Get Advanced Insights on Any Topic
Discover Trends 12+ Months Before Everyone Else
How We Find Trends Before They Take Off
Exploding Topics’ advanced algorithm monitors millions of unstructured data points to spot trends early on.
Keyword Research
Performance Tracking
Competitor Intelligence
Fix Your Site’s SEO Issues in 30 Seconds
Find technical issues blocking search visibility. Get prioritized, actionable fixes in seconds.
Powered by data from
6 Super Important IT Trends for 2024-2027
You may also like:
The global information technology (IT) market is estimated to be worth over $5 trillion.
It’s fair to say that information technology is more important to the global business community than ever.
But thanks to emerging technology, the IT space is also changing faster than ever.
To learn more about changes impacting the IT space, read our list of trends below.
1. New IT Initiatives Change How Data is Processed and Stored
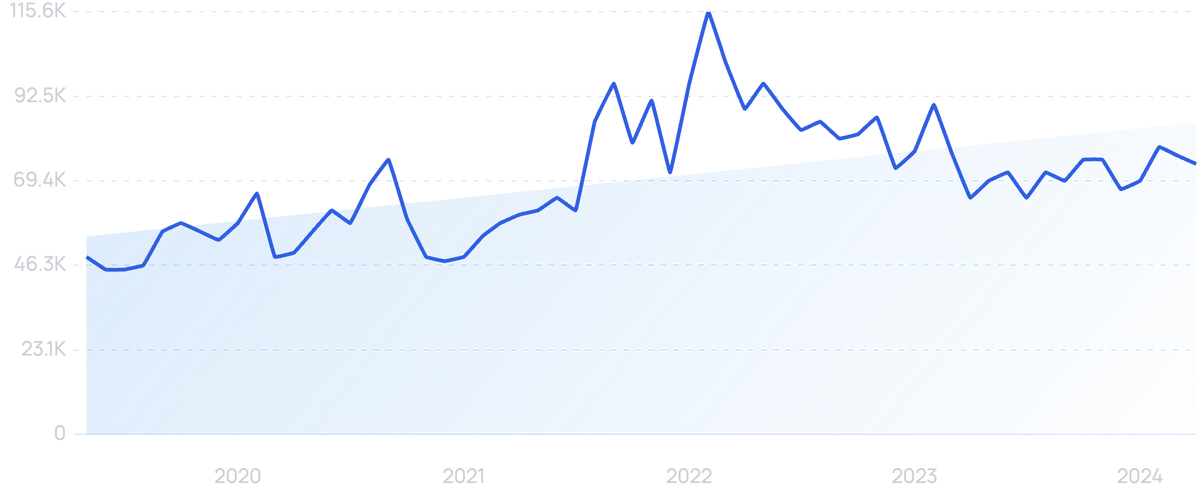
Edge computing is a form of distributed computing where computation and data storage take place closer to the end user.
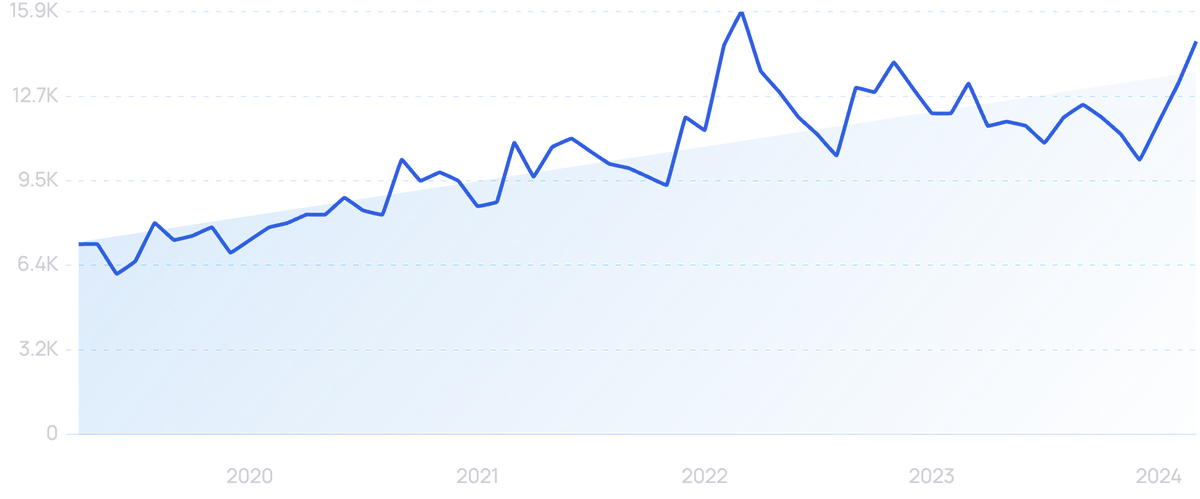
Searches for "Edge Computing" have increased by 74% over the past 5 years.
As more data is processed and stored each day, it is becoming difficult to process data that is located in far-off data centers.
Edge computing looks to solve this by using smart objects and network gateways to process and store data near the end user’s location.
