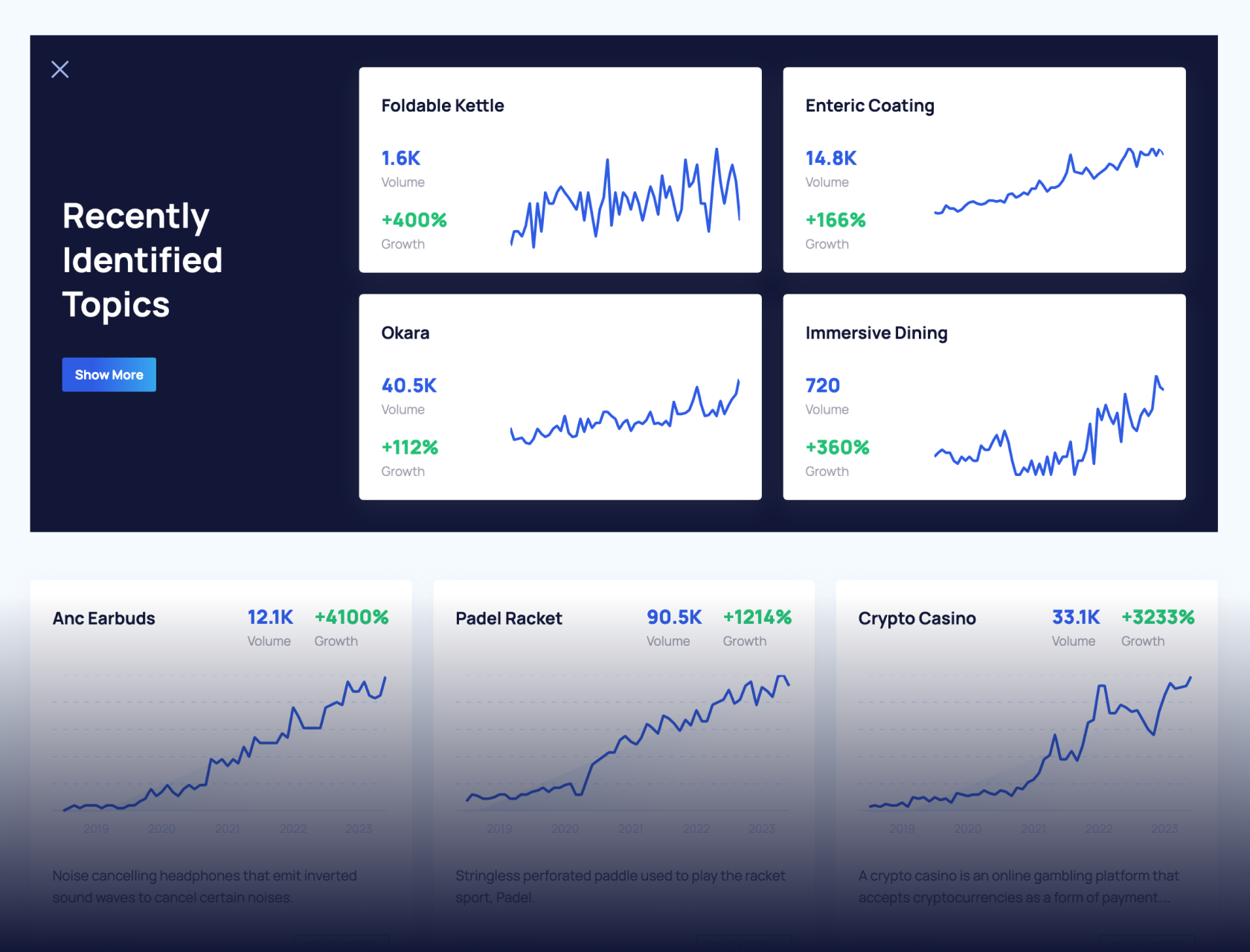
Get Advanced Insights on Any Topic
Discover Trends 12+ Months Before Everyone Else
How We Find Trends Before They Take Off
Exploding Topics’ advanced algorithm monitors millions of unstructured data points to spot trends early on.
Keyword Research
Performance Tracking
Competitor Intelligence
Fix Your Site’s SEO Issues in 30 Seconds
Find technical issues blocking search visibility. Get prioritized, actionable fixes in seconds.
Powered by data from
7 AI Cybersecurity Trends For The 2025 Cybercrime Landscape
AI is critical to the future of cybersecurity. The technology is making defenses more sophisticated, but it’s also a tool in the arsenal of attackers.
In this article, I cover both sides of the changing landscape: AI cybercrime and AI cybersecurity.
Read on to find out about trends including AI-supercharged malware, ransomware, phishing, and “vishing” attacks, along with the response from the cybersecurity sector.
You’ll discover how the multi-billion-dollar industry is working to tackle new threats, protect the cloud, and ultimately even take aim at “zero-day” vulnerabilities.
1. AI Leads To More Sophisticated Malware And Ransomware
Almost three-quarters of data breaches are attributable to human error. But the threat of malicious third parties certainly cannot be ignored.
According to the ITRC Annual Data Breach Report, there are as many as 11 victims of a malware attack per second. That’s more than 340 million victims per year.
And in 2024, North America saw a 15% increase in the number of ransomware attacks.
(It’s little wonder that cybersecurity is an increasingly tough search keyword to target for companies within the industry.)
Get More Search Traffic
Use trending keywords to create content your audience craves.
Rising AI cybercrime
AI can be part of the solution. But it is also a growing part of the problem.
