Get Advanced Insights on Any Topic
Discover Trends 12+ Months Before Everyone Else
How We Find Trends Before They Take Off
Exploding Topics’ advanced algorithm monitors millions of unstructured data points to spot trends early on.
Keyword Research
Performance Tracking
Competitor Intelligence
Fix Your Site’s SEO Issues in 30 Seconds
Find technical issues blocking search visibility. Get prioritized, actionable fixes in seconds.
Powered by data from
24+ Fascinating BYOD Statistics (2024)
BYOD (bring your own device) is a workplace trend where employees use their own desktops, tablets, and smartphones instead of employer-provided devices.
In a time when most working-age American adults own a smartphone, BYOD seems like a logical next step. It boosts productivity, gives employees more freedom, and saves companies money.
But there are drawbacks to BYOD. When employees access sensitive company data on their own devices, cybersecurity risks abound. Existing risks like data leaks, malware, and other threats are an even greater concern when BYOD enters the picture.
So what is the state of BYOD in 2024? Keep reading to find out.
Want to Spy on Your Competition?
Explore competitors’ website traffic stats, discover growth points, and expand your market share.
Top BYOD Statistics
Before jumping into the full list of stats, here are the top 6 bring your own device statistics to get you started:
- The BYOD market is worth nearly $100 billion.
- 82% of organizations have a BYOD program.
- 68% of organizations see a jump in productivity after switching to BYOD.
- Companies that switch to BYOD smartphones can save up to $341 per employee.
- Data loss is the #1 security concern surrounding BYOD.
- 45% of employees don’t change their passwords after a data breach.
We cover more of the top BYOD stats below.
General BYOD Statistics
Today’s work environments fall into three categories: 100% work-issued devices, 100% BYOD, or hybrid environments that combine the two. Here’s a look at how the broader business world approaches BYOD.
The BYOD market is worth an estimated $98.8 billion (Research and Markets)
According to the latest data, the global BYOD and enterprise mobility market is currently worth $98.8 billion.
By 2026, that figure is expected to hit $157.3 billion — good for a 16.7% CAGR. In the US market alone, the BYOD and Enterprise Mobility market is worth over $26 billion.
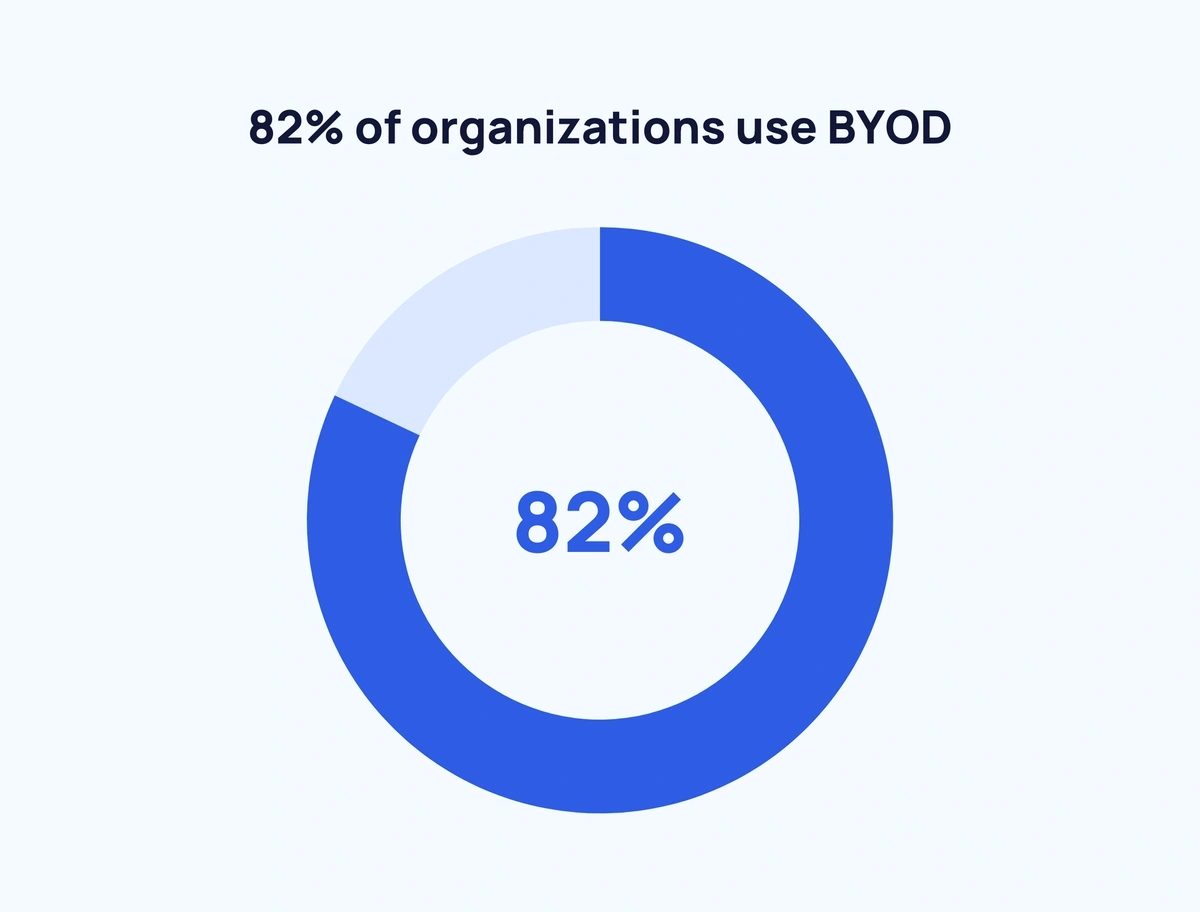
In total, 82% of organizations currently use BYOD (Cybersecurity Insiders)