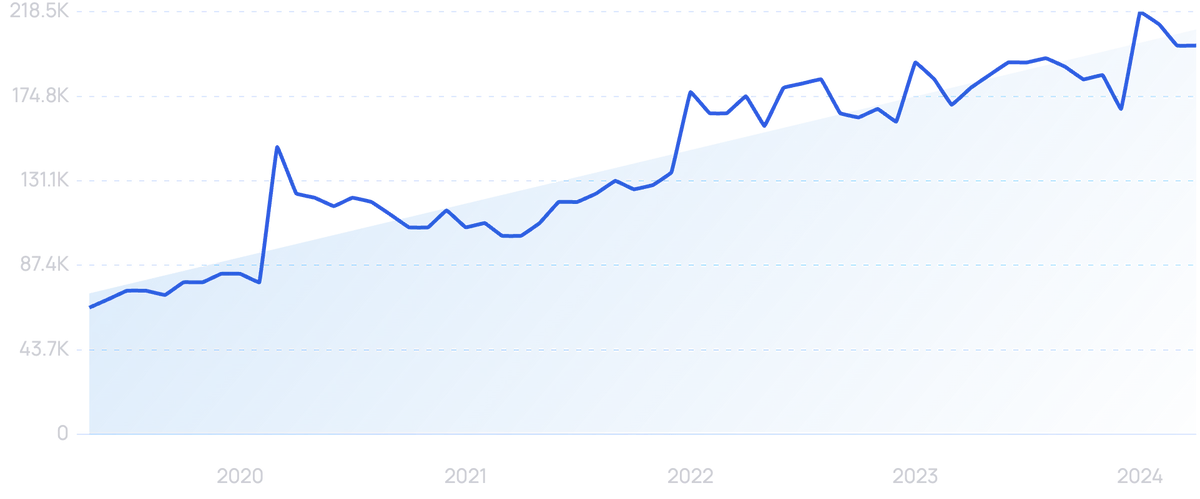
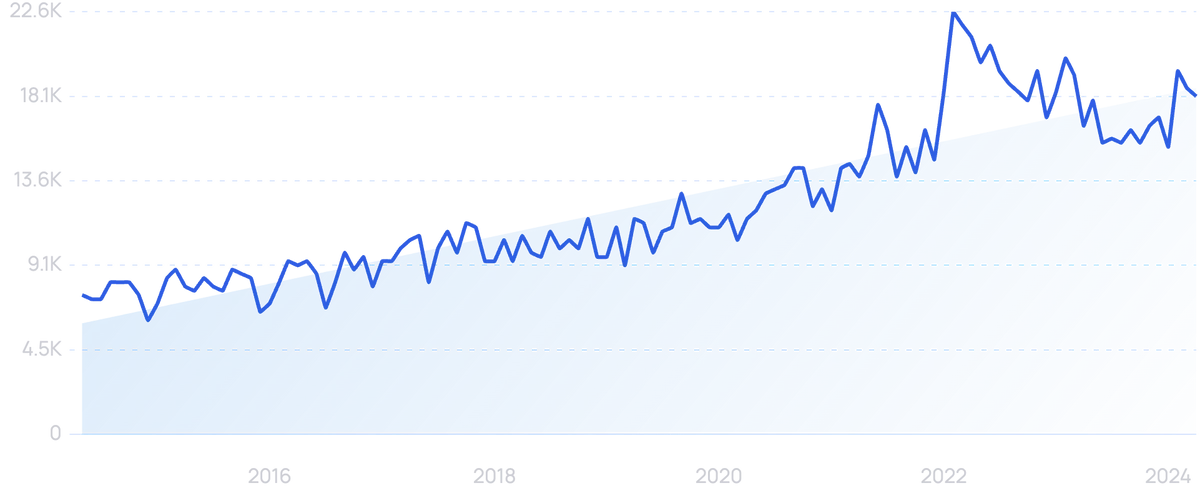
The rise of remote work, as well as the growth of IoT and smart devices, has pushed this market forward.
Searches for "remote work" are up 207% over 5 years.
IDC predicts that the workforce impacts of COVID-19 will be responsible for 80% of edge computing investment over the next few years.
Overall, the edge computing market is expected to reach $250.6 billion in 2024.
In fact, IDC expects that more than 90% of new organizational operating procedures will be deployed on an edge computing network in 2024.
That’s compared to less than 20% today.