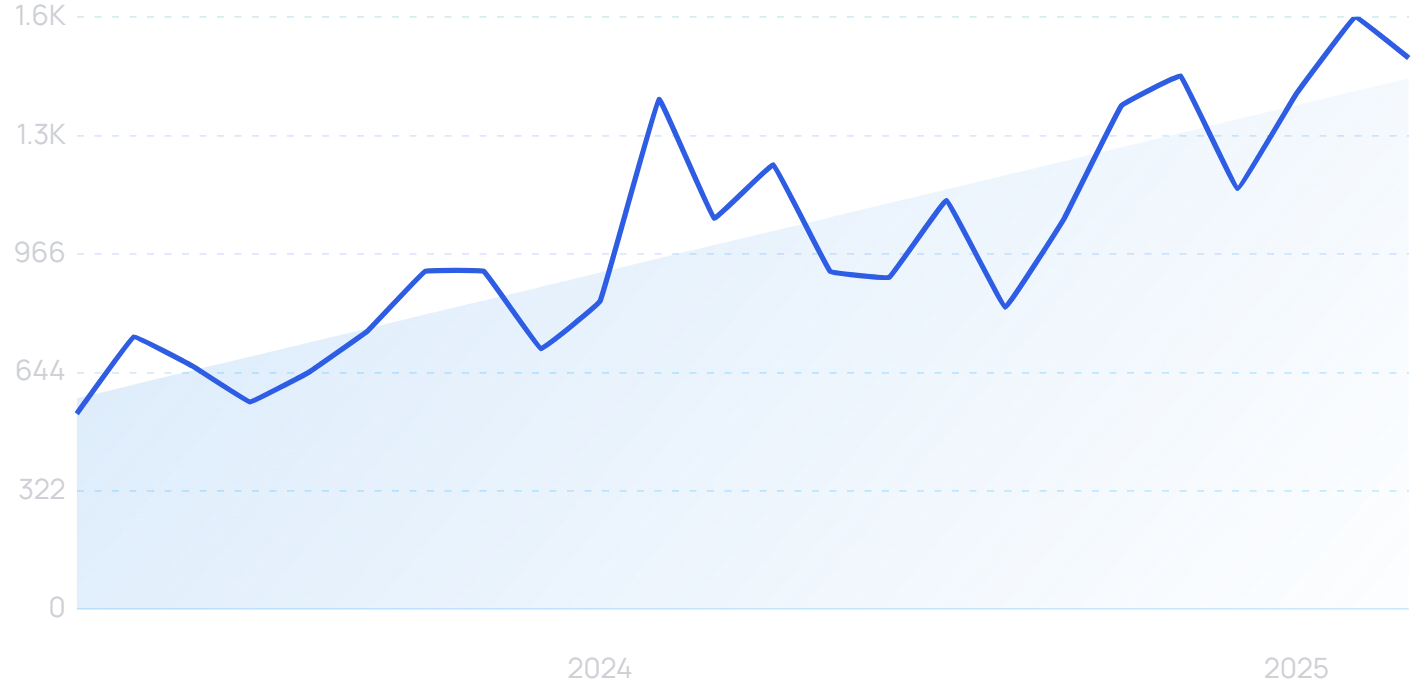
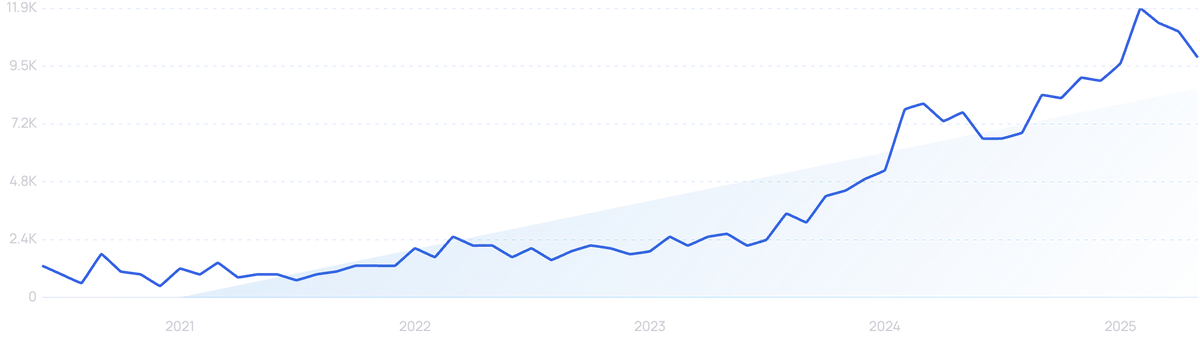
Searches for “AI cyber attacks” have increased by 186% in the last 2 years.
AI is transforming entire industries. Unfortunately, cybercrime is no exception.
Bad actors can reap all the familiar benefits of AI: automation, efficient data collection, and continual evolution and improvement of methodologies, to name a few.
In fact, one survey found that 56% of business and cyber leaders expect AI to hand an advantage to cybercriminals, not cybersecurity professionals.
Malicious GPTs can generate malware. AI can adapt ransomware files over time, reducing their detectability and improving their efficacy.
And the power of AI to assist in writing code has lowered the skill barrier for cybercriminals. HP has found real-world evidence of malware partially written by AI.
In the last year, 87% of global organizations have faced an AI-powered cyber attack. Cybercrime is expected to cost $13.82 trillion globally by 2032.
2. AI Phishing Attacks Increase
Artificial intelligence technology can even help to target humans, the greatest vulnerability in most security networks.
Generative AI can be a legitimate, useful and powerful writing assistant. But in the wrong hands, these capabilities can greatly enhance phishing attacks.
Phishing is the most common kind of cyberattack. That’s when grouped together with “pretexting”, a similar but more targeted attempt to extract details from a system user.
In 50% of cases, phishing targets user credentials. That often means going after passwords to gain entry.
You might not imagine AI having a particularly sizable effect in this relatively low-tech area of cybercrime. But the technology can help hackers to devise more believable personas in order to convince victims to part with sensitive information.
A study published last year found that 60% of participants were convinced by AI-created phishing attacks. That was comparable to the success rate of messages devised by human experts.
One of the phishing emails generated by AI for the purposes of a recent study.
Moreover, follow-up research found that AI is able to automate the entire phishing process. That means these broadly equivalent success rates are being achieved at a 95% reduced cost.
And AI-generated phishing schemes are only going to get better. A 2025 CrowdStrike study found that phishing emails created by AI have a 54% click-through rate, compared to 12% for human-written content.
3. Phishing Makes Way For Vishing
Voice phishing — or “vishing” — brings another layer of sophistication to phishing attacks.
