Get Advanced Insights on Any Topic
Discover Trends 12+ Months Before Everyone Else
How We Find Trends Before They Take Off
Exploding Topics’ advanced algorithm monitors millions of unstructured data points to spot trends early on.
Keyword Research
Performance Tracking
Competitor Intelligence
Fix Your Site’s SEO Issues in 30 Seconds
Find technical issues blocking search visibility. Get prioritized, actionable fixes in seconds.
Powered by data from
How Many Cyber Attacks Occur Each Day? (2025)
In 2024, there were 600 million cybersecurity attacks each day.
And the risk of cyberattacks has increased substantially in recent years due to AI and new technologies.
In this report, we'll cover the latest data on cybersecurity threats, the average cost of a data breach, and the ways cybercriminals look to steal organizations’ sensitive data.
Build a winning strategy
Get a complete view of your competitors to anticipate trends and lead your market
Top Cyberattack Statistics – Editor's Choice
- There are 600 million cyberattacks per day.
- Nearly 54 people per second fall victim to a cyber attack.
- Almost 6 in 10 businesses have suffered a ransomware attack this year.
- North America has seen a 8% increase in ransomware attacks this year.
- The average cost of a successful attack on an Internet of Things (IoT) device is more than $330,000.
- More than $6.3 billion was transferred in business email compromise scams in the past year.
- The largest recorded data breach compromised more than 3 billion user accounts.
How Many Cyberattacks Happen per Day?
Cyberattacks have become increasingly common in recent years.
The exact numbers vary massively depending on how you choose to define an attack. By Microsoft's estimates, there are 600 million cyberattacks per day.
The Identity Theft Resource Center (ITRC) Annual Data Breach Report recorded 3,205 cyberattacks leading to data compromises in 2024. This marks an increase from 2,365 in 2023, 1,584 in 2022, and just 754 in 2018.
That’s approximately 8.7 attacks per day. However, the number of victims is substantially higher: over 1.7 billion per year. That’s more than 4.6 million per day, or nearly 54 per second.
Source: ITRC Annual Data Breach Report, Microsoft
How Many Businesses Get Hacked Each Year?
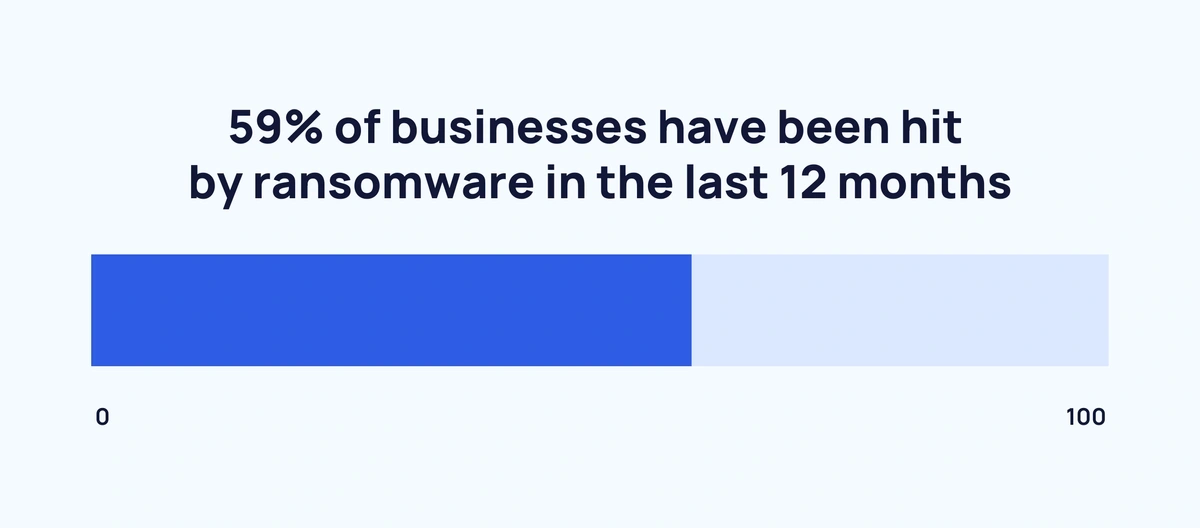
According to a 2024 Sophos study, 59% of businesses were hit by ransomware in the last 12 months. That’s a drop from a high of 66% in each of the previous two years.