In addition, edge computing has the potential to capture much more useful data than current infrastructures.
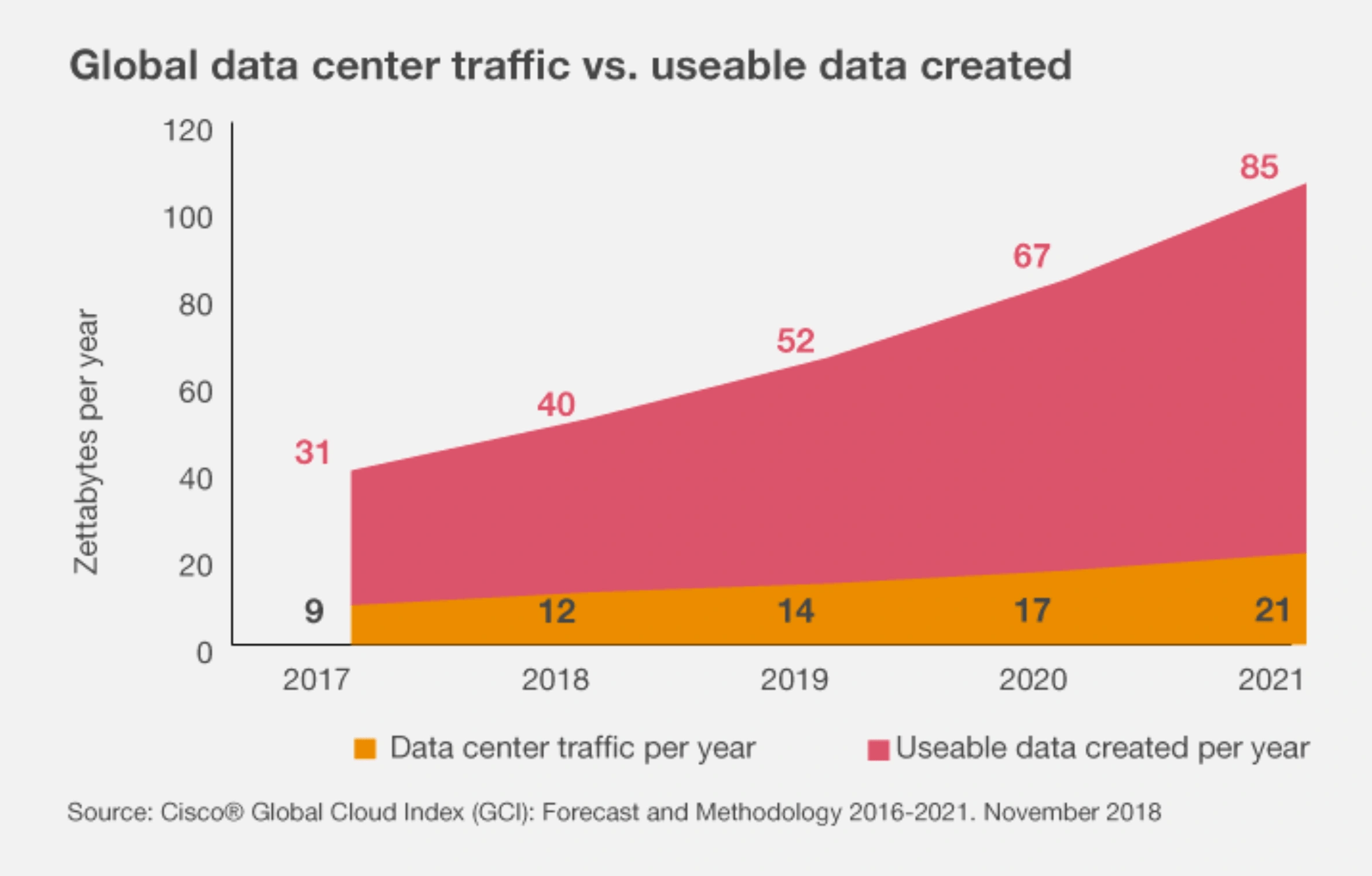
It’s estimated that 85 zettabytes of useful data was be created in 2021. But only a small percentage of that data will be captured by data centers.
Only a fraction of usable data is captured by data centers.
Edge computing can help close this gap.
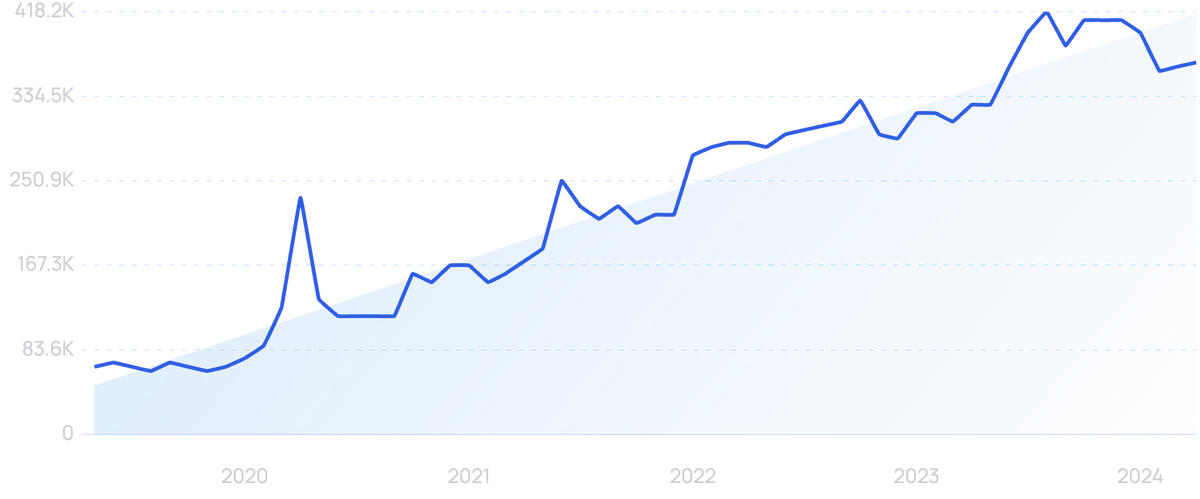
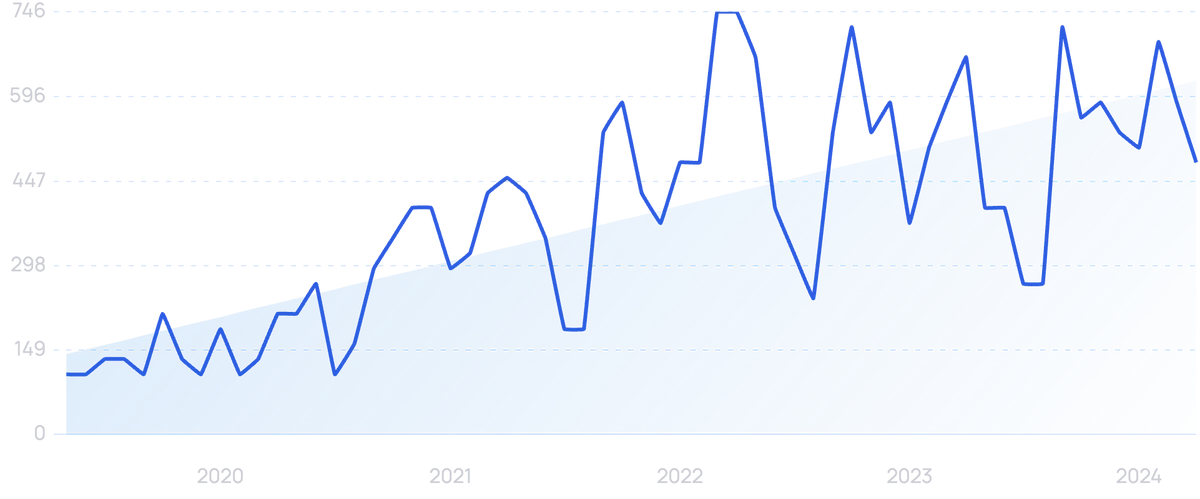
As 5G and the IoT proliferate, devices close to the data source can capture and process a larger portion of the new data that is created.
