Get Advanced Insights on Any Topic
Discover Trends 12+ Months Before Everyone Else
How We Find Trends Before They Take Off
Exploding Topics’ advanced algorithm monitors millions of unstructured data points to spot trends early on.
Keyword Research
Performance Tracking
Competitor Intelligence
Fix Your Site’s SEO Issues in 30 Seconds
Find technical issues blocking search visibility. Get prioritized, actionable fixes in seconds.
Powered by data from
5 Important Restaurant Industry Trends (2024-2026)
You may also like:
Technology impacts just about every industry under the sun.
And the restaurant industry is no exception.
New software and hardware are transforming how food is prepared, served, and delivered.
If you want to learn more about 5 of the most important restaurant trends for 2024-2026, read on.
1. Delivery is More Important Than Ever
The global food delivery market is making up an increasingly larger part of the restaurant industry.
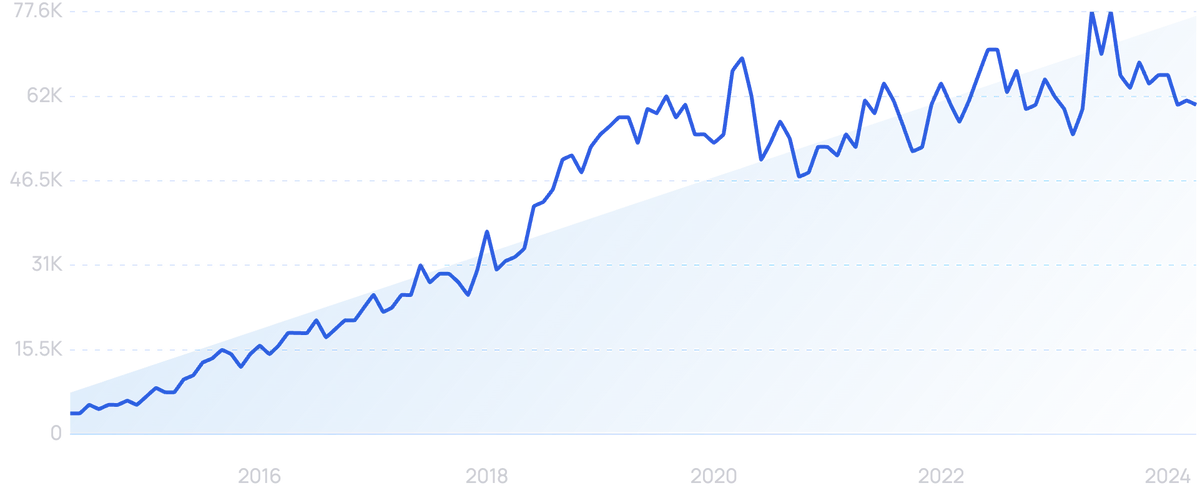
Searches for “food delivery app” have grown over the last 10 years.
On the back of widespread restaurant closures due to coronavirus, the online food delivery market grew by an estimated 27% in 2020.
The collective revenue of food delivery companies stood at $151.5 billion by the end of 2021.
Overall, the food delivery space is expected to grow to $182.3 billion by the end of 2024.
The global online food delivery market is expected to grow to $182.3 billion this year.
The number of online food delivery service users also rose from 1.17 billion in 2019 to 1.43 billion in 2020.
As of 2023, there are over 2.85 billion online food delivery service users.
China made up the largest segment of the market in 2020 ($51.5 billion), growing by 28% year-over-year.
And its 650 million delivery customers make up close to half of the global user base.
