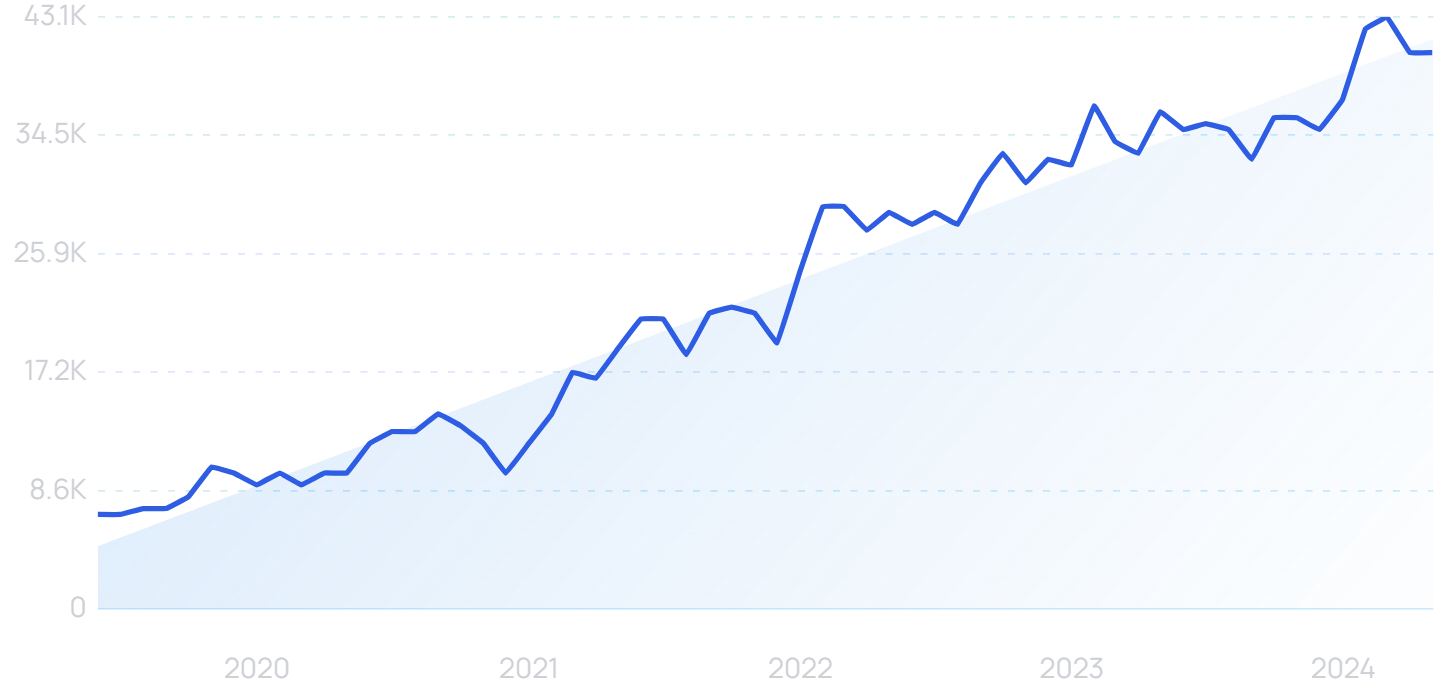
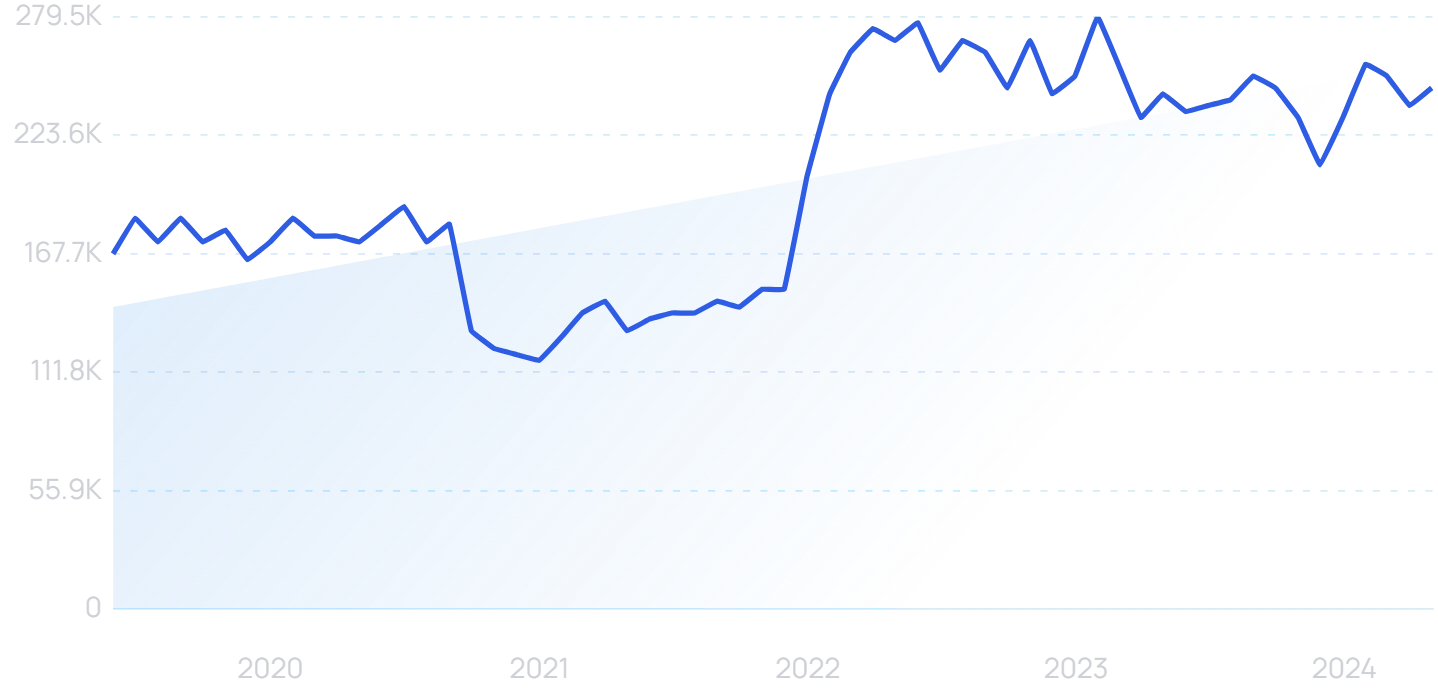
“Zero Trust” searches have increased by 488% since 2019.
Most information security frameworks used by organizations use traditional trust authentication methods (like passwords).
These frameworks focus on protecting network access.
And they assume that anyone that has access to the network should be able to access any data and resources they'd like.
There's a big downside to this approach: a bad actor who has got in via any entry point can then move around freely to access all data or delete it altogether.
Zero Trust information security models aim to prevent this potential vulnerability.