Searches for "5G" have increased by 450% over the last 5 years.
In addition, local edge data centers are being built to help with the increasing glut of data.
There are currently around 2.5 million edge servers deployed.
This figure is predicted to nearly double in 2024.
PwC also predicts that in 2024 the global market for edge data centers will have tripled to $13.5 billion.
The edge computing movement is directly related to the rise of distributed cloud infrastructure.
Search interest in "Distributed Cloud" is up 120% in 5 years.
Distributed cloud computing takes the geographical location of data centers into account.
A customer’s data is stored, processed, and transferred from different locations to increase the efficiency of the network.
In the past, the geographical location of the end user wasn't super relevant.
But, as discussed above, increasing data and network traffic make it more difficult to move large quantities of data to the public cloud.
And considering companies are literally paying Amazon to haul their data centers by truck, it looks like the distributed cloud could solve some serious problems.
Gartner predicts that in 2024 most cloud service providers will offer some form of distributed cloud services.
2. Rising Cyberattacks Highlight the Importance of Cybersecurity
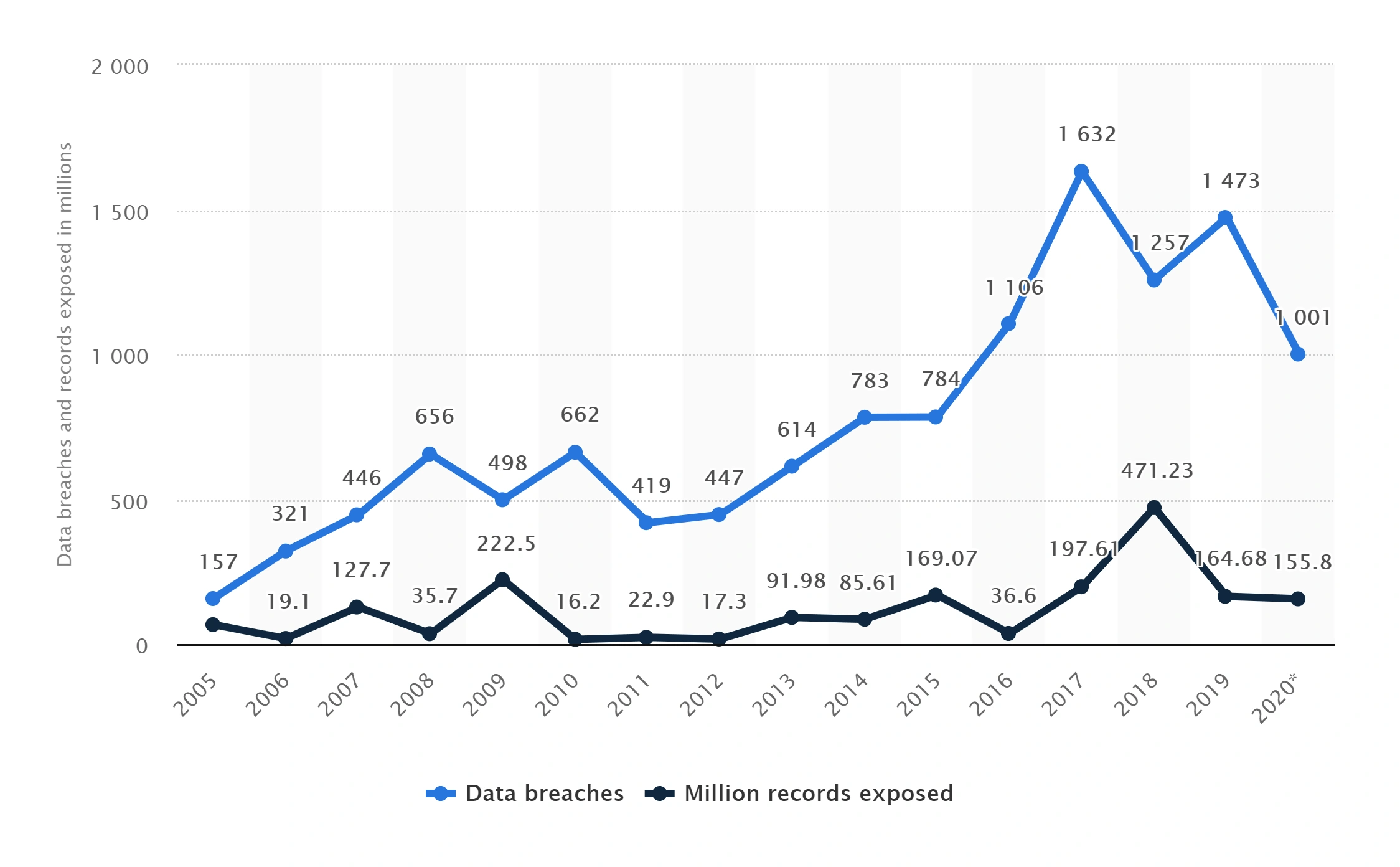
Data breaches in the US have been steadily rising over the last 15 years.