A survey of 271 cybersecurity professionals found that 70% of organizations have employees bring their own devices into the workplace.
But BYOD goes beyond typical employees. BYOD applies to contractors (26% of organizations), partners (21%), customers (18%), and suppliers (14%) as well.
82% of IT senior executives feel that smartphones are important to employee productivity and help with fast decision-making (Samsung)
Over three-quarters of executives believe mobile helps improve customer service, innovation, and collaboration.
61% of organizations expect employees to have remote availability — even if they don’t provide a company phone (Samsung)
31% of IT executives say their organizations are fully BYOD when it comes to mobile. One of the motivators behind having employees use their own mobile devices is cost — companies can save over $300 each year per employee with a mobile BYOD program.
Only 15% of companies currently provide employees with a work-issued smartphone (Samsung)
46% of organizations take a hybrid approach — they issue smartphones to some employees, while others use BYOD. The remaining 39% are fully BYOD and don’t issue smartphones to any employees.
Companies can save $341 per employee by switching from work-issued to BYOD smartphones (Samsung)
Companies spend an average of $1234 per year for each employee when they use work-issued smartphones. Costs include the phone itself ($212), monthly service plans ($504), software ($60), and management ($458). With BYOD, that average cost drops to just $893 per year.
68% of organizations see a jump in productivity after enabling BYOD (Cybersecurity Insiders)
Productivity isn’t the only way companies benefit from BYOD. 53% of organizations see increased employee satisfaction, 45% have their overall costs lowered, and 7% improve employee mobility.
30% of IT organizations plan to explore “bring your own enhancement” (BYOE) (Gartner)
Wearable devices and augmented reality have already arrived in the workplace, and experts predict more companies will jump on board. Even back in 2016, almost one-quarter of companies said they planned on implementing wearables in the workplace. Like other BYOD devices, enhancement devices can create potential security concerns for IT departments.
BYOD User Stats
BYOD is all about giving employees the freedom to use their own devices at work. What does that look like from the employee's perspective? These stats are all about BYOD from an employee’s perspective.