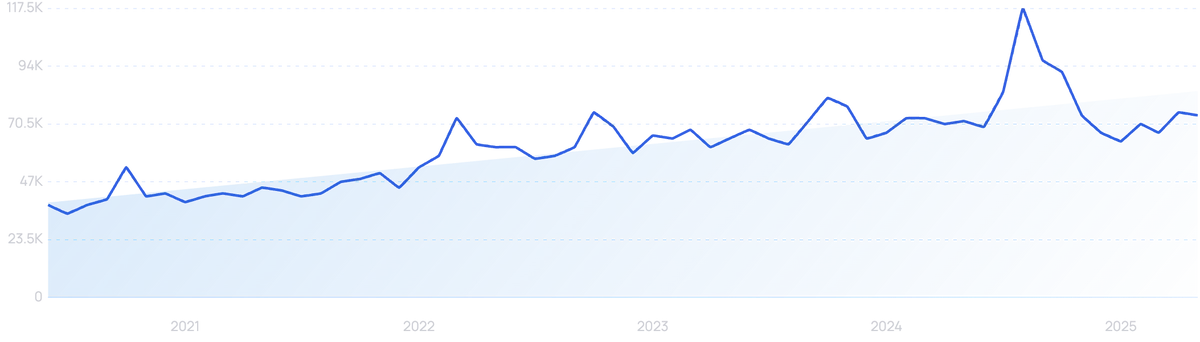
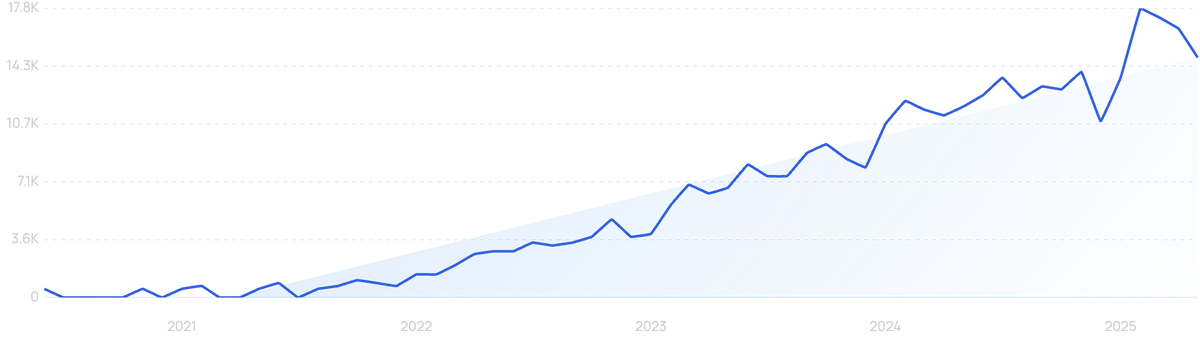
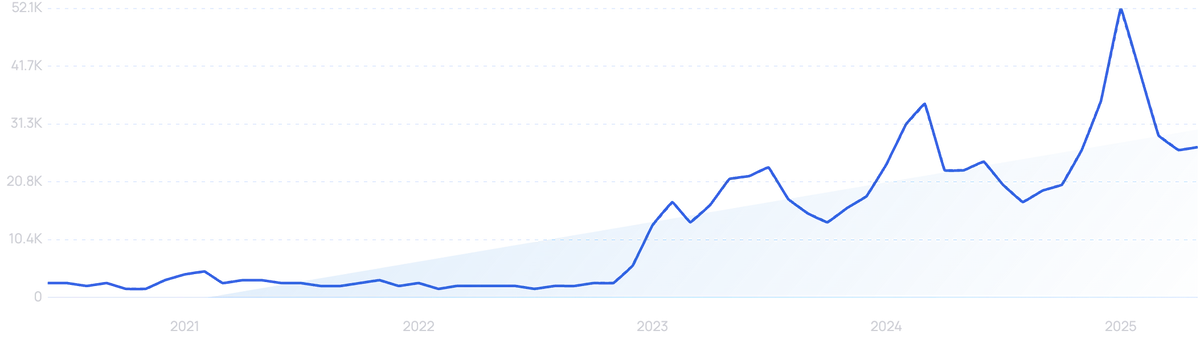
“Vishing” searches are up 97% in the last 5 years.
Vishing is the process of impersonating a trusted person’s voice in order to access information or money. AI has made that task far easier, and the technology is now used in 80% of vishing attacks.
There are a number of legitimate uses for voice cloning technology. Lovo offers it for content creation purposes.
“Lovo” searches are up 6,300% in the past 5 years.
But this AI-powered technological development has been a gold mine for vishing schemes too. Voice phishing attacks increased by 442% in the second half of last year as AI voice cloning grew ever more sophisticated.
As many as 1 in 4 employees have difficulty distinguishing real and deepfaked audio. 6.5% gave away sensitive data during fake vishing calls.
There have been some high-profile real-world examples. In 2023, MGM Resorts was the victim of a cyberattack that ended up costing $100 million.
It all started with a voice phishing scam, where artificial intelligence was used to replicate an employee’s voice and secure system access.
The following year, a finance worker in Hong Kong was tricked into wiring $25 million to a scammer following a faked Zoom call with the CFO.