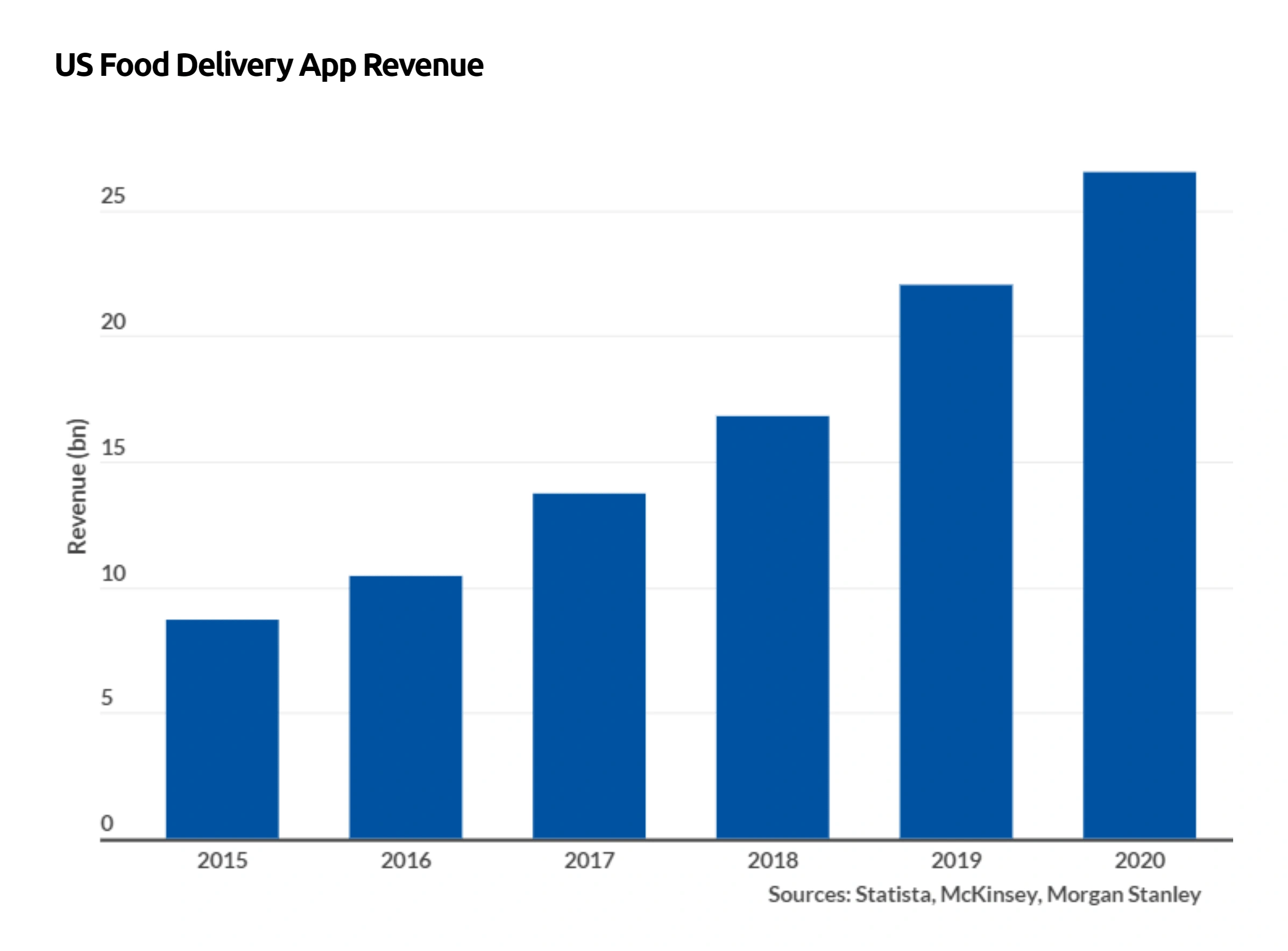
In the US, online food delivery apps bring in a collective $26.5 billion.
That’s 3x more revenue than they generated just five prior.
Source: Business of Apps
And the US market is expected to almost double by 2025, reaching about $42 billion.
It’s estimated that, by the end of 2020, the food delivery market made up 13% of the total restaurant sector.
This is compared to a predicted 9% before COVID-19.
And this sector of the market isn’t expected to slow anytime soon.
Statista predicts that online food delivery’s share of the market will be over 20% by 2025.