In the UK, half of all businesses and 32% of charities report being targeted by some form of cyberattack within the past 12 months.
Source: Sophos, UK Government
Phishing Attack Statistics
Phishing and pretexting are among the most common types of cyberattacks.
(Pretexting is effectively a kind of phishing where attackers seek to build up a prior relationship of trust before trying to exploit it.)
There were more than 4,000 incidents of social engineering attacks last year, 87% of which were phishing or pretexting. 3,405 led to confirmed data disclosure.
55% of these phishing attacks were financially motivated, while 52% were driven by espionage. (Some overlap accounts for the mismatched percentages).
When phishing or pretexting leads to a transaction, the median amount is approximately $50,000. More than $6.3 billion was transferred in business email compromise scams in 2024.
As of Q4 2024, cybercriminals create nearly 1 million phishing sites per month – that's almost 7x as many as in Q2 2020.
Through these sites, cybercriminals send over 3.4 billion phishing emails per day.
Meanwhile, “vishing” (voice phishing) attacks increased by 442% in the second half of last year. That’s part of a wave of increasingly sophisticated AI cybercrime.
Sources: Verizon 2025 Data Breach Investigations Report, APWG, CrowdStrike
Malware Statistics
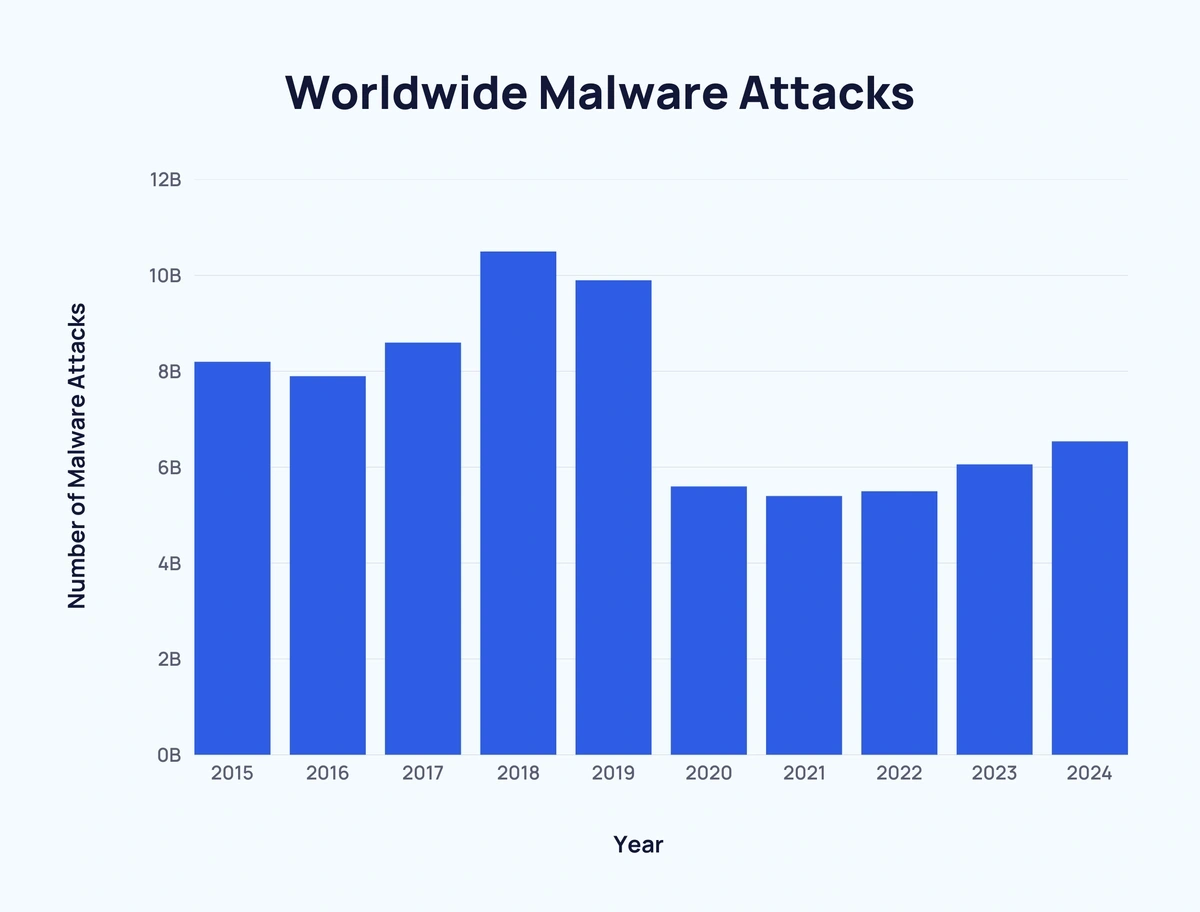
In 2024, there were over 6.5 billion malware attacks worldwide, up 8% year over year. The number of attacks has ranged from 5.4 billion to 6.54 billion between 2020 and 2024.
The single worst year for malware attacks over the last decade was 2018 (10.5 billion attacks).
Here's a breakdown of the number of malware attacks worldwide since 2015:
| Year | Number of Malware Attacks |
| 2015 | 8.2 billion |
| 2016 | 7.9 billion |
| 2017 | 8.6 billion |
| 2018 | 10.5 billion |
| 2019 | 9.9 billion |
| 2020 | 5.6 billion |
| 2021 | 5.4 billion |
| 2022 | 5.5 billion |
| 2023 | 6.06 billion |
| 2024 | 6.54 billion |
Encrypted threats increased by 93% in 2024, indicating that malware attacks are growing more sophisticated.