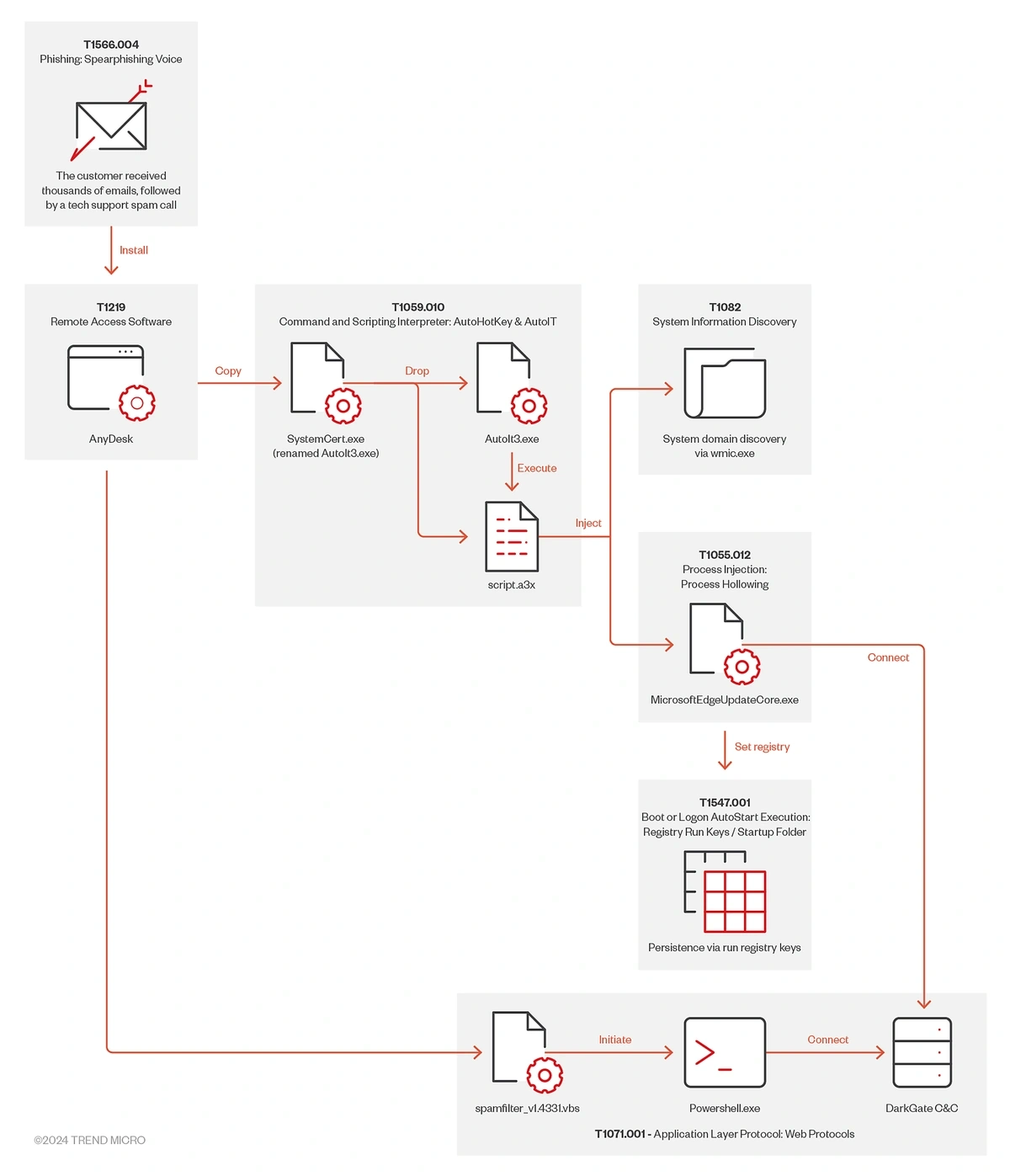
And vishing can be combined with persistent and targeted “traditional” phishing campaigns too. In one example, thousands of emails were sent to the victim to lay the groundwork for a fraudulent “tech support” vishing call on Microsoft Teams.
The timeline of one attempted attack that combined phishing and vishing.
This particular attempt was foiled. But it illustrates the increasingly powerful role of AI in cyber attacks.
4. AI Cybersecurity Tackles AI Cybercrime Directly
Increasingly sophisticated threats require increasingly sophisticated cybersecurity. AI is being used in highly innovative ways in order to keep data safe.
The benefits of AI for cybersecurity experts are not too dissimilar to the benefits for cyber criminals: the ability to quickly analyze large amounts of data, automate repetitive processes, and spot vulnerabilities.
As a result, 61% of Chief Information Security Officers believe they are likely to use generative AI as part of their cybersecurity setup within the next 12 months. More than a third have already done so.
And according to IBM, the average saving in data breach costs for organizations that already use security AI and automation extensively is $2.22 million.
It’s little wonder that the AI cybersecurity market was valued at $24.82 billion in 2024. By 2034, that figure is forecast to reach $146.5 billion (a 19.4% CAGR).
AI solutions for AI threats
Some of the uses for AI in cybersecurity have arisen directly from a need to counter new AI threats. For example, AI voice detectors to combat vishing.
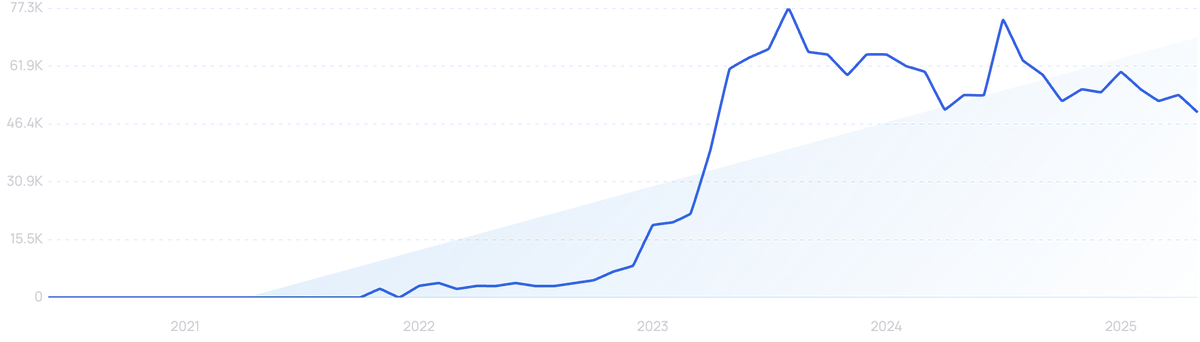
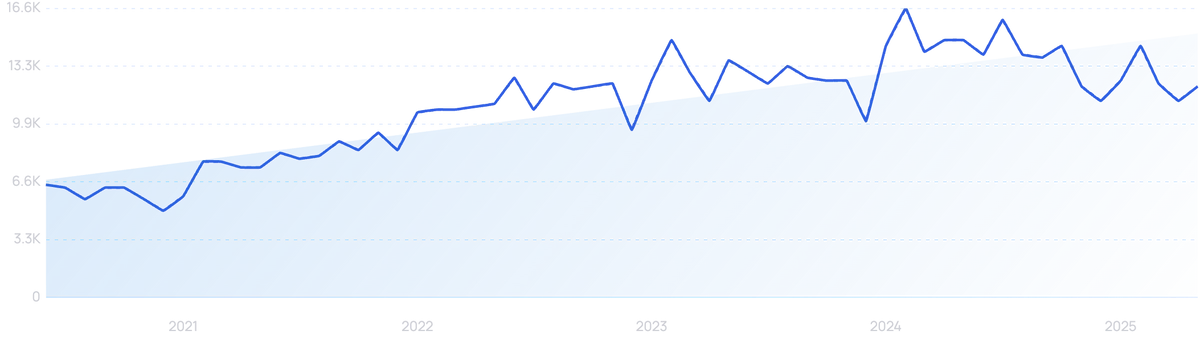
“AI voice detector” searches are up 6,500% in the last 5 years.