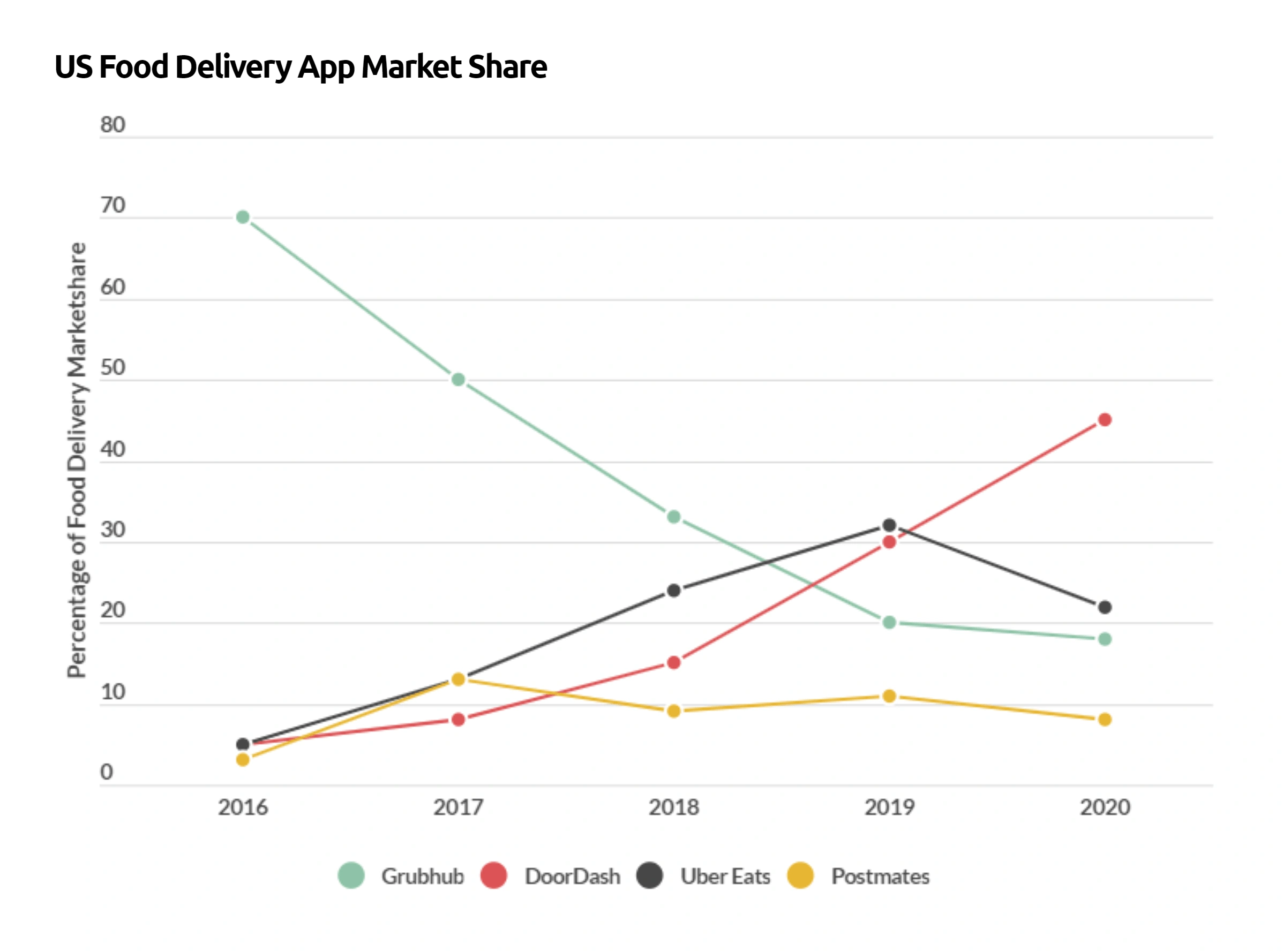
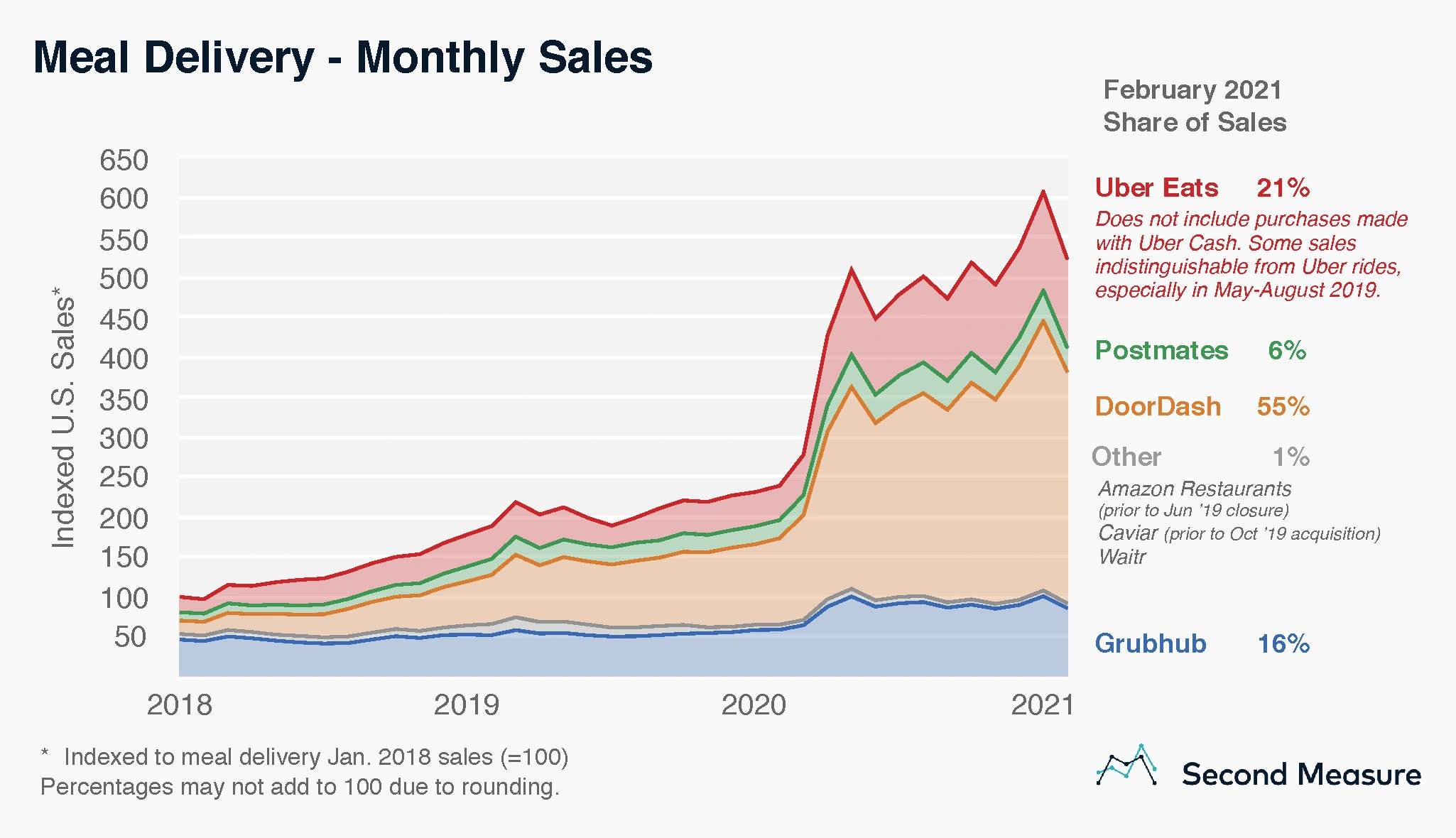
Food Delivery Company Market Share in the US as of 2020.
Doordash is the largest food-delivery service in the US, capturing 45% of the market.
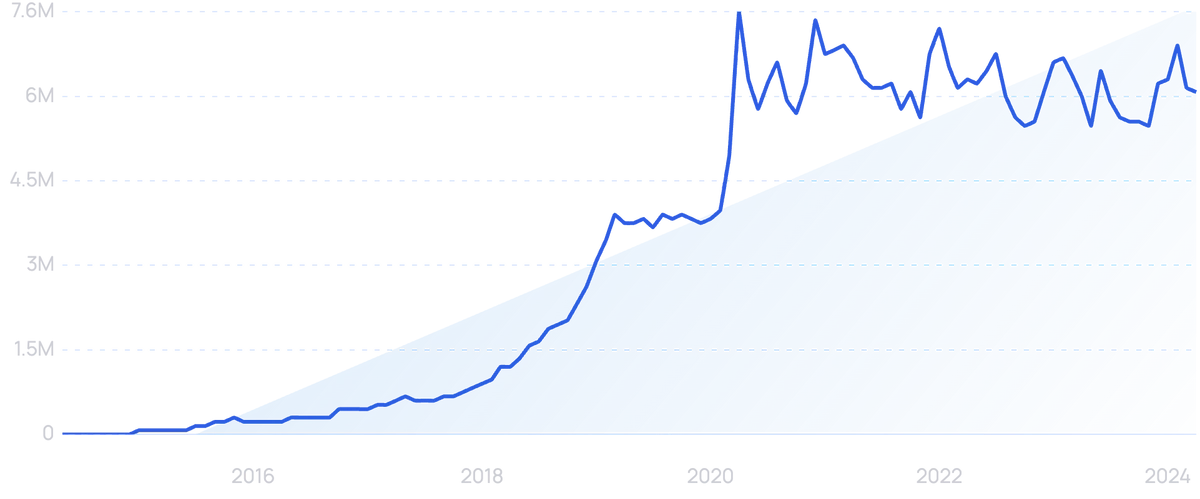
Searches for the popular food delivery and takeout app “DoorDash” have grown by 8,000% over the last 10 years, to roughly 6 million a month.
According to its 2020 Annual Report, Doordash has over 450,000 merchants on its platform and 20 million customers.
(About 18% of the US’s 111 million total customers.)
And by February of 2021, Doordash’s market share had expanded even more.