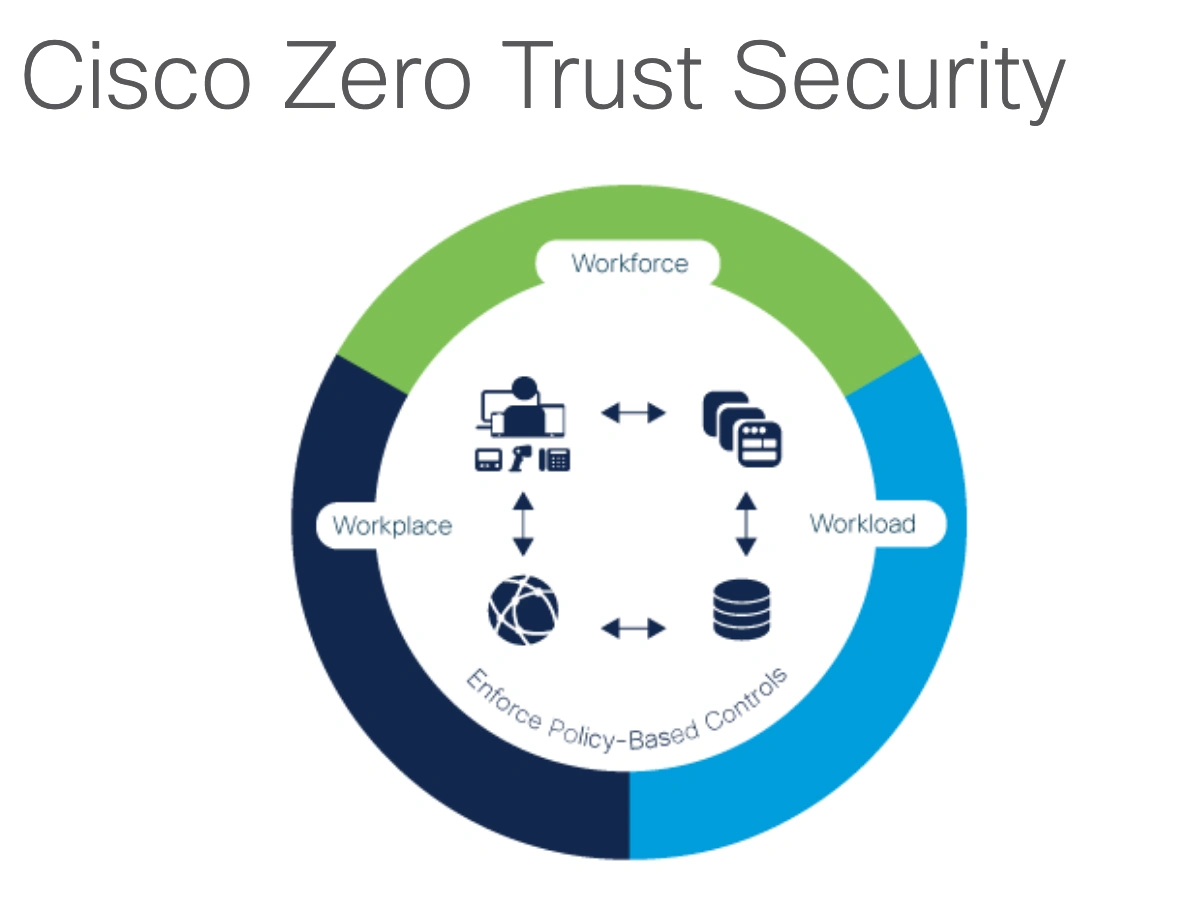
Zero Trust models replace the old assumption that every user within an organization’s network can be trusted.
Instead, nobody is trusted, whether they’re already inside or outside the network.
Verification is required from everyone trying to gain access to any resource on the network.
Huge companies like Cisco are investing heavily to develop Zero Trust solutions.
This security architecture is quickly moving from just a computer science concept to industry best practice.
And it’s little wonder why: IBM reports that the average data breach costs a company $3.86 million in damages.
And that it takes an average of 280 days to fully recover.
We will see demand for this technology continue to skyrocket in 2024 and beyond as businesses adopt zero-trust security to mitigate this risk.
4. Cloud computing hits the edge
“Edge computing” searches have risen steadily over the last 5 years.
Gartner estimates that 80% of enterprises will shut down their traditional data centers by 2025.
This is mainly because traditional cloud computing relies on servers in one central location.