The average employee uses 2.5 devices for work (Beyond Identity)
Of employees who use technology as part of their job, 97% regularly use either a desktop or laptop device and 66% use smartphones for work. Tablets have significant usage too, with over 24% of employees reporting using them on a regular basis.
85% of Americans own a smartphone (Pew Research)
Smartphone ownership is constantly increasing in the United States. In 2011, just 35% of Americans owned a smartphone. Today, over 95% of Americans in the 18-49 demographic own a smartphone, and they’re bringing those devices to work.
3 in 4 people claim smartphones aid productivity (Google)
Letting employees use their own smartphones at work could lead to a number of benefits. 60% of people say their smartphones help them feel more confident and prepared.
Employees gain 58 minutes of work time each day when they use smartphones to get work done (Samsung)
That’s over 240 hours per year. Employees who use their smartphones for work tasks can boost their efficiency by up to 34% according to research by Samsung and Frost & Sullivan. The research also found that the larger the organization, the more smartphones can improve productivity.
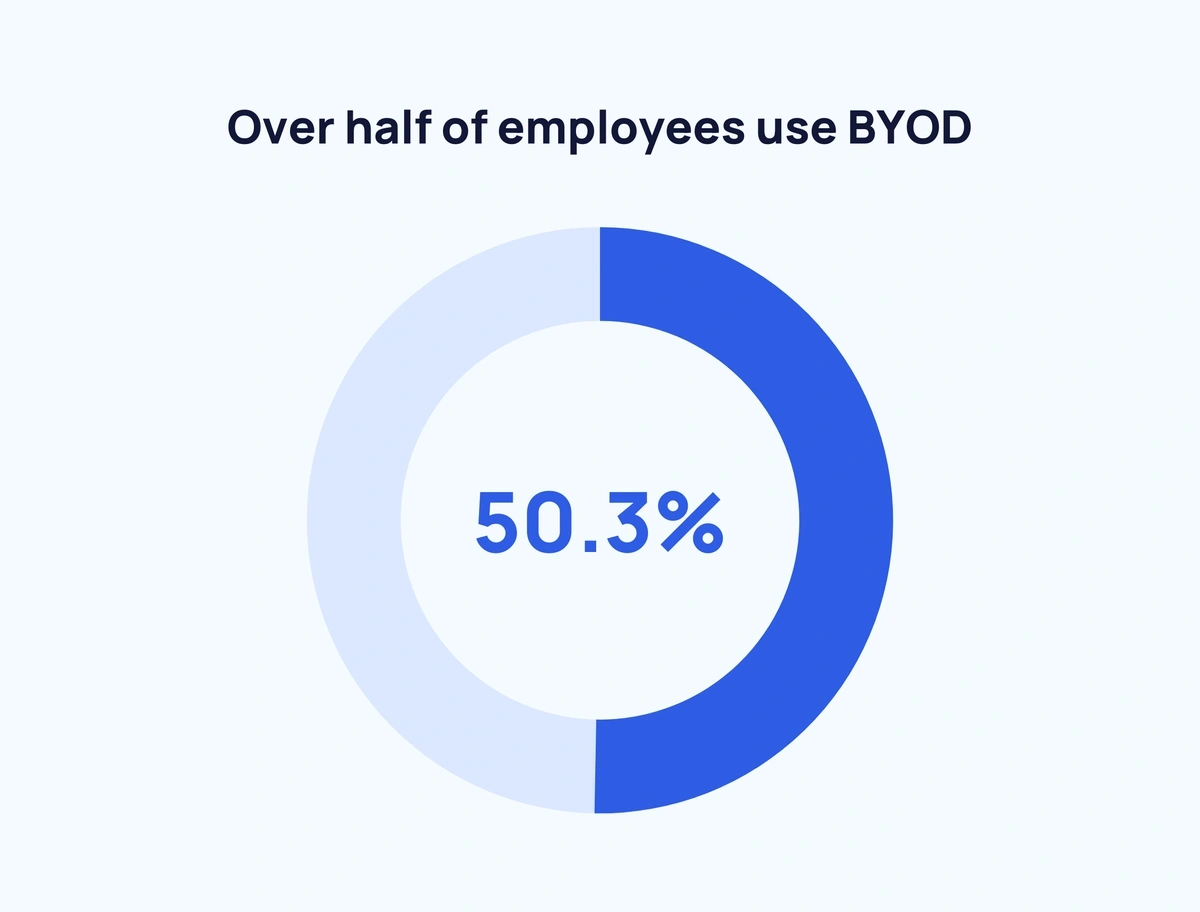
50.3% of employees use BYOD (Beyond Identity)
A survey of over 1,000 employees who use tech at work found that 49.7% used only employer-provided devices. 36.1% used a combination of company and personal devices. 14.4% said they only use personal devices at work.