Source: Second Measure
Doordash captured 55% of US food delivery sales made in February 2021.
Doordash also saw its revenue rise by about 226% in 2020, blowing past its competitors.
Uber Eats and Grubhub are fighting for second place.
And the two are both experiencing consolidation in different ways.
Uber Eats grew its gross delivery bookings by 110% in 2020.
And it acquired fourth-place Postmates for $2.65 billion in 2020 as well.
Grubhub, on the other hand, acquired by Danish food delivery company Just Eat for $7.3 billion.
2. Ghost Kitchens are Popping Up Everywhere
A ghost kitchen (or cloud/dark kitchens as they’re also known) is a cooking facility that is set up for the sole purpose of preparing food for delivery orders.
There is no dine-in or customer-facing experience. And many ghost kitchens contract with multiple restaurants at a time.
Searches for “ghost kitchen” have grown by 700% over the last 5 years.
As online ordering becomes all the more common, ghost kitchens are becoming more important than ever.
In 2020, there were an estimated 1,500 ghost kitchens in the US.
This trails China and India, which have over 7,500 and 3,500 ghost kitchens respectively.
The market may be small, but it is expected to grow very fast.
Euromonitor predicts that the entire ghost kitchen market will be worth $1 trillion by 2030.
And there’s no shortage of new companies popping up in this space.
The industry itself attracted $5.5 billion in investments in 2021.
CloudKitchens is probably the most well-known of the pure-play ghost kitchen companies.
“CloudKitchens” searches have grown by 133% in the last 5 years.
It was started by former Uber co-founder and CEO Travis Kalanick.
And it has already raised $400 million from Saudi Arabia’s sovereign wealth fund.
The company offers local food-prep services for restaurants and contracts with food delivery companies to offer speedy preparation and delivery.
Kalanick has also reportedly spent up to $130 million buying real estate for CloudKitchen locations between 2018 and 2020.
Another promising start-up is Kitchen United.
The company has locations in Chicago, Pasadena, and Austin, among other cities.
Kitchen United offers a multi-restaurant selection, allowing customers to order from popular restaurants, like Panera Bread, Wendy’s, White Castle, and other regional or local favorites.
Kitchen United is currently in 6 locations throughout the US.
Compared to CloudKitchens’ true “ghost” approach, Kitchen United is more customer-facing.
Consumers can order directly from the website and choose any restaurant partner they want.
They can even pick up their food (via a contactless experience) from the Kitchen United location.
Kitchen United is still in its early days.
But the CEO has already announced an expansion to 20 locations in 2021 – compared to the current 6.
The CEO also touted the company’s value proposition for restaurant partners.
Brands partnering with Kitchen United have experienced, on average, 600-700% growth in order volume.
And 90% of the top restaurant brands in the US have expressed interest in working with them.
REEF Technology is another fast-growing ghost kitchen company.
REEF began as a parking lot management company but has since expanded into opening ghost kitchens in its network of more than 4,500 parking lots.
The company has already opened more than 100 of its “neighborhood kitchens” across the US It places its mobile food truck ghost kitchens in its parking lots and licenses them out to popular brands (like Nathan’s Famous).
A REEF ghost kitchen
REEF has already raised $1.5 billion from a variety of investors, including Softbank, UBS Asset Management, and the Mubadala Investment Company.
It has also partnered with Oaktree Capital Management, creating a $300 million real estate investment vehicle in order to expand its presence to 10,000 parking lot locations.
Another ghost kitchen company, JustKitchen, said it is able to cut food delivery times in half for traditional restaurants.
JustKitchen started in Taiwan, where food delivery penetration was already higher than in the US pre-pandemic (30-40% in Taiwan vs. below 20% in the US).
JustKitchen claims that its restaurant partners experience a 40% monthly increase in sales after using its platform.
Overall, expect the ghost kitchen industry to force major changes for many restaurant owners moving forward.
3. Virtual Restaurants are Starting to Take Market Share
With the help of ghost kitchens and online food delivery, virtual restaurants experienced their first year of real success in 2020.
Searches for “virtual restaurants” have risen by 28% in 5 years.
By the end of 2020, there were an estimated 100,000 virtual restaurants in the US.
Food service giant Brinker International, the parent company of Chili’s and Maggiano’s, launched the “It’s Just Wings” delivery-only brand in the second half of 2020.
It’s Just Wings now operates out of over 1,000 Chili’s and Maggiano’s restaurants.
And it’s on pace to bring in over $150 million in its first year of operation.
Chuck E. Cheese also launched its own virtual “Pasquale’s Pizza and Wings” brand in 2020.