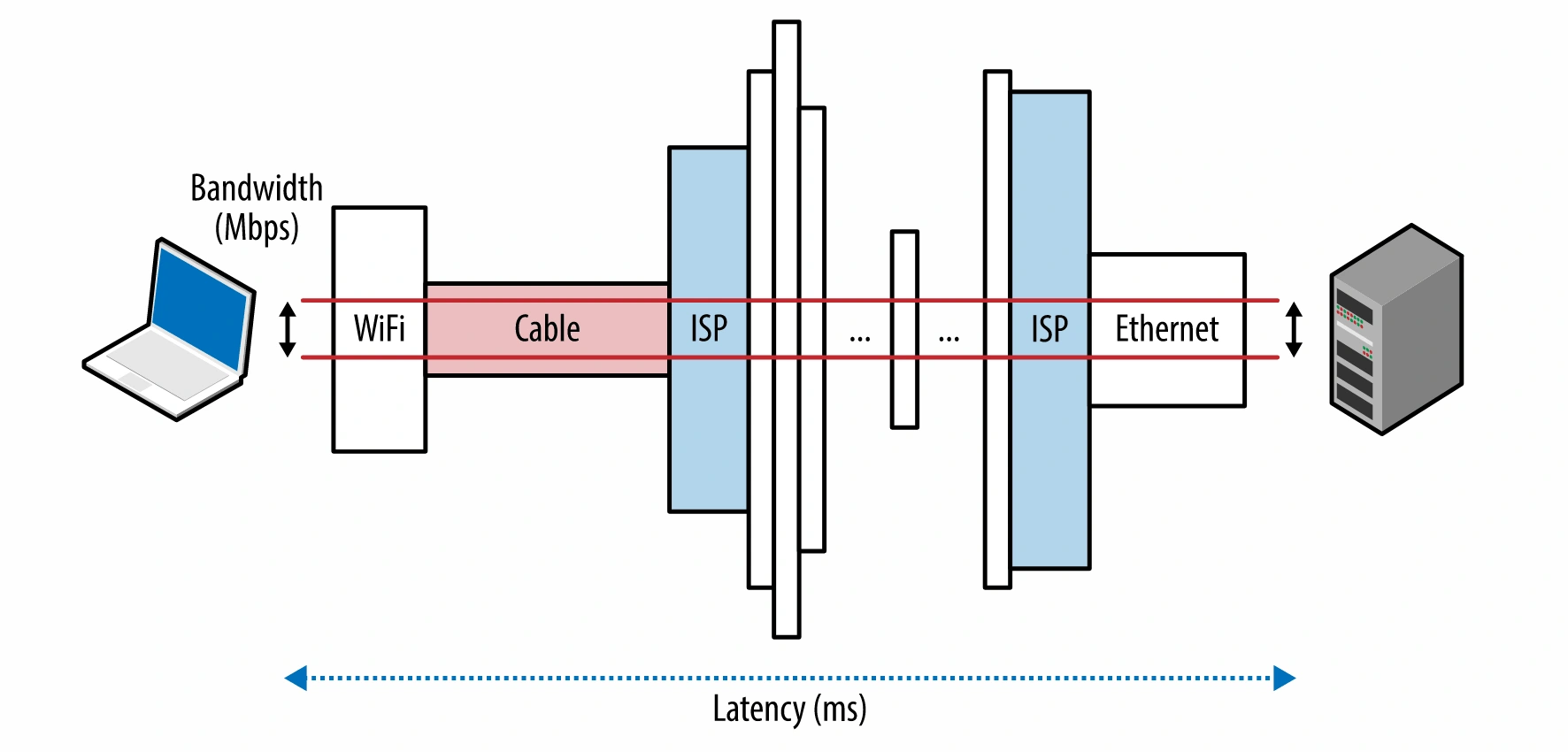
Network latency is one downside of traditional cloud computing.
If the end-user is in another country, they have to wait while data travels thousands of miles.
Latency issues like this can really hamper an application’s performance (especially for high-bandwidth media, like video).
Which is why many companies are moving over to edge computing service providers instead.
Modern edge computing brings computation, data storage, and data analytics as close as possible to the end-user location.
And when edge servers host web applications the result is massively improved response times.
According to Wired, approximately 10% of web traffic now goes through CloudFlare.
As a result, some estimates suggest that the edge computing market will be worth $61.14 billion by 2028.
And Content Delivery Networks like Cloudflare that make edge computing easy and accessible will increasingly power the web.
5. Kotlin overtakes Java
Kotlin is a general-purpose programming language that first appeared in 2011.
It’s designed specifically to be a more concise and streamlined version of Java.
And so it works for both JVM (Java Virtual Machine) and Android development.
Kotlin is billed as a modern programming language that makes developers happier.
There are over 7 million Java programmers in the world right now.