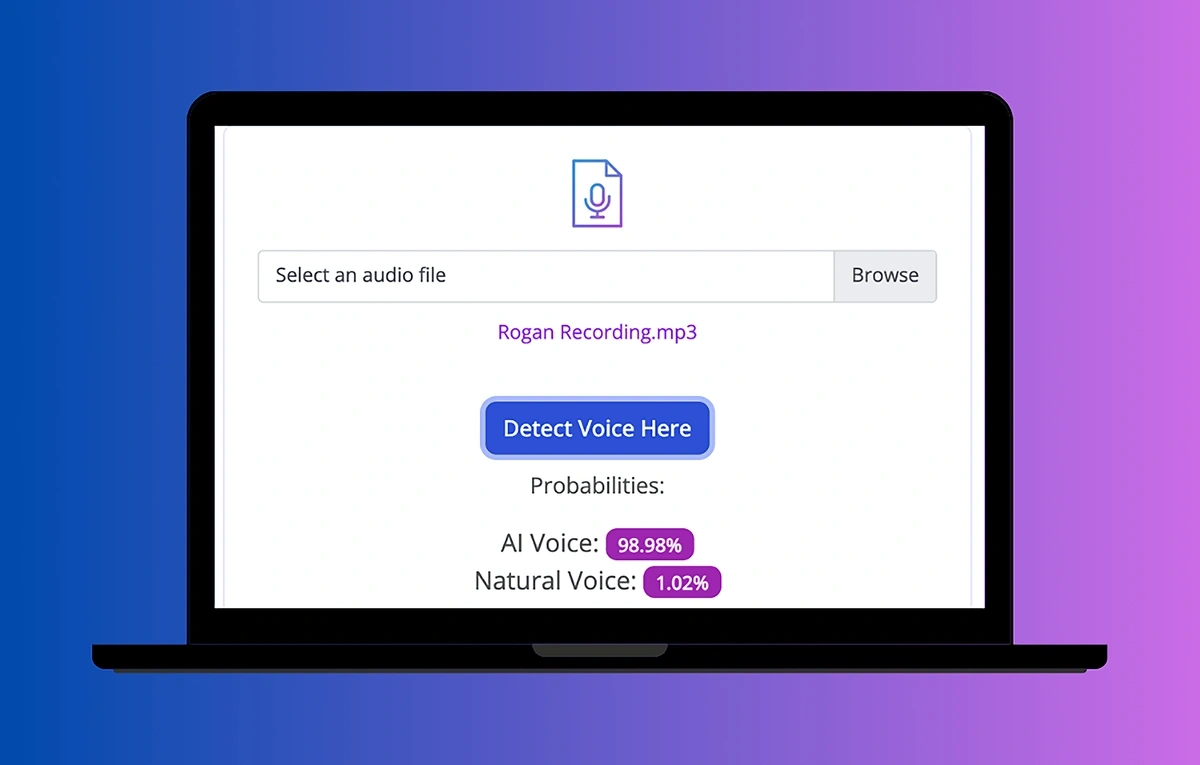
An early market leader is simply named AI Voice Detector. Users can upload audio files or download a browser extension to check for AI voices online (for instance, in a Zoom or Google Meet call).
Detection is powered by an AI tool. It has already detected 90,000 AI voices, serving more than 25,000 clients.
AI Voice Detector returns probabilities of a voice being natural or AI-generated.
Meanwhile, some of the cybersecurity responsibility for preventing voice phishing falls on the makers of the AI voice cloning technology. A process known as AI watermarking is rising to prominence.
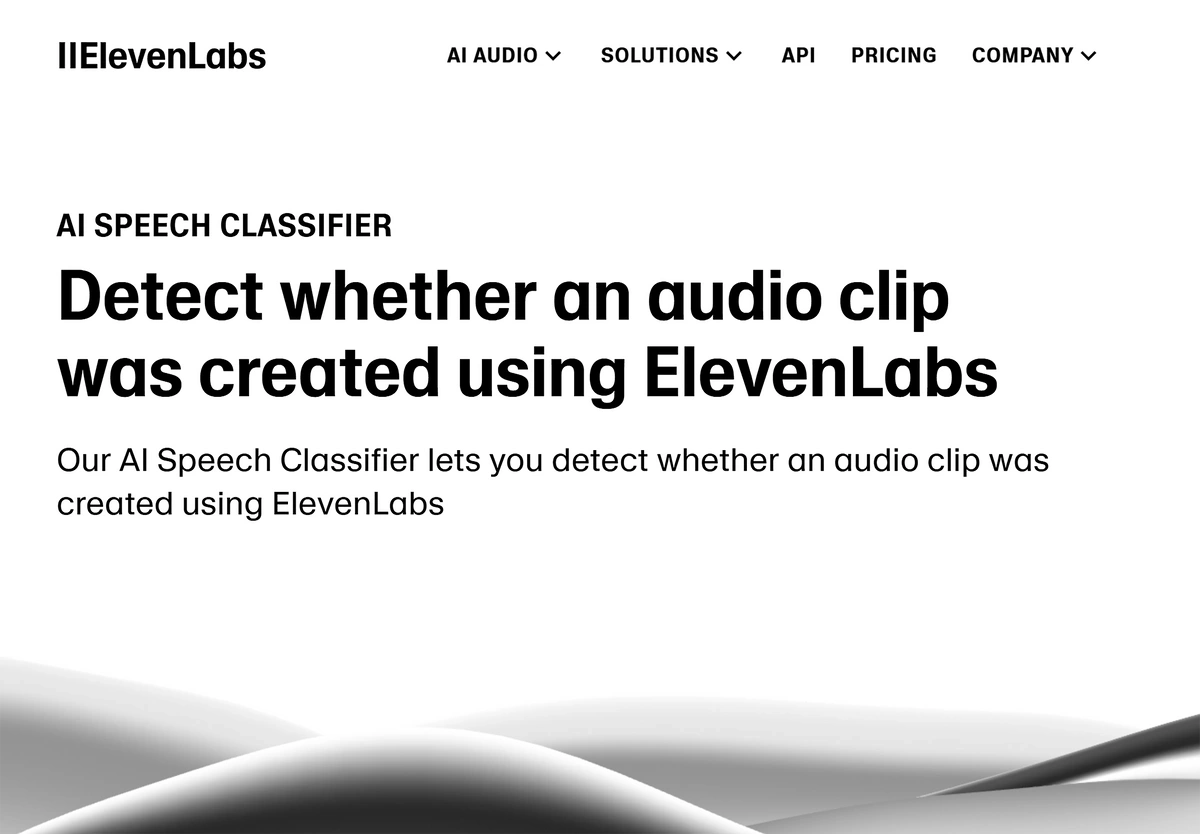
ElevenLabs is one of the leading AI voice cloning providers. It has taken steps to ensure listeners can find out whether a clip originates from its own AI generator.