Ransomware Statistics
Ransomware has become one of the most pervasive and fast-growing threats to individuals and organizations worldwide. There are more than 300 million attacks per year.
Last year (2024), ransomware attacks increased by 8% in North America, and by 259% in LATAM.
The average ransomware payment is now $850,700. When factoring in downtime, recovery costs and related expenses, losses reach an average of $4.91 million.
Here's a look at the number of ransomware attacks per year since 2017:
| Year | Number of Ransomware Attacks |
| 2017 | 186.3 million |
| 2018 | 206.4 million |
| 2019 | 187.91 million |
| 2020 | 304.64 million |
| 2021 | 623.25 million |
| 2022 | 493.33 million |
| 2023 | 317.59 million |
North America currently receives the largest proportion of industrial ransomware attacks (43%).
Here's a breakdown of industrial ransomware attacks by region:
| Region | Distribution of Ransomware Attacks |
| North America | 43% |
| Europe | 32% |
| Asia | 14.4% |
| South America | 4.4% |
| Middle East | 2.5% |
| Africa | 1.5% |
| Australia | 1.5% |
Sources: SonicWall, WatchGuard, Dragos, SonicWall (2), SonicWall (3)
Cryptojacking Statistics
Cryptojacking is a form of cybercrime in which hackers use an individual or organization's computer system to mine cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin. While relatively new, the latest data indicates an uptick in unauthorized mining activities.
Criminals may initiate a cryptojacking attack in several ways, such as installing malicious software through an email attachment or infecting a webpage with JavaScript that launches the mining process when opened in a browser.
Two years ago, the volume of cryptojacking attacks in the first quarter alone reached 332.3 million. In 2025, cloud cryptojacking attacks are expected to rise by 20%.
Sources: SonicWall, Cloud Tweaks
IoT, DDoS, and Other Attacks
Internet of Things (IoT) attacks target connected devices to find vulnerabilities within networks.
There has been a 124% increase in IoT attacks in the past year.