Number of Data Breaches and Records Exposed Annually in the US.
In its 2020 Data Breach Investigations Report, Verizon found that 3,950 data breaches occurred around the globe in 2020.
That’s 96% more data breaches than in 2019.
In fact, it’s estimated that cybercrime is costing the global economy $16.4 billion a day.
And as the 2020 SolarWinds hack shows, the IT industry is highly susceptible to cyberattacks.
To combat this, spending on cybersecurity services was expected to increase by 10% to over $60 billion in 2020.
Search interest in “Cybersecurity” has risen by 214% over 5 years.
A PwC study also found that over half of corporate executives expected to expand their cybersecurity budgets and increase their cybersecurity staff in 2021.
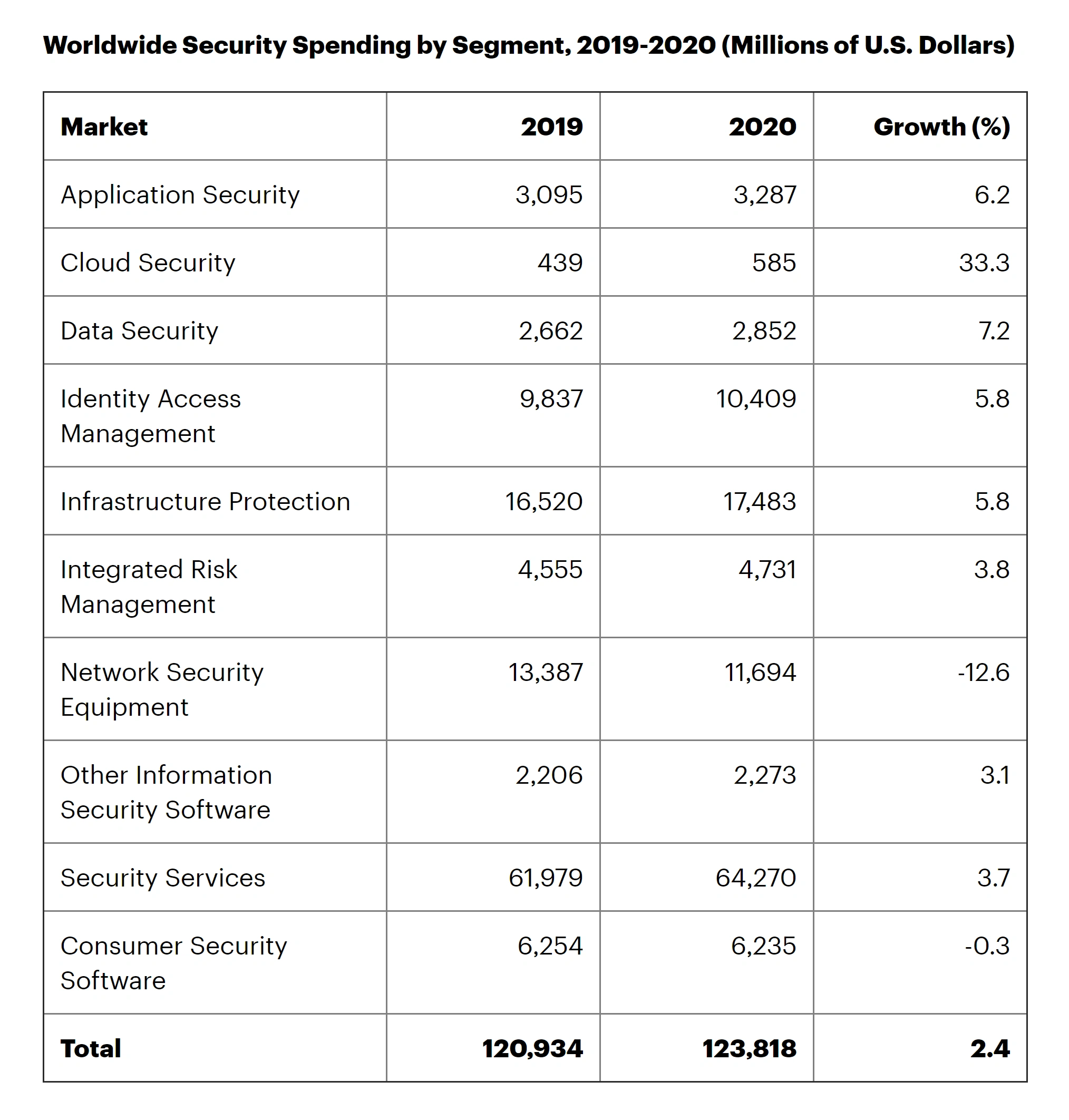
Source: Gartner
As you can see from the chart above, roughly 85% of total spending goes toward four segments: Security Services, Infrastructure Protection, Network Security Equipment, and Identity Access Management.
According to Statista, the total cybersecurity market (including services, software, hardware, etc.) is now worth $166.2 billion.
The fastest-growing markets, however, are Data Security and Cloud Security.
This makes sense, considering that largely thanks to digital transformation initiatives, 92% of enterprises are now using some form of cloud technology.
And as data storage changes, so must data and network protection.
Cybersecurity mesh is one of the most innovative new ways that companies are protecting their networks and data.
The cybersecurity mesh concept essentially seeks to develop security protocols that can prevent exposure at every single entry point of a network.
If there is some kind of breach, the cybersecurity mesh system should be able to prevent the bad actor from gaining access to other parts of the network.
Visual of the cybersecurity mesh approach (Stefanini).
