Get Advanced Insights on Any Topic
Discover Trends 12+ Months Before Everyone Else
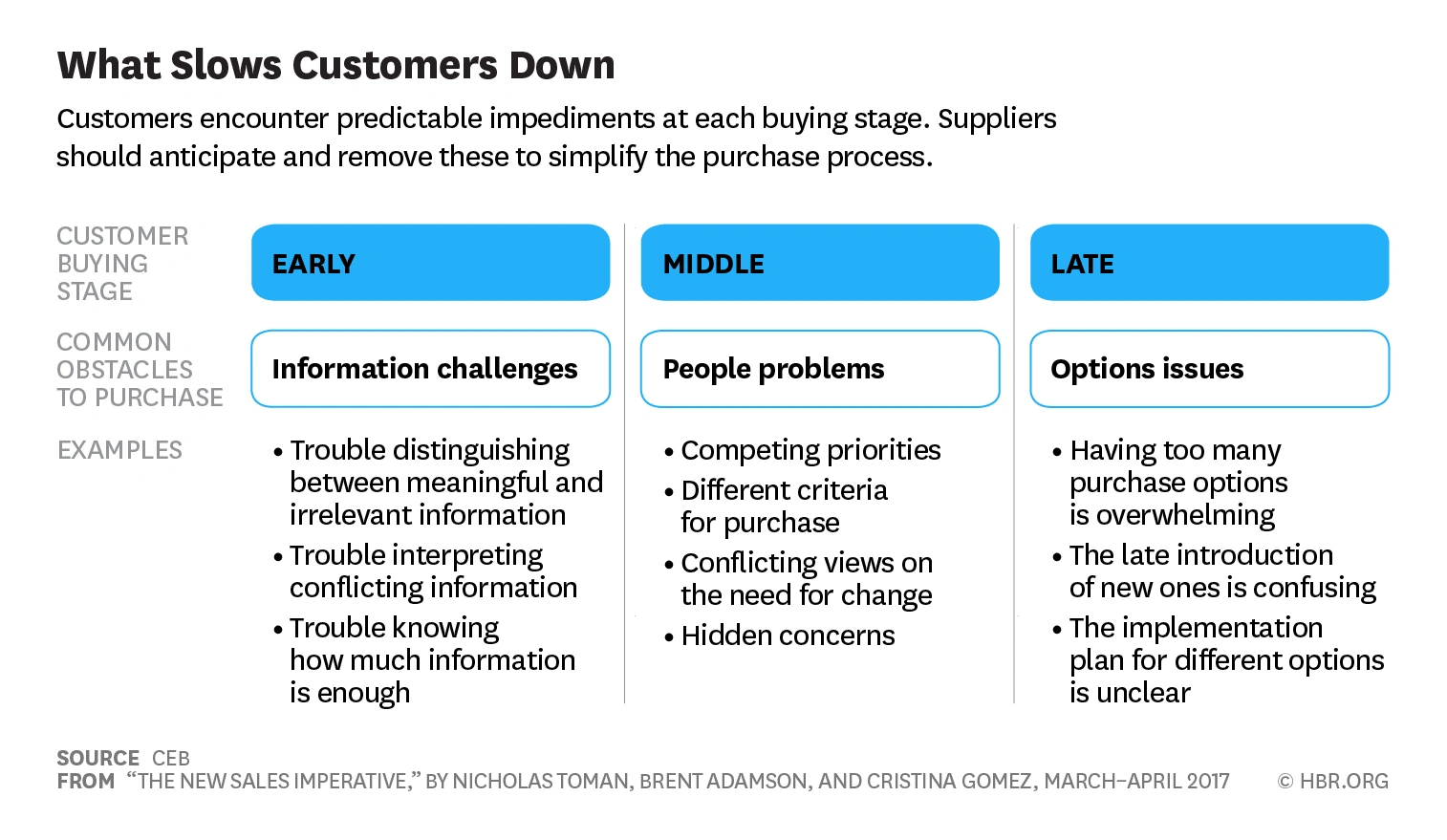
How We Find Trends Before They Take Off
Exploding Topics’ advanced algorithm monitors millions of unstructured data points to spot trends early on.