And the average cost of a successful IoT device attack is more than $330,000.
IoT devices can also be turned into “zombies” for carrying out distributed denial of service (DDOS) attacks, flooding a target server with traffic in order to crash it.
There is an average of 125 DDOS attacks per week worldwide.
Sources: PSA Certified, World Economic Forum, Verizon 2025 Data Breach Investigations Report
Most Common Causes of Data Breaches in Cybersecurity
Of the 3,158 cyberattacks recorded in 2024 by the Annual Data Breach Report, 455 were phishing or related “social engineering” attacks. This made it the most common form of attack.
Ransomware accounted for 188 of the cyberattacks, roughly 6%. It was the second most common kind of attack in all four quarters of 2024.
Malware was the next most common cyberattack leading to a data breach. There were 48 recorded malware attacks last year.
“Zero-day attacks” and “credential stuffing” made up the majority of remaining classified cyberattacks.
A further 310 breaches were caused by system or human error without any malicious intent, while 33 came from physical attacks. But cyberattacks accounted for the vast majority of data breach victims.
It’s important to note that by far the largest group is “not specified”, where details of specific attack vectors have not been provided.
Source: ITRC Annual Data Breach Report
Cost of Cybersecurity
Cyberattackers have begun launching more advanced – and expensive – attacks in recent years.
Data breaches caused by malicious insiders come at the highest average cost to organizations, calculated at $4.99 million.
That’s closely followed by phishing and other business email compromise (BEC). Data breaches that come about in this manner cost an average of $4.88 million.
Data breaches from stolen or compromised credentials cost businesses an average of $4.81 million.
As of 2024, the average cybersecurity spending per employee is an estimated $52.16.
Cybersecurity Growth Rate
A US Bureau of Labor forecast indicates that information security analyst roles will increase by 33% through 2033. That’s much faster than average.
This will result in more than 17,000 openings each year.
The cybersecurity market is worth $202.9 billion. That’s projected to reach $271.9 billion by 2029 at a CAGR of nearly 8%.
Sources: US Bureau of Labor Statistics, Statista
Data Breach Statistics
There were 12,195 data breaches recorded in Verizon’s 2025 report.
The manufacturing, finance and healthcare sectors were among the hardest hit in terms of the number of breaches.
And healthcare breaches exposed the data of more than 198 million Americans, thanks in large part to the significant Change Healthcare breach.
Sources: Verizon 2025 Data Breach Investigations Report, Sonic Wall
Cybersecurity Risks
15.7 million encrypted attacks were recorded last year. There was a 30% increase in North America, but triple-digit percentage jumps were recorded in Europe, Asia and Latin America.
Legacy firewalls are often unable to detect these threats.
In total, 74% of CEOs are concerned about their organization’s ability to avert or minimize damage from cyberattacks.
Businesses of all sizes can be targeted by cyberattacks. However, given the typically financial motivations, large organizations are the most common targets.
47% of businesses with annual revenue of less than $10 million have been targeted by ransomware, compared to 59% of businesses with annual revenue between $250 million and $500 million. Among businesses making $5 billion or more, 67% have been targeted.
In the UK, across all kinds of cyberattack, 25% of small businesses and 43% of medium-sized businesses have been targeted in the last 12 months. In the same time frame, 52% of large businesses have identified breaches or attacks.
Sources: SonicWall, Accenture, Sophos, UK Government
Largest Data Breaches and Hacking Statistics
2024 saw a number of significant (and well-publicized) cyberattacks, and that trend has continued into 2025. Some of the biggest attacks have occurred in the telecoms and healthcare industries.
Change Healthcare Hack
In February 2024, the cybercrime group known as BlackCat/AlphV staged a ransomware attack against Change Healthcare (part of United Healthcare, a large organization with annual revenues of $370 billion).
Handling 15 billion healthcare transactions annually, Change Healthcare counts the US military among its service users. The hack caused difficulties in filling prescriptions and collecting payments from insurers.