4-in-5 employees would rather have separate devices for work and personal use (Beyond Identity)
Despite the high adoption rate of BYOD, the vast majority of employees would prefer to keep their work away from their personal devices. Only 19.3% say they’d rather use a single device for work and personal use.
Over half of employers let their employees choose between company-provided and personal devices (Beyond Identity)
50.3% of employees say their employer lets them decide if they want to bring their own devices to work. 49.7% say they don’t have a say in the matter.
48% of users believe BYOD adoption would increase if IT departments didn’t have access to their devices (Cybersecurity Insiders)
When asked what would happen if IT couldn’t view or alter personal data in their devices, 20% of the 271 survey respondents said they expected BYOD adoption to increase dramatically. 28% said they expected it to increase somewhat, while 33% said there would be little to no change.
20% of organizations don’t provide support for employees who bring their own devices to work (Cybersecurity Insiders)
25% provide “ad hoc” support — which means IT departments will assist employees in an informal or unofficial capacity. 26% only provide support for company-approved devices. Only 22% of organizations provide full BYOD support to their employees.
BYOD Security Stats
BYOD’s benefits are easily understood. Cost-cutting, improving employee efficiency and satisfaction are all reasons to implement BYOD in an organization. But there’s one serious roadblock: security. How to keep hundreds — or thousands — of personal devices secure in the workplace is something IT departments are still grappling with.
Security is the biggest concern related to implementing BYOD (Cybersecurity Insiders)
Around 30% of organizations cite security concerns as the number one thing holding them back from adopting BYOD. It’s not just management that has those concerns either. 15% of organizations cite employee concerns about security as a barrier to implementation.
Data loss is the #1 security concern surrounding BYOD (Cybersecurity Insiders)
Cyberattacks are on the rise. Unfortunately, BYOD programs can make them more likely. In fact, 62% of cybersecurity professionals cite data loss and leaks as their top BYOD-related concerns. Here are some other top BYOD security worries:
- Users downloading unsafe content or apps (54%)
- Lost or stolen devices (53%)
- Unauthorized access to company data and systems (51%)
- Malware (51%)
- Vulnerability exploits (48%)
- Inability to control endpoint security (45%)
Companies like CrowdStrike help businesses using BYOD by protecting users against data breaches and other cyberattacks.
45% of employees don’t change their passwords — even after a data breach (LastPass)
Even though 79% of employees say they’re aware that compromised passwords are a huge security threat, 51% say they rely on their memories for passwords. On top of that, 65% say they typically use different variations of the same password.