“Kotlin” searches have grown steadily since 2022.
Since Kotlin offers major advantages over Java, we can expect more and more programmers to make the switch in 2024 and 2025.
Google even made an official announcement that Kotlin is now its preferred language for Android app developers.
6. The web becomes more standardized
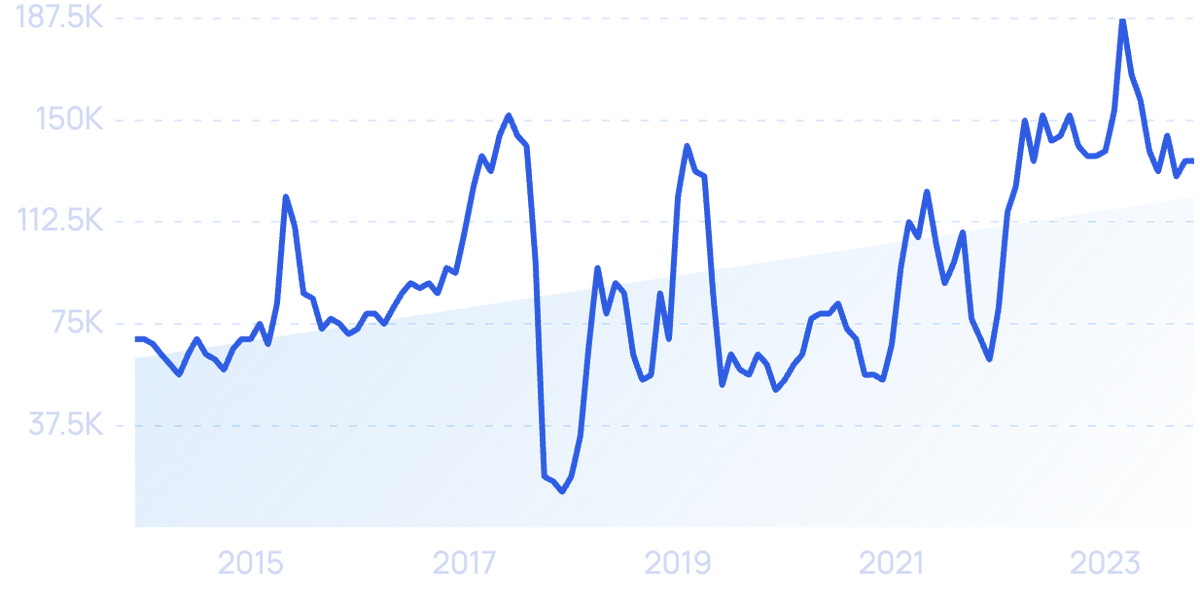
“OpenAPI Specification” searches over 10 years.
REST (Representational State Transfer) web services power the internet and the data behind it.
But the structure of each REST API data source varies wildly.
It depends entirely on how the individual programmer behind it decided to design it.
The OpenAPI Specification (OAS) changes this. It’s essentially a description format for REST APIs.
OpenAPI attempts to streamline APIs.
Data sources that implement OAS are easy to learn and readable to both humans and machines.
This is because an OpenAPI file describes the entire API, including available endpoints, operations and outputs.
This standardization enables the automation of previously time-consuming tasks.
For example, tools like Swagger generate code, documentation and test cases given the OAS interface file.
This can save a huge amount of engineering time both upfront and in the long run.
Another technology that takes this concept to the next level is GraphQL. This is a data query language for APIs developed at Facebook.
It provides a complete description of the data available in a particular source. And it also gives clients the ability to ask for only the specific parts of the data they need and nothing more.
GraphQL is a query language for APIs and a runtime for fulfilling those queries with your existing data.
It too has become widely used and massively popular. Frameworks and specifications like this that standardize all aspects of the internet will continue to gain wide adoption.
7. More digital twins
A digital twin is a software representation of a real-world entity or process, from which you can generate and analyze simulation data.
Interest in “Digital twin” has more than doubled since mid-2019.
This way you can improve efficiency and avoid problems before devices are even built and deployed.