Change Healthcare filed an 8-K report to the SEC, attributing the attack to a “nation-state associated cyber security threat actor.” It ultimately paid a $22 million ransom.
AT&T Breach
In March 2024, telecoms giant AT&T confirmed that customer data had been released on the dark web. Personal records including social security numbers were compromised.
The actual breach appeared to be from 2019 or earlier. Around 7.6 million current customers and more than 65 million former customers were impacted.
Ascension Attack
In another instance of a healthcare provider being targeted, Ascension suffered an attack in May 2024 after an employee inadvertently downloaded malware. It forced the organization to divert emergency care from some of its hospitals.
Ascension confirmed that there is evidence of data being stolen.
M&S, Co-op and Harrods Hacks
In April 2025, UK retail giant M&S confirmed that customer data had been accessed in a cyberattack.
The retailer admitted that some payment information may have been stolen, although detailed card data was masked, and therefore unusable. No password information was stolen, although customers were prompted to change their logins.
Two more British stores, Harrods and the Co-op, were affected by attacks at the same time, with cybercrime group Scattered Spider linked to the intrusions.
The retailers elected to restrict or shut down their computer systems, causing significant disruption to in-store and online sales. But the attempt to upload ransomware was ultimately unsuccessful.
Sources: BCS, CRN, Cybersecurity Dive, BBC
Historic Data Breaches
According to ArcticWolf, the “modern history of cybercrime” began in 1962, when Allen Scherr stole passwords from an MIT database via punch card.
Since then, cybercriminals have moved with the times, ramping up their efforts and impacting major corporations, government organizations and social media platforms.
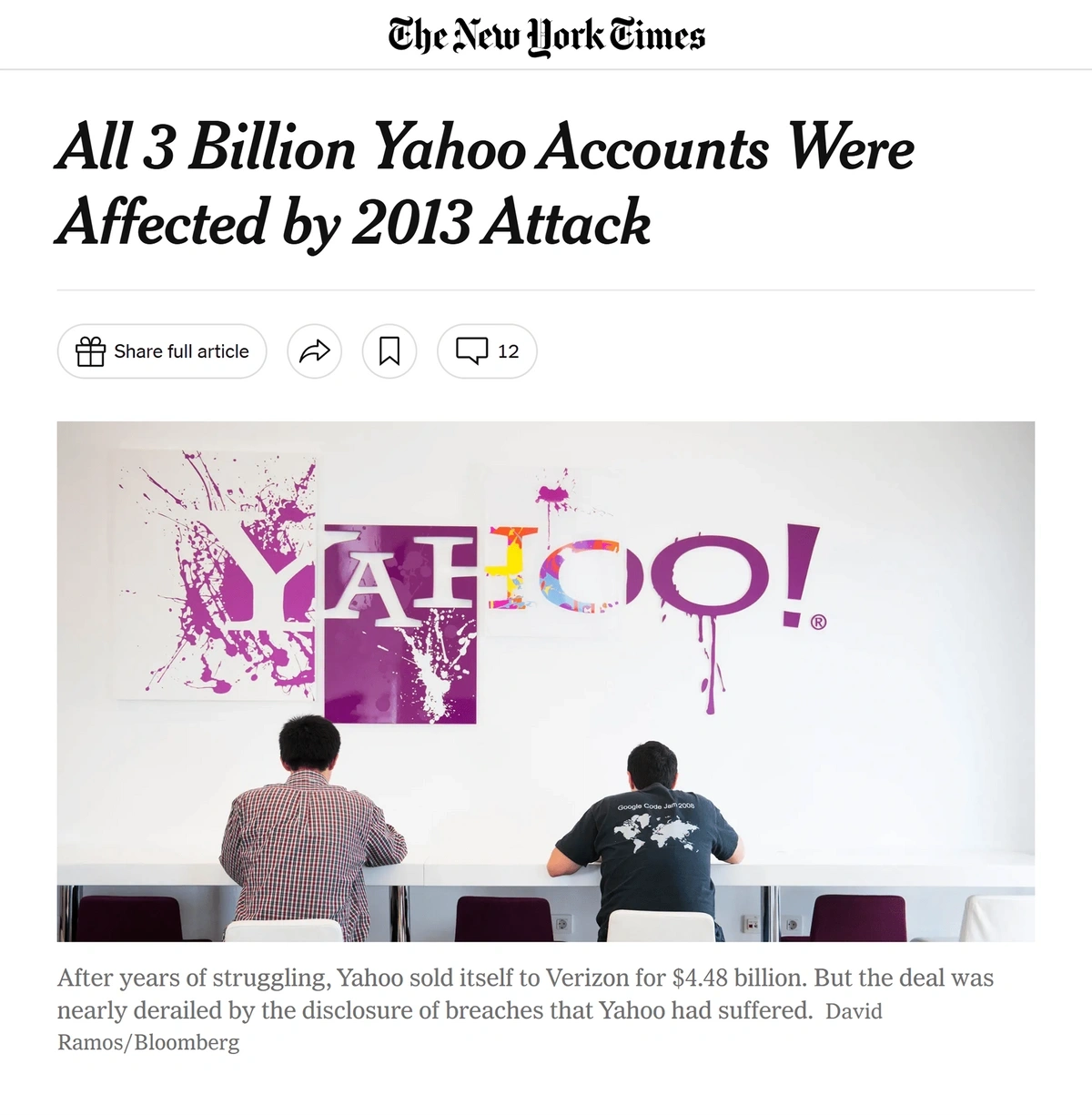
For example, the Wannacry virus affected thousands of groups worldwide, resulting in $4 billion or more in costs. The biggest data breach in history occurred at Yahoo in 2013, with in excess of 3 billion user accounts exposed.
Notable Breaches:
- A security breach that exposed the information of more than 339 million guests came to light at Marriott in 2018.