In addition, Applebee’s has been testing its “Neighborhood Wings” virtual brand in 700 restaurants throughout 2020.
It’s easy to see why these traditional restaurants are going this route.
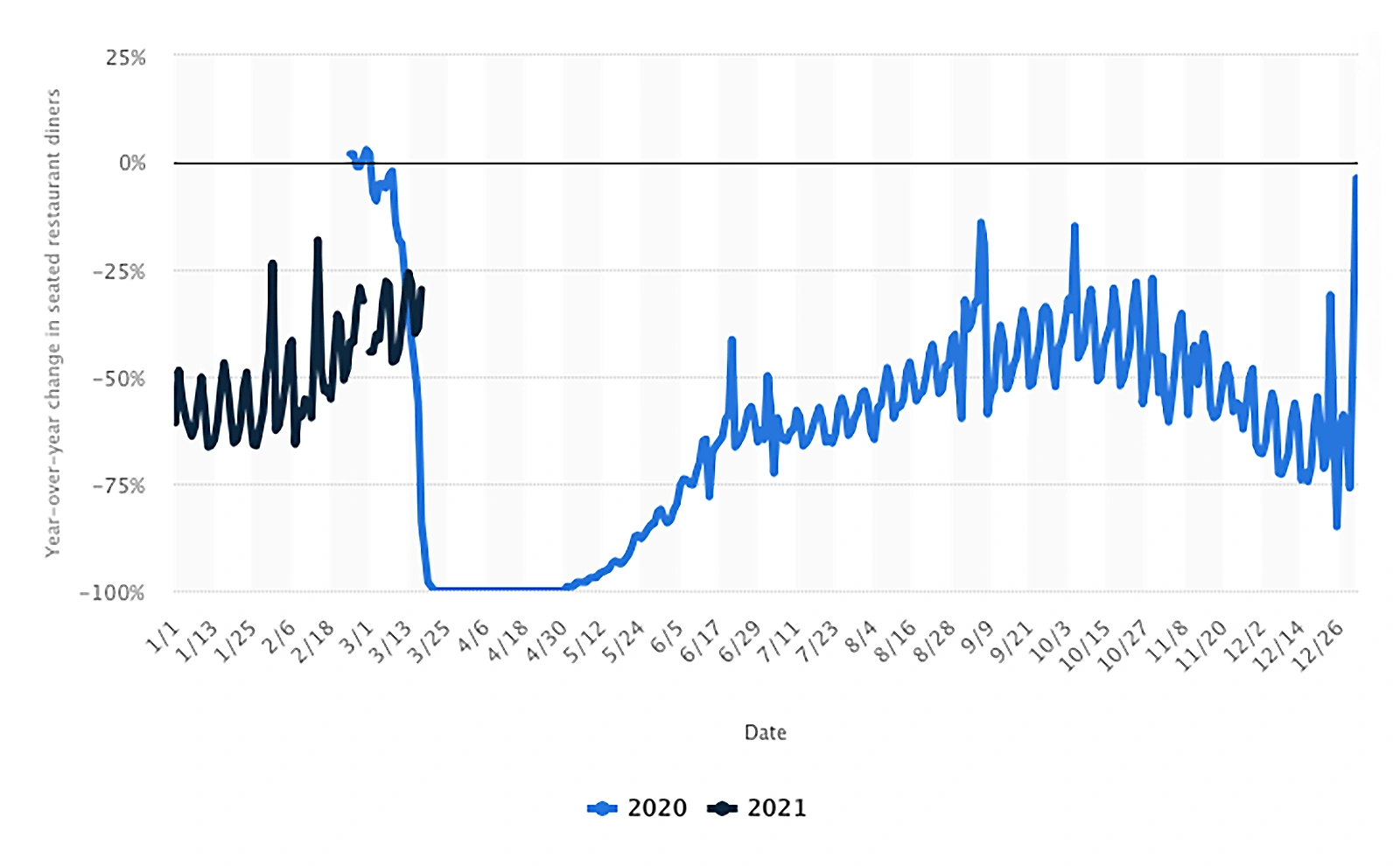
The number of in-house diners declined by 50-60% in 2020.
And that number was still down by roughly 30% in March of 2021.
Year-over-year change in seated restaurant diners compared to 2019.
Traditional Restaurants have been using this tactic to recapture lost business during the pandemic.
However, creating a virtual brand has also been a great way for traditional restaurant brands to capture a market that they couldn’t get before.
It’s estimated that over three-fourths of customers ordering from spin-off brands on GrubHub have never even made an order from the traditional brand.