Keyword Research
Performance Tracking
Competitor Intelligence
Fix Your Site’s SEO Issues in 30 Seconds
Find technical issues blocking search visibility. Get prioritized, actionable fixes in seconds.
Powered by data from
6 Important Sales Trends (2024-2025)
You may also like:
Having dealt with the changes forced upon them for more than a year, businesses that survived the global pandemic now find themselves more focused on sales effectiveness than ever before.
In fact, a 2021 survey of business leaders worldwide found that 75% believe that the steps they’ve taken to adapt to recent challenges will serve them well in the future.
In this post, we present a collection of the six most significant sales trends that are transforming how businesses win customers and close deals.
1. “Virtual Selling” Is Now Just “Selling”
Everyone has endured more than their fair share of video calls over the last few years, but nobody’s had more of them than sales teams.
A recent study by Bain found that across industries, 79% of businesses were effectively using virtual selling in 2020 – an increase of 46.2% over the previous year.
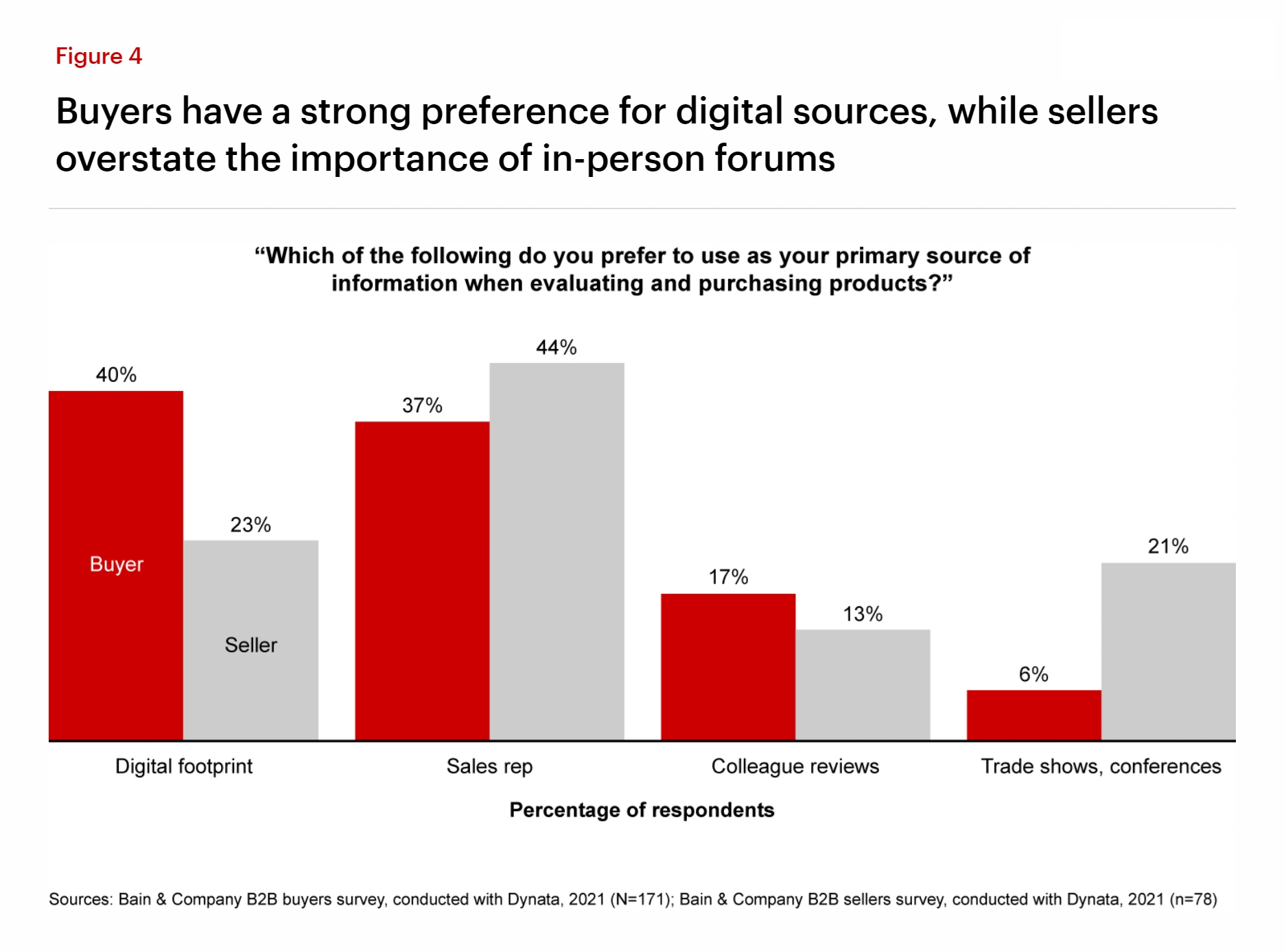
Buyers now primarily learn about new products through digital channels.