This is compared to the traditional perimeter-based approach, where security systems seek to protect the entire “walled-city” of devices and users.
If one entry point is compromised at a certain level of the network in this system, the entire network could be compromised.
This approach is especially important as corporate teams become more decentralized.
Companies can’t control how employees and others access their network, so it’s important to focus security around each access point or potential user.
Gartner predicts that in five years, over 50% of all digital access control requests will be supported by cybersecurity mesh.
Cybersecurity mesh is part of a larger cybersecurity movement, known as “zero-trust security”.
Searches for “Zero Trust” have jumped by 725% in 5 years.
Zero-trust security systems like cybersecurity mesh are witnessing rapid adoption.
Over half of all cybersecurity decision-makers planned to implement some kind of zero-trust security system in 2020.
3. IT Spending Shifts to the Cloud
Much of the IT market is now directly tied to the cloud.
As a result, remote “as a service” models are proliferating.
The Software as a Service (SaaS), Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Artificial Intelligence as a Service (AIaaS), and Platform as a Service (PaaS) markets are growing at a significant rate.
Search growth for "SaaS" over 10 years.
Today, many companies have their entire IT infrastructure on the public cloud.
In fact, 59% of tech executives said that they expect most or all of their IT environment to be in the cloud next year.
And ICD predicted that in 2021, 80% of enterprises would switch to a cloud-based IT infrastructure twice as fast as they did before COVID-19.
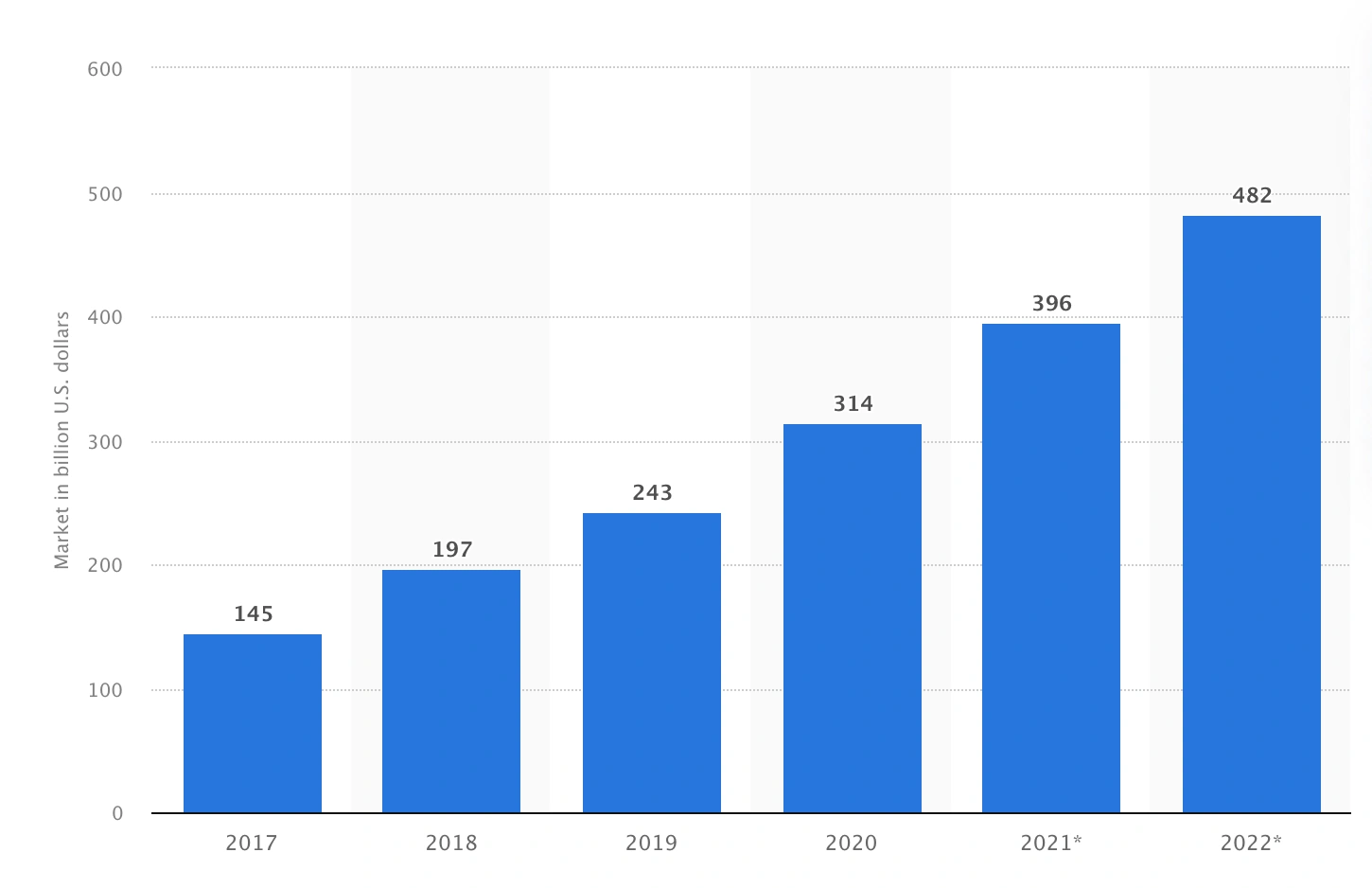
According to Statista, the public cloud services market was worth $314 billion at the end of 2020. And was predicted to hit $482 billion in 2022.
Source: Statista
The largest segment of the cloud services market is the traditional SaaS market, at just over $100 billion in 2020.
Software as a Service allows companies to take advantage of software that is developed and maintained in another location.