In addition, there are now virtual restaurants that aren’t tied to any traditional brands.
Ghost kitchen company JustKitchen has, in addition to serving traditional brands, created its own virtual food brands as well.
The company uses data derived from its ghost kitchen services to decide how and when to launch a new food brand. And since customers use JustKitchen’s software to order from its partner brands, it already has a locked-in user base to sell to.
The YouTube star, MrBeast, has also created his own virtual restaurant – MrBeast Burger.
MrBeast burger sold 1 million burgers in its first 90 days.
MrBeast has leveraged his 250 million+ subscribers to create a successful virtual restaurant, launching in 300 locations as of December 2020.
The MrBeast Burger app also jumped to the top of the Apple Store shortly after launch, surpassing other food industry competitors
The Local Culinary has taken a different route, becoming a sort of virtual restaurant franchisor.
By partnering with brick-and-mortar restaurants, it is essentially turning them into ghost kitchens.
Here’s how it works: A restaurant signs up with The Local Culinary and chooses from among 50 virtual, delivery-only brands to partner with. The brick-and-mortar restaurant then cooks and prepares the food for the virtual brand, which delivers it through third-party delivery partners.
The overall business model is designed to expand distribution for virtual restaurants while also helping brick-and-mortar restaurants add to their bottom line without having to establish a delivery business.
4. Automation Offers New Avenues for Improvement
Automation is becoming a larger and larger part of the restaurant industry.
With labor typically making up the largest cost of restaurant operations, many are hoping to cut costs by automating some tasks.
The global food automation market is predicted to grow at an annual rate of 7% over the next few years.
By 2026, it’s expected to be worth $28 billion.
Most of this value is in large-scale food processing and packaging.
But automation is starting to reach the restaurant business as well.
As far back as 2018, restaurants like the Boston-based Spyce Kitchen were using robotic chefs to prepare meals efficiently and cheaply.
Although being used since 2018, robotic chefs still haven't gone mainstream.
A more common mode of automation has taken the form of self-pay tablets.
Restaurants like Chili’s and Olive Garden were responsible for installing more than 200,000 of these over the last few years.
Applebee’s has found that over 70% of their customers interacted with these devices.
Ziosk is the leading provider of these tablets.
It has conducted studies finding that the tablets speed up the dining process by six to nine minutes.
Tableside tablets can increase table turnover.
This can mean increased profits for restaurants as more diners can be accommodated throughout the day.
(Not to mention the fact that this creates an easy contactless payment option for diners).
Darden Restaurants (owner of Olive Garden) also reported that Ziosk tablets are helping close checkouts 7 minutes faster than before. Darden has even seen kiosk usage rise to 92% post-COVID from 71% before.