Several surveys have also found that customers prefer digital over in-person sales interactions – 92% of B2B buyers said they prefer virtual sales pitches.
And the preference of B2C buyers for online over physical channels is well-established, with 64% of consumers rating online experiences as better.
In addition to lowering the cost of interactions, virtual selling also enables sales personnel to interact with more customers.
Even for high-ticket sales, the era of face-to-face selling as the ultimate method is now over.
A McKinsey study found that 90% of companies were willing to complete deals worth up to $100,000 without in-person interactions.
Further, 27% were willing to do so for purchases over $500,000, and 15% were comfortable with remote sales to close deals for over $1 million.
That said, virtual selling also has its share of challenges.
Bain reports that, on average, C-suite executives feel that their organization’s win rate through virtual selling was 48.8% lower than their expectations. They also discovered that revenue was 44% lower than expected when focused on virtual sales processes.
2. Self-Service Is on the Rise
The trend towards reduced face-to-face interactions isn’t just restricted to the digital space.
Self-service and contactless selling have been around for years, particularly in Japan, but their adoption has exploded over the last few years.
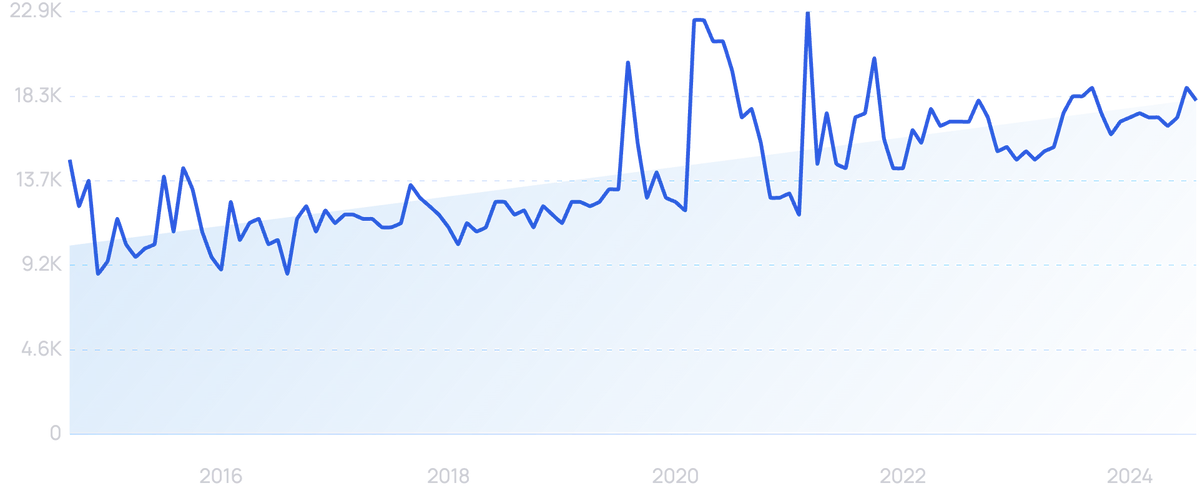
Searches for “Contactless Payment” have jumped by 22% over the last decade.
In 2021, 79% of shoppers say that contactless experiences are important in stores.