“ElevenLabs” searches are up 99x+ in the last 5 years.
Its “speech classifier” tool analyzes the first minute of uploaded clips. From that, it is able to detect the likelihood that it was created using ElevenLabs in the first place.
ElevenLabs can check for the involvement of its own AI in the creation of voice clips.
Away from vishing, Google recently created an invisible watermark capable of labeling all text that has been generated by Gemini, its AI software.
Unlike the leading AI voice detection tools, this does not deal in probabilities. It is a true watermark, denoting the provenance of AI-generated text beyond any doubt.
The watermark is now applied to all of Google’s AI-generated content.
Wider adoption of this technology by generative AI providers would be warmly received by educational institutions. But it would also be huge for cybersecurity, with users able to easily determine whether potentially suspicious emails were crafted using artificial intelligence.
Meta has followed suit when it comes to detecting the use of AI in creating “deepfakes”.
“Deepfake detection” searches are up 655% in the last 5 years.
Meta Video Seal has been open-sourced and can be integrated into existing software. Meta is launching a public leaderboard to compare the effectiveness of various video watermarking software.
5. AI Cybersecurity Protects The Cloud
Cybersecurity has to keep pace with more than just AI threats. There’s also been a mass migration to cloud services over the past few years.
By 2023, 70% of organizations reported that more than half of their infrastructure had moved to the cloud. 65% operate a multi-cloud system, and 80% store sensitive data in the cloud.
Forecasts predict that 90% of organizations will use a hybrid cloud approach by 2027. Public cloud spending is set to hit $720 billion this year.
There has been a corresponding surge in Cloud-Native Application Protection Platforms (CNAPPs) within the cybersecurity space.
“CNAPP” searches are up 2,667% in the last 5 years.
CNAPPs are all about building cybersecurity solutions specifically for the cloud. As opposed to playing catch-up by tacking on ad-hoc fixes and adjusting existing measures that may no longer be fit for purpose.
AI can play a key role in these systems. Ron Matchoro, Head of Product at Microsoft Defender for Cloud, called AI the “final missing piece of the CNAPP puzzle”.
Prisma Cloud brands itself as a CNAPP. And it has integrated AI into its cybersecurity solutions.
“Prisma Cloud” searches are up 87% in the last 5 years.
Prisma uses AI as a “force multiplier” when it comes to Attack Surface Management (ASM). By improving the speed, quality, and reliability of data collection, AI can make ASM more efficient and effective.
Prisma integrates AI into its holistic cybersecurity platform.
The platform also works to counter cybersecurity risks associated with the legitimate use of AI in a business setting. Prisma secures vulnerabilities relating to potential data exposure or unsafe/unauthorized model usage.
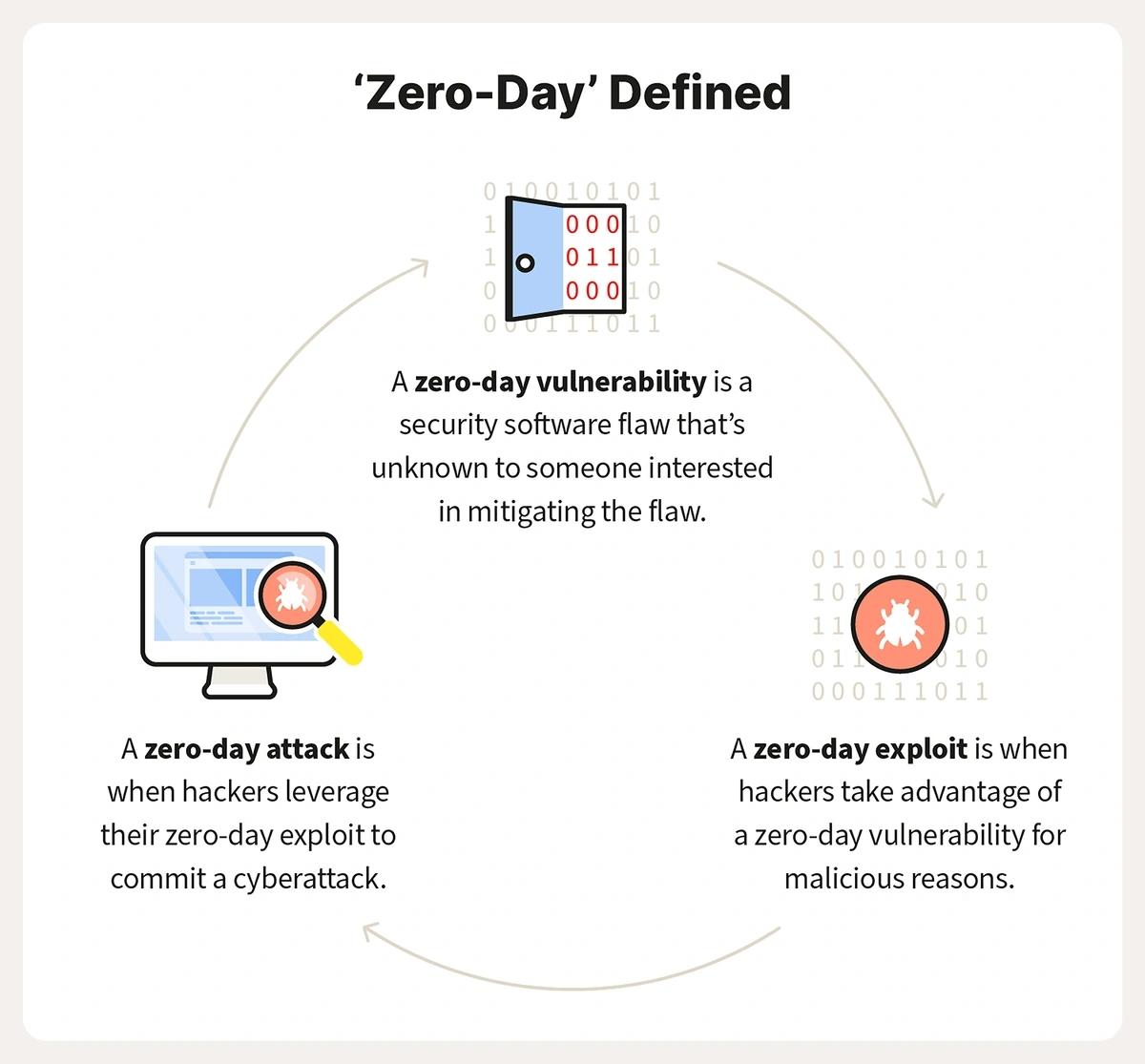
6. AI takes aim at “zero-day” vulnerabilities
Cybersecurity is inherently on the defensive against cyber threats. AI can strengthen that defense.