Ziosk also reported that its customers have found that the table-top tablets increase dessert sales by an average of 30%.
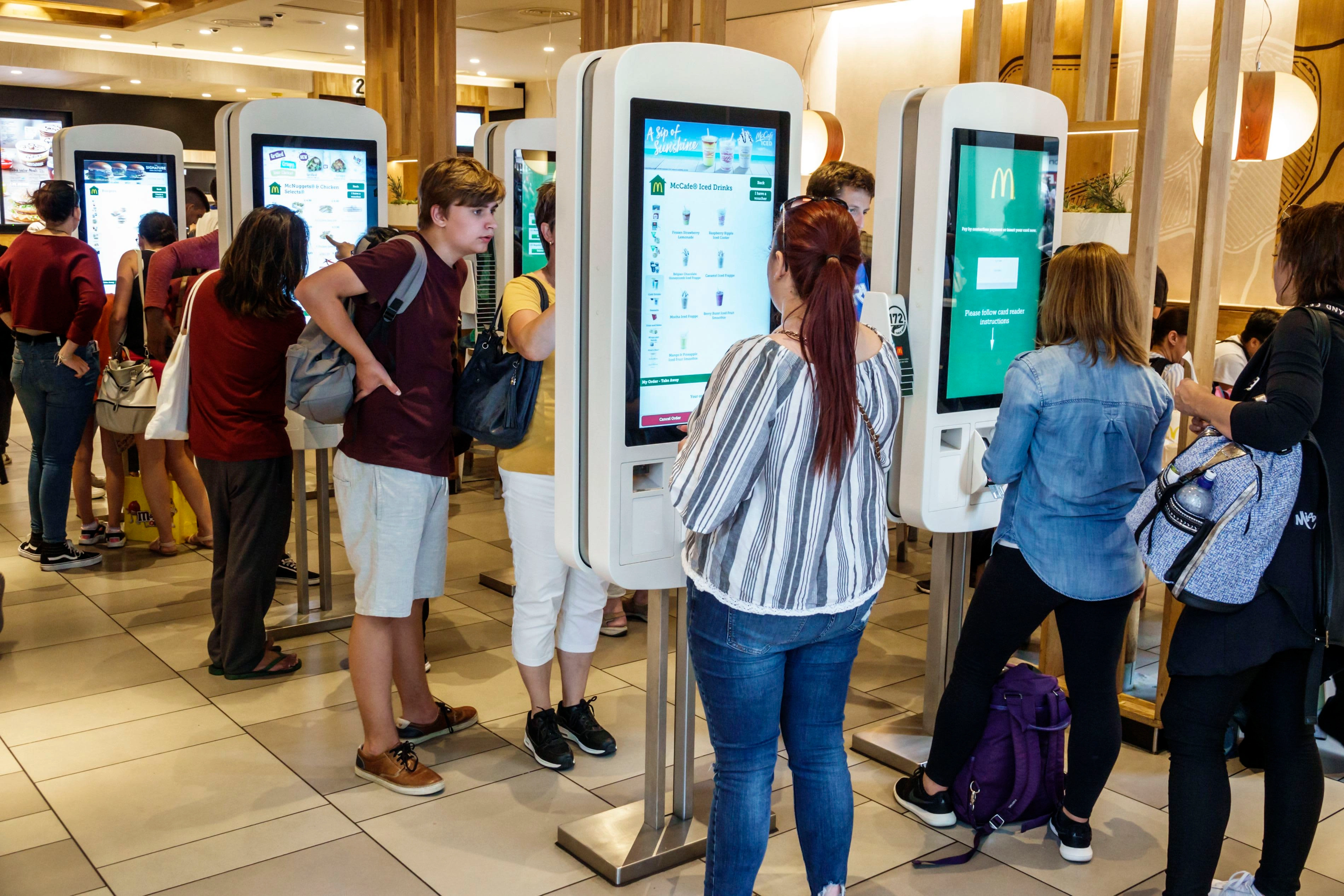
Restaurants like McDonald’s have also been installing self-serve kiosks in many of their locations.
McDonald’s Self-Serve Kiosks
Because of this, digital sales have grown to $26.8 billion as of 2020 – an increase of 23% over the previous three years.
Automation is helping a variety of restaurants achieve greater efficiency as well as expand their services.
5. Restaurants Seek Personalized Customer Experiences
Restaurant chains and brands are increasingly trying to find new ways to personalize the customer’s experience.
For instance, research by PSFK shows that 79% of consumers want personalized menu items based on past data.
Personalized dining experiences are now an expectation for many restaurant-goers.
To meet this growing need, restaurant chains like McDonald’s are looking to capture customer data.
The fast-food giant acquired AI and data collection company Dynamic Yield for $300 million in 2019.
This technology personalizes the customer’s order based on data from past orders.
By the beginning of 2020, McDonald’s had installed Dynamic Yield’s technology in 9,500 of its US drive-throughs.
Fast casual chain Chipotle has also gotten involved in the customer personalization space.
Search interest in “Chipotle” has increased by 300% over the last 15 years.
Chipotle launched its customer loyalty program in 2019.
The loyalty program now has over 17 million members.
Chipotle selected Microsoft Dynamic 365 Customer Insights to help it implement a personalization program based on the data.
Chipotle now uses this data to create profiles of users, in order to personalize their experience.
After hearing this, you may be tempted to think that customers would be skeptical about giving their data to massive fast-food franchises.
But the numbers say otherwise.
According to the earlier mentioned PSFK report, 84% of consumers are fine with giving their order history data to restaurants in return for a more personalized experience.
Conclusion
That concludes our list of important restaurant industry trends.
At a high level, the biggest changes are taking place in distribution and customer interactions.
(Even more than the food itself.)
As technology advances, expect the traditional concept of a restaurant to change even more.
Stop Guessing, Start Growing 🚀
Use real-time topic data to create content that resonates and brings results.
Exploding Topics is owned by Semrush. Our mission is to provide accurate data and expert insights on emerging trends. Unless otherwise noted, this page’s content was written by either an employee or a paid contractor of Semrush Inc.
Share
Newsletter Signup
By clicking “Subscribe” you agree to Semrush Privacy Policy and consent to Semrush using your contact data for newsletter purposes
Written By


Josh is the Co-Founder and CTO of Exploding Topics. Josh has led Exploding Topics product development from the first line of co... Read more