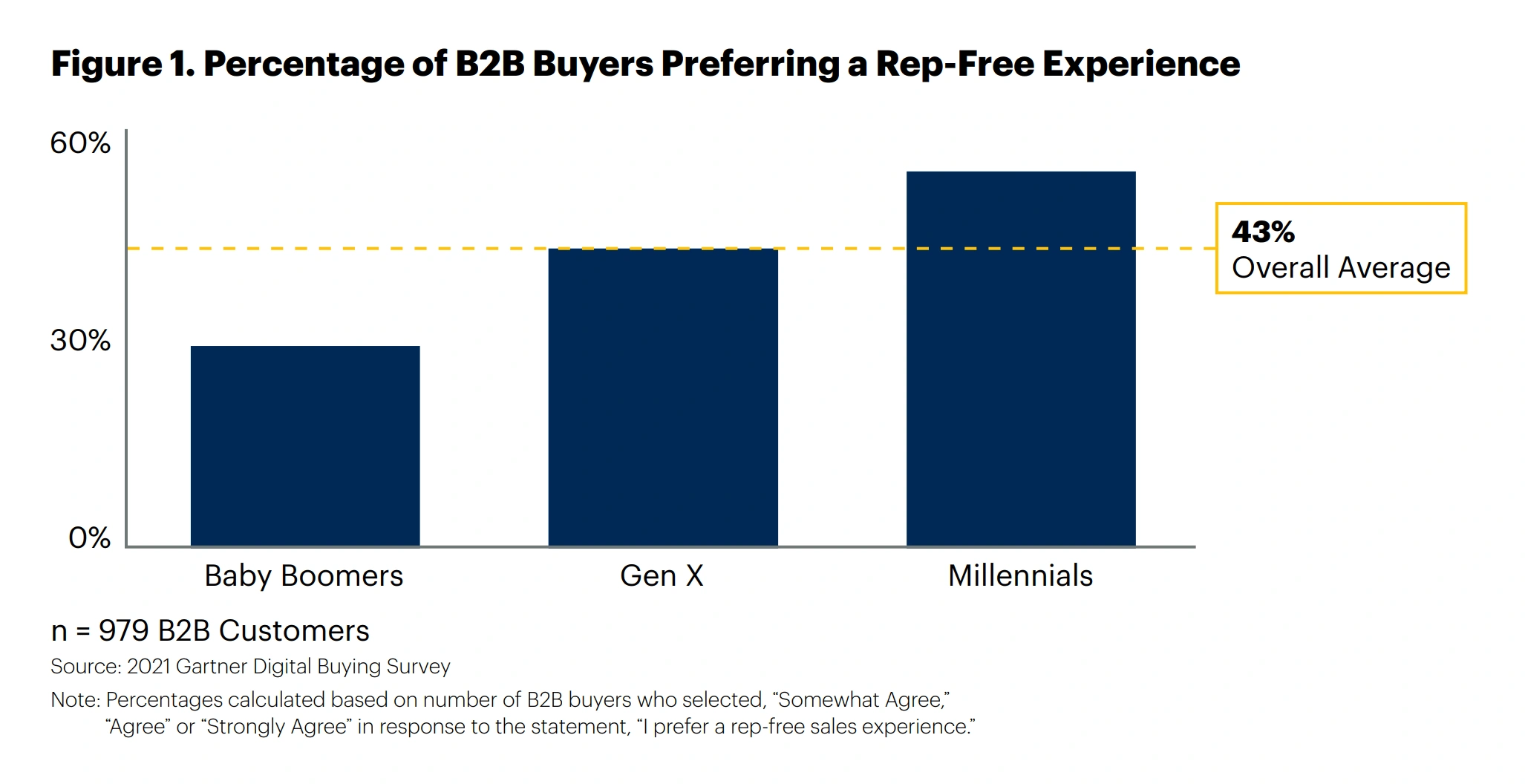
Given the choice, 43% of consumers around the world would opt for a buying process that involves no interaction with sellers.
Sales preference by generation.
(For millennials, that ratio is as high as 57%.)
A study by Salesforce of over 2,500 businesses worldwide found that adoption of self-service and contactless checkout models was very high across industry verticals.