GE is the big name in the field and has developed internal digital twin technology to improve its own jet-engine manufacturing process.
GE's Predix platform is a huge player in the digital twin technology market.
This technology was initially only available at the big enterprise level, with GE’s Predix industrial Internet of Things (IoT) platform.
But now we’re seeing its usage permeate across other sectors like retail warehousing, auto manufacturing, and healthcare planning.
Yet case studies of these real-world use cases are thin on the ground, so the people who produce them will set themselves up as industry experts in their field.
8. Demand for cybersecurity expertise skyrockets
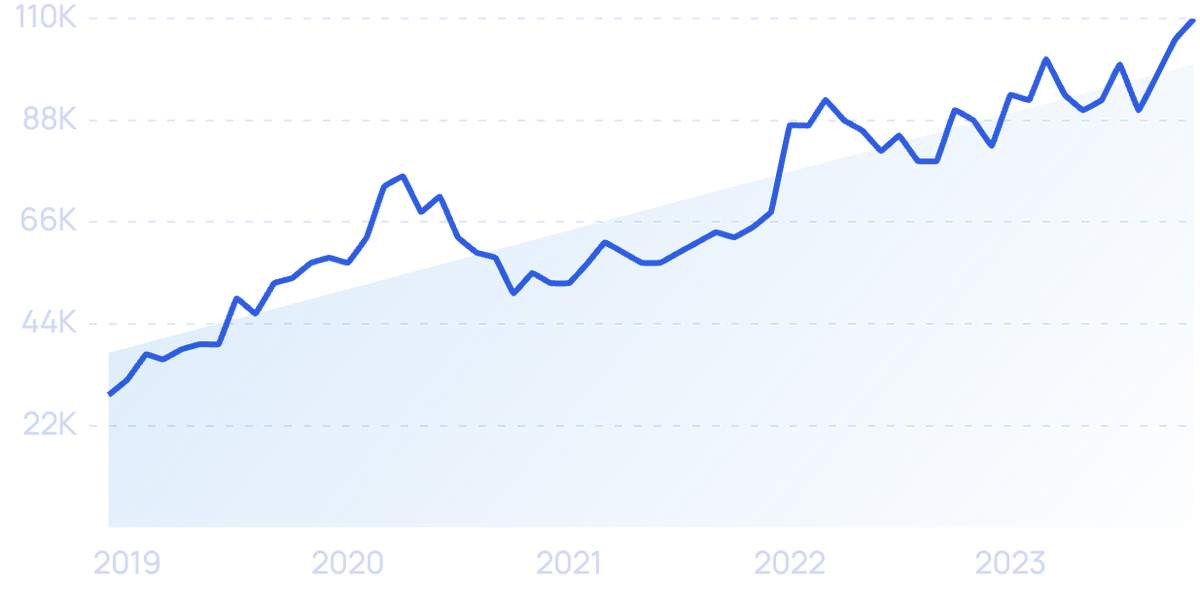
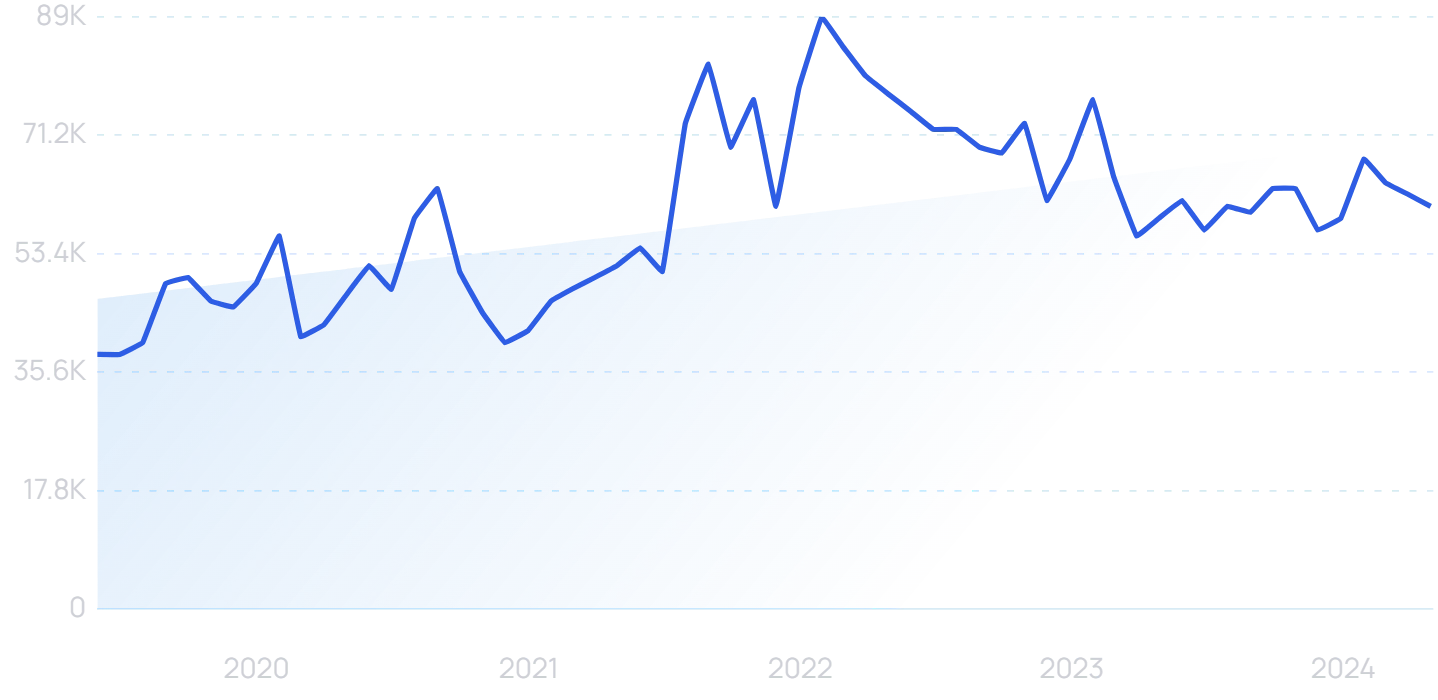
“Hack The Box” searches have increased by 285% over 5 years.
According to CNET, at least 7.9 billion records (including credit card numbers, home addresses and phone numbers) were exposed through data breaches in 2019 alone.
As a consequence, large numbers of companies seek cybersecurity expertise to protect themselves.
Searches for "cybersecurity" have increased by more than 292% over 5 years.
Hack The Box is an online platform that has a wealth of educational information and hundreds of cybersecurity-themed challenges.
And they have 290,000 active users that test and improve their skills in penetration testing.
So they’ve become the go-to place for companies to recruit new talent for their cybersecurity teams.
Hack The Box is a hacker haven both in terms of content and design.
And software that helps people to identify if they’ve had their credentials compromised by data breaches will also trend.
One of the most well-known tools currently is Have I Been Pwned.
It allows you to search across multiple data breaches to see if your email address has been compromised.
Conclusion
That's our list of the 8 most important computer science trends to keep an eye on over the next 3-4 years.
From machine learning to cybersecurity, it's an exciting time to be in the computer science field.
CS has always been a rapidly changing industry.
But with the growth of completely new technologies (especially cloud computing and machine learning), it's fair to expect that the rate of change will increase in 2024 and beyond.
If you want to learn more about this space, read our report on the most new important tech trends and our regularly-updated list of AI statistics.
Stop Guessing, Start Growing 🚀
Use real-time topic data to create content that resonates and brings results.
Exploding Topics is owned by Semrush. Our mission is to provide accurate data and expert insights on emerging trends. Unless otherwise noted, this page’s content was written by either an employee or a paid contractor of Semrush Inc.
Share
Newsletter Signup
By clicking “Subscribe” you agree to Semrush Privacy Policy and consent to Semrush using your contact data for newsletter purposes
Written By


Josh is the Co-Founder and CTO of Exploding Topics. Josh has led Exploding Topics product development from the first line of co... Read more