The customers simply pay a subscription. There’s no need for on-premises installation or updates.
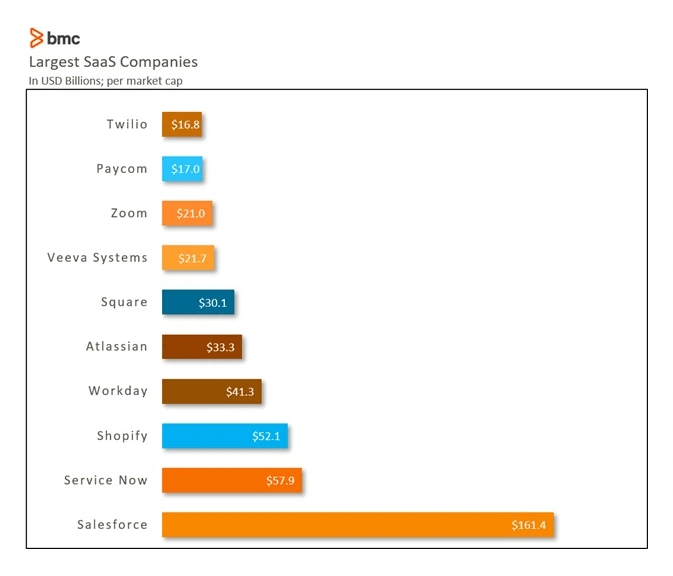
The largest pure-play SaaS provider is Salesforce.
Source: BMC
But competition in this space is growing extremely fast.
Twilio’s revenue grew by 9% year-over-year in 2023. And Shopify’s grew by 12%.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) is the second largest segment, at $64 billion.
The IaaS market is predicted to be worth roughly $110.5 billion in 2024.
Search interest for "Infrastructure as a Service" is up 107% over 10 years.
The advent of the IaaS market has seriously changed how IT infrastructure is handled.
In the second quarter of 2020, spending on public cloud IT infrastructure surpassed on-premises IT infrastructure spending for the first time.
Gartner also shows that IT spending on traditional data center systems shrank by 10% in 2020.
The largest IaaS vendors are the three largest public cloud providers: Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Compute Edge.
As of 2019, AWS controlled roughly 45% of the total IaaS market.
The next largest competitor, Microsoft Azure, captured about 17.9%.
The Platform as a Service (PaaS) market accounts for just over 15% of the overall cloud services market.
PaaS consists of cloud computing services that allow customers to develop, launch, and run an app on a cloud-based platform, instead of developing it using in-house tools.
Search interest in "Platform as a Service" has risen by 142% over the past decade.
The PaaS market was estimated to be worth $59 billion in 2020. And grew to approximately $80 billion in 2021.
The growth isn’t expected to stop anytime soon.
According to Statista, the PaaS market is worth almost $101 billion.
In the PaaS market, the three largest cloud providers and IBM control over 50% of the PaaS market share.
In addition to the three “as-a-service” categories listed above, IT services are also being productized.
IT as a Service (ITaas) allows enterprise IT service providers to deliver traditional IT services through a subscription-based model.
ITaaS doesn’t necessarily have to be a cloud offering. Many times, on-premises work is still necessary.
The ITaaS instead allows enterprises to completely outsource and reliably estimate IT spending without needing to do things like invest in a native data center.
4. The Internet of Behaviors Takes Advantage of New Data
We’re all familiar with the Internet of Things (IoT).
But there’s a new IT trend that you may not have heard of:
It’s called the Internet of Behaviors (IoB).
Searches for "Internet of Behaviors" over the last 10 years.
The IoB interprets the data collected by the IoT. It then uses this data to influence customer (or employee) behavior.
And the IoB model is quickly gaining traction.
Gartner predicted that in 2023, 40% of people worldwide would be influenced by the IoB.
That’s equivalent to roughly 3 billion people.
The growth of the IoT market (estimated $1.4 trillion by 2027) along with the adoption of edge computing will allow for more data collection and storage than ever before.
And advances in AI and big data will help organizations process the massive amount of behavioral data being collected.
This will only increase the influence of the IoB over people’s lives.
And while there may be benefits, many people are also focused on the risks.
A survey by the Internet Society found that 63% of people think it’s “creepy” that IoT devices are constantly collecting data on them.
In addition, the Economist Intelligence Unit polled 1,600 consumers to find that 92% of them want control over their own data.
So, as the IoB continues to grow, expect increasing social and regulatory pushback.
5. The Role of The CIO Expands
Chief Information Officers (CIOs) are typically the leaders of IT departments.
Because they oversee information technology, rapid change is something they are used to dealing with.
And as things like ITaaS gain acceptance, new data indicate that the role of the CIO is changing faster than ever.
CIO’s 2021 State of the CIO report found that 82% of CIOs said they had implemented some new form of technology or methodology because of the pandemic.