But AI could have the potential to go even further. It could strike against “zero-day” vulnerabilities — weak points in systems that have not previously been exposed, and for which no known fixes or patches are readily available.
“Zero-day” vulnerabilities can be particularly hard for cybersecurity to mitigate.
This is a more proactive form of cybersecurity, and it’s one being pioneered by Google. Its Project Zero team has long been taking aim at zero-day threats, and has now joined forces with AI team DeepMind.
The result is Big Sleep. And the technology has already discovered its first real-world zero-day vulnerability: an “exploitable stack buffer underflow” in SQLite.
The open-source database is widely used. Google’s Big Sleep team reported the vulnerability to the developers in early October, and it was fixed on the same day.
Big Sleep believes this is the first time an AI agent has found a “previously unknown memory-safety issue in widely-used real-world software.”
Microsoft is also active in the AI zero-day space. It has expanded its Zero Day Quest bug bounty program, making $4 million in awards available in the “high-impact” areas of cloud and AI.
Of course, if AI can find zero-day vulnerabilities for defenders, it can do the same for attackers. Cybersecurity professionals need to be more watchful than ever when it comes to novel forms of cybercrime.
This is still a nascent area of AI cybersecurity. But it is certainly an interesting one to watch.
7. AI Cybersecurity Sees New Investment
There is a rush to invest in new AI cybersecurity technology. Internally, cybersecurity firms are consistently committing a greater percentage of their revenue to research and development than other businesses in the software industry.
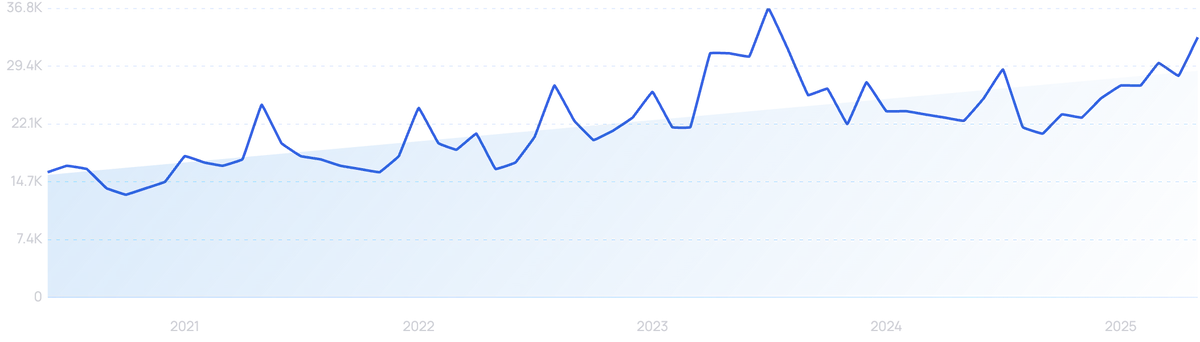
“Invest in AI” searches are up 940% in 5 years.
Meanwhile, there is no shortage of external investment either. Venture investment into the cybersecurity industry rose by 43% in 2024, hitting almost $11.6 billion — excluding seven “COVID bubble” quarters, that’s an all-time high.
Wiz, Dazz, and Alphabet
Cybersecurity giant Wiz last year confirmed its acquisition of Israeli startup Dazz. The deal will enhance the US firm’s AI credentials as it seeks to build a strong CNAPP.
Dazz, which specializes in cloud security remediation, only completed a $50 million funding round back in July 2024. That came at a valuation of $400 million.
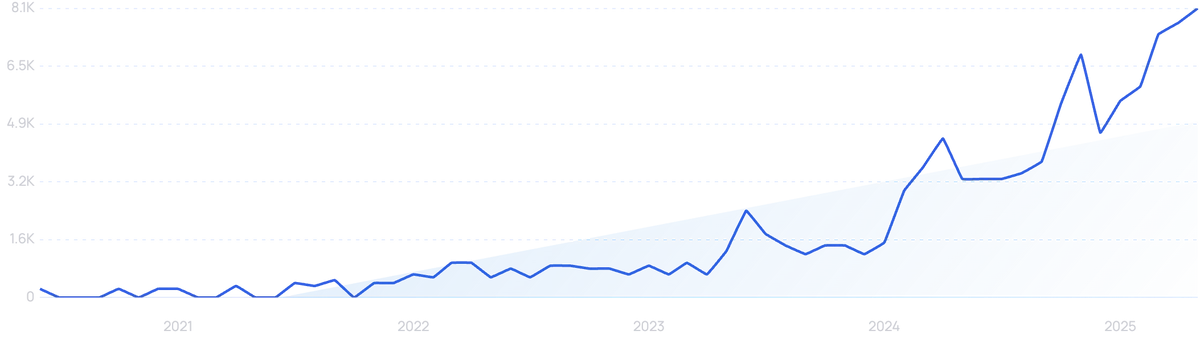
“Dazz” searches are up in the last 6 months following the takeover.
According to TechCrunch, the eventual deal closed at a slightly higher price of $450 million. That figure is made up of cash and shares.
It comes amid information from Dazz that it has grown its annual recurring revenue by 400% between 2023 and 2024. It also says that it has tripled its workforce and expanded operations throughout the US and Europe.