- A 2020 Twitter (now X) breach accessed accounts of former presidents and world figures like Elon Musk and BIll Gates, promoting a cryptocurrency scam that netted $120,000 in a matter of hours.
- In 2016, hackers stole the information of more than 57 million Uber drivers and customers.
- In 2015, the Pentagon was forced to take an email system used by the Joint Chiefs of Staff offline after a phishing attack that was traced to Russia compromised the details of thousands of military and civilian personnel.
Sources: Arctic Wolf, New York Times, The Hacker News, Uber, CBS
Cybersecurity Job Statistics
The cybersecurity space continues to grow. 75% of organizations within the industry expect to recruit more permanent staff this year.
There are roughly 5.5 million global cybersecurity professionals, yet more than 7 in 10 businesses have vacant cybersecurity positions.
In the public sector, 52% of organizations cite resources or skills gaps as the “biggest challenge” when designing for cyber resilience.
The median wage for an information security analyst is $124,910.
Sources: Barclay Simpson, World Economic Forum, US Bureau of Labor Statistics, Cybercrime Magazine
Conclusion
There's no doubt about it: cyberattacks have become an increasing concern for major organizations, small businesses, and individuals.
With data showing that the cybersecurity industry will be worth more than $270 billion within the next five years, it pays to invest in training, tools, and professionals to protect sensitive information from cybercriminals.
For more related content, check out Huge Cybersecurity Trends, Top Cybersecurity Startups to Watch, AI Cybersecurity Trends, Scam Statistics and The Ultimate List of Cybersecurity Statistics.
Stop Guessing, Start Growing 🚀
Use real-time topic data to create content that resonates and brings results.
Exploding Topics is owned by Semrush. Our mission is to provide accurate data and expert insights on emerging trends. Unless otherwise noted, this page’s content was written by either an employee or a paid contractor of Semrush Inc.
Share
Newsletter Signup
By clicking “Subscribe” you agree to Semrush Privacy Policy and consent to Semrush using your contact data for newsletter purposes
Written By


James is a Journalist at Exploding Topics. After graduating from the University of Oxford with a degree in Law, he completed a... Read more