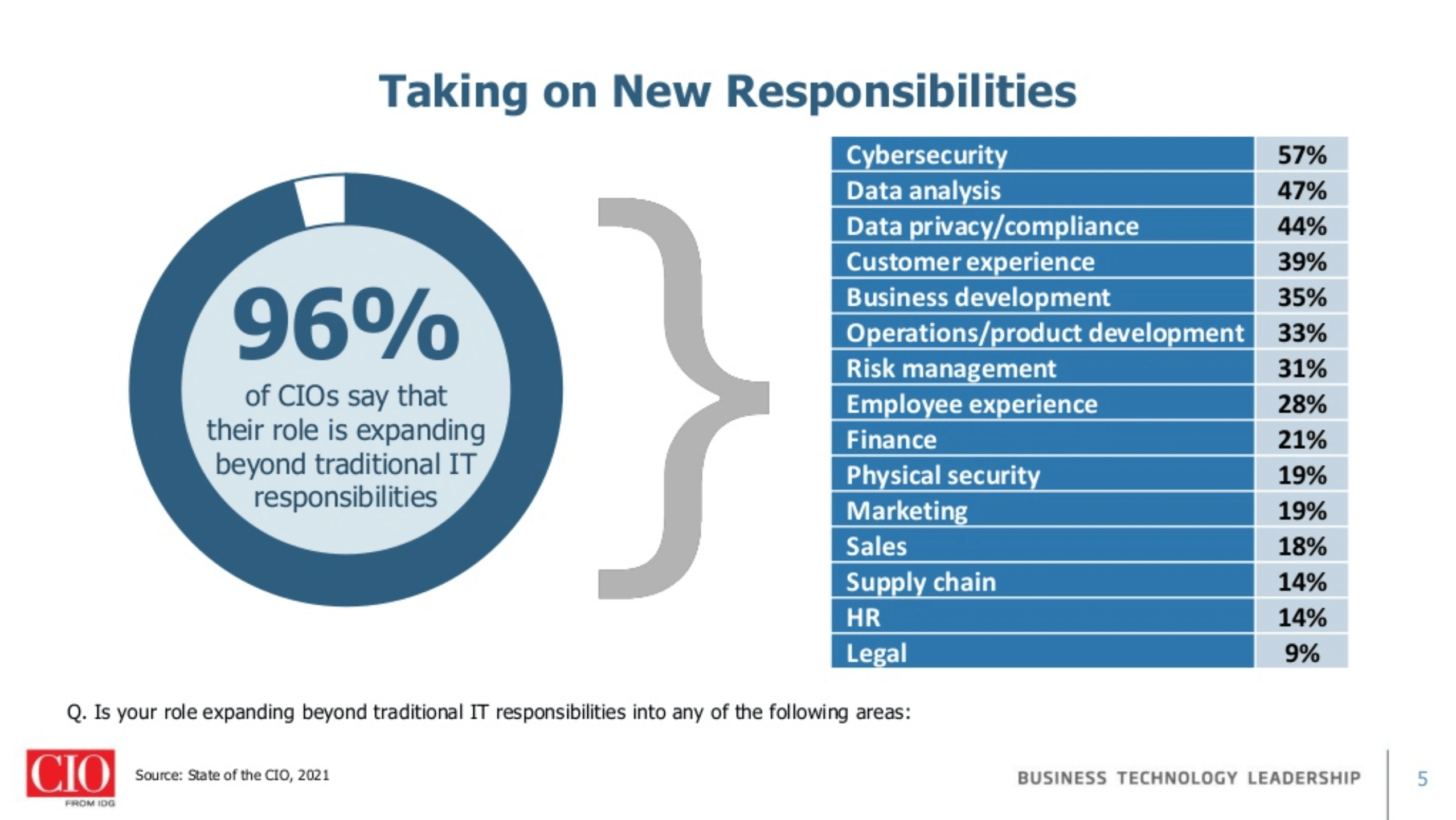
In addition, 96% of CIOs feel that their job is expanding beyond the traditional IT boundaries.
The many new roles a CIO must Play, including user experience optimization, data analytics, and sales.
As you can see, more than half of CIOs say their job now includes cybersecurity obligations.
This has even led some organizations to create a new position - the Chief Information Security Officer.
Searches for "Chief Information Security Officer" have increased by 69% over 10 years.
Every corporation in the Fortune 500 now has a CISO.
IT’s increasing importance is also driving the need for more IT personnel.
In December 2020, when the total US economy lost 140,000 jobs, the IT market grew by 391,000. IT service companies also added a net of 22,000 jobs in December 2020.
6. Privacy-Enhancing Computation Aims to Secure Customer Data
As discussed in the section on data breaches, internet privacy is a big concern for consumers.
In fact, 82% of consumers avoid revealing their personal information online for fear of interference by third parties.
Searches for "Data Privacy" has grown by 355% over the last decade.
IT departments are addressing this by deploying privacy-enhancing technologies.
These technologies basically allow businesses to collect data while, at the same time, putting consumer privacy protections in place.
This is very different from typical data protection methods.
Privacy-enhancing computation is software that actively protects data while it is being used – even by third parties.
And the need for this technology will only increase as consumer privacy regulation grows.
Gartner predicted that between 2020 and 2023, 65% of the world’s population would be covered by some kind of consumer privacy regulations like the GDPR and CCPA.
That’s compared to about a fifth of the population today.
To combat the problems associated with this, it’s estimated that 50% of all enterprises will implement some kind of privacy-enhancing computation to process data over the next few years.
Conclusion
That’s all for the top information technology trends for 2024-2027.
As digital innovation changes everything about the economy, IT departments and initiatives are becoming more important than ever.
As one would expect, most of these changes (like edge computing and automation) are driven by new technology. But others (like a focus on privacy) are in many ways cultural trends.
Stop Guessing, Start Growing 🚀
Use real-time topic data to create content that resonates and brings results.
Exploding Topics is owned by Semrush. Our mission is to provide accurate data and expert insights on emerging trends. Unless otherwise noted, this page’s content was written by either an employee or a paid contractor of Semrush Inc.
Share
Newsletter Signup
By clicking “Subscribe” you agree to Semrush Privacy Policy and consent to Semrush using your contact data for newsletter purposes
Written By


Josh is the Co-Founder and CTO of Exploding Topics. Josh has led Exploding Topics product development from the first line of co... Read more