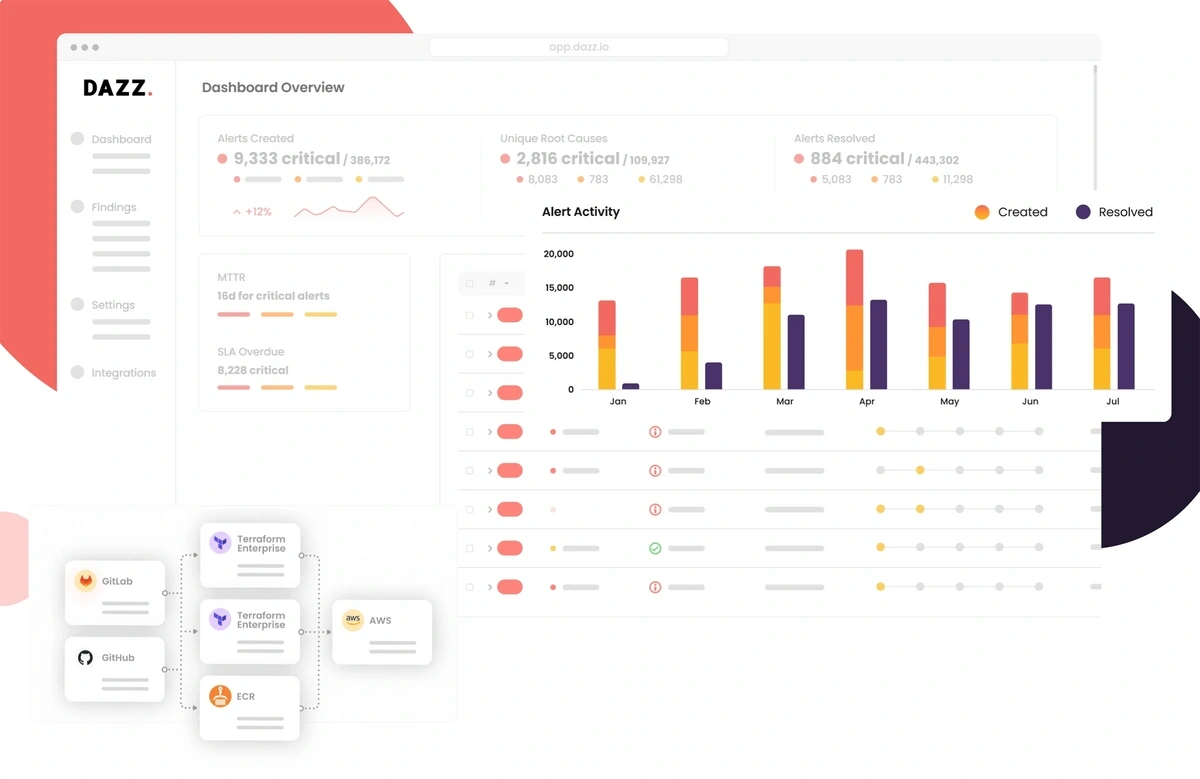
Its technology, which uses AI to help find and fix critical issues within cloud infrastructures, claims to reduce the mean time to remediation by 810%, cutting down risk windows from weeks to hours.
Dazz tracks down security issues within cloud infrastructures.
Both Wiz and Dazz were present alongside Amazon Web Services in July 2023 at an event organized by the Boston chapter of the Cloud Security Alliance.
VC firm Cyberstarts, comprising a number of successful founders from the cybersecurity industry, has previously backed both businesses.
And now Alphabet, the parent company of Google, has agreed to acquire Wiz, subject to regulatory scrutiny. That deal could be worth as much as $32 billion.
More Cybersecurity Investments
An Alphabet takeover of Wiz would be major news for the industry.
But this deal is far from the only one happening in a booming AI cybersecurity space.
Branding itself “the data-first security company”, Normalyze has become part of Proofpoint after the latter signed a “definitive agreement”.
Normalyze has been acquired by Proofpoint.
Normalyze uses AI to “classify valuable and sensitive data at scale”. After that, the platform assesses and prioritizes potential risks and vulnerabilities before providing insights into possible remedial and preventive steps.
The deal “closes AI security gaps” for Proofpoint. Up to now, the company’s main area of operation has been the human element of data protection.
Elsewhere, Crowdstrike has acquired Adaptive Shield. That deal was worth $300 million, according to Security Week.
And away from acquisitions, data loss prevention startup MIND.io has raised $11 million in seed funding. It uses advanced AI and automations to identify and prevent data leaks.
Meanwhile, Cyera raised its second $300 million funding round of the year with its Series D in November 2024.
“Cyera” searches are up 3,233% in the last 5 years.
The startup uses AI to boost data cyber-resilience and compliance. Its latest funding round came at a $3 billion valuation.
In December, SandboxAQ also raised $300 million. It is seeking to apply quantum technology to the development of AI in fields including cybersecurity.
Stay ahead of AI cybersecurity trends
AI is having a transformative effect everywhere. But few industries have been affected as profoundly as cybersecurity.
The threats posed by cyber criminals will never be the same again. They have gotten smarter, more efficient, and harder to contain. It's little wonder that the number of scams is increasing.
Yet at the same time, the tools in the cybersecurity arsenal have become far more sophisticated as well. AI can help to counter the arising novel threats and to provide improved defense against the threats that already exist.
AI cybersecurity solutions are in high demand, as seen by the slew of big-money investments and acquisitions. This is undoubtedly a space to watch closely.
You can stay ahead of the game with the Semrush Traffic & Market. As AI cybersecurity develops, this tool will summarize market size, traffic, and traffic cost for you, along with a breakdown of niche players, established players, game-changers, and leaders.
Stop Guessing, Start Growing 🚀
Use real-time topic data to create content that resonates and brings results.
Exploding Topics is owned by Semrush. Our mission is to provide accurate data and expert insights on emerging trends. Unless otherwise noted, this page’s content was written by either an employee or a paid contractor of Semrush Inc.
Share
Newsletter Signup
By clicking “Subscribe” you agree to Semrush Privacy Policy and consent to Semrush using your contact data for newsletter purposes
Written By


James is a Journalist at Exploding Topics. After graduating from the University of Oxford with a degree in Law, he completed a... Read more