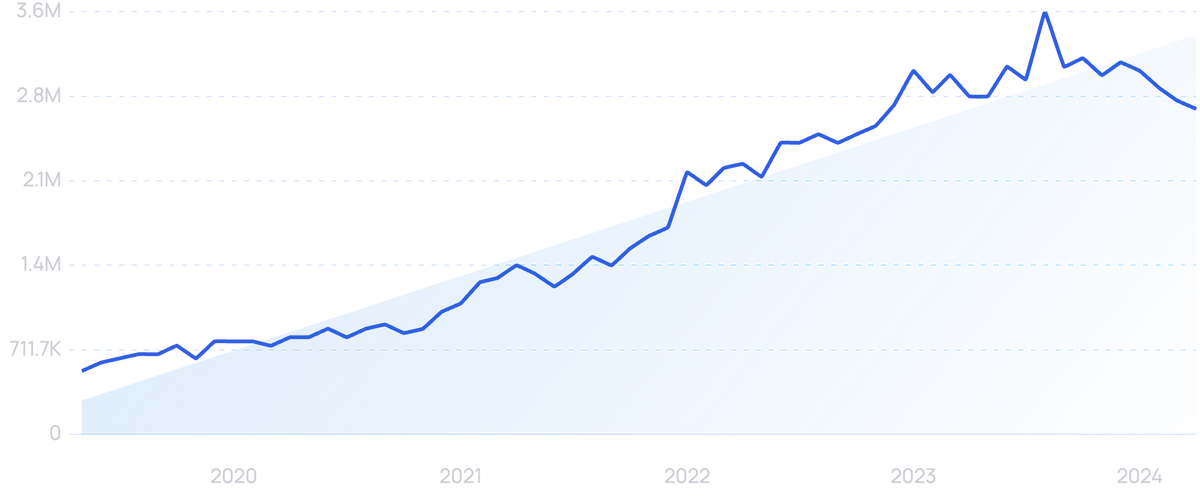
Google searches for “password manager” over the past 5 years.
30% of organizations have zero visibility or control over employees’ mobile messaging (BitGlass)
41% of organizations have control over file sharing on employee-owned devices and 37% have control over cloud-connected apps. 28% of companies have visibility over messages employees send across private and public channels.
Almost 3 in 4 organizations have visibility over employee emails on BYOD devices (BitGlass)
Email accounts, contact lists, and file-sharing apps are common areas for data leaks on BYOD devices. While most companies keep tabs on employee emails, they lag behind in other critical areas.
Only 57% of companies have visibility over calendars and contact lists, and just 50% have visibility over messaging apps. Less than half of organizations monitor file sharding, cloud backups, and document editing on employee-owned devices.
22% of organizations say their employees’ BYOD devices have downloaded malware over the past 12 months (Cybersecurity Insiders)
Nearly half (49%) of organizations either aren’t sure or can’t disclose if employees have downloaded malware on private devices at work. 30% of organizations don’t have protocols in place to protect their employees’ devices from malware, and 41% rely on endpoint malware protection.
22% of organizations say their employees’ devices have connected to malicious WiFi over the past year (Cybersecurity Insiders)
51% of organizations don’t know whether or not their employees are connected to malicious WiFi on their private devices while at work.
Wrap Up
Bringing your own devices to work isn’t a new concept, but the rise of smartphones has made BYOD or hybrid approaches the de facto work model.
And while the majority of employees seem to enjoy the extra freedom and productivity BYOD brings to the table, IT departments are more cautious. Finding the best way to keep corporate data and user devices secure is a work in progress.
For the BYOD industry, that means there’s still plenty of room for growth as new solutions are sure to revolutionize the BYOD security world. If you'd like to see more up-and-coming technology trends, check out our recent report: Workplace Trends to Watch.
Stop Guessing, Start Growing 🚀
Use real-time topic data to create content that resonates and brings results.
Exploding Topics is owned by Semrush. Our mission is to provide accurate data and expert insights on emerging trends. Unless otherwise noted, this page’s content was written by either an employee or a paid contractor of Semrush Inc.
Share
Newsletter Signup
By clicking “Subscribe” you agree to Semrush Privacy Policy and consent to Semrush using your contact data for newsletter purposes
Written By


Josh is the Co-Founder and CTO of Exploding Topics. Josh has led Exploding Topics product development from the first line of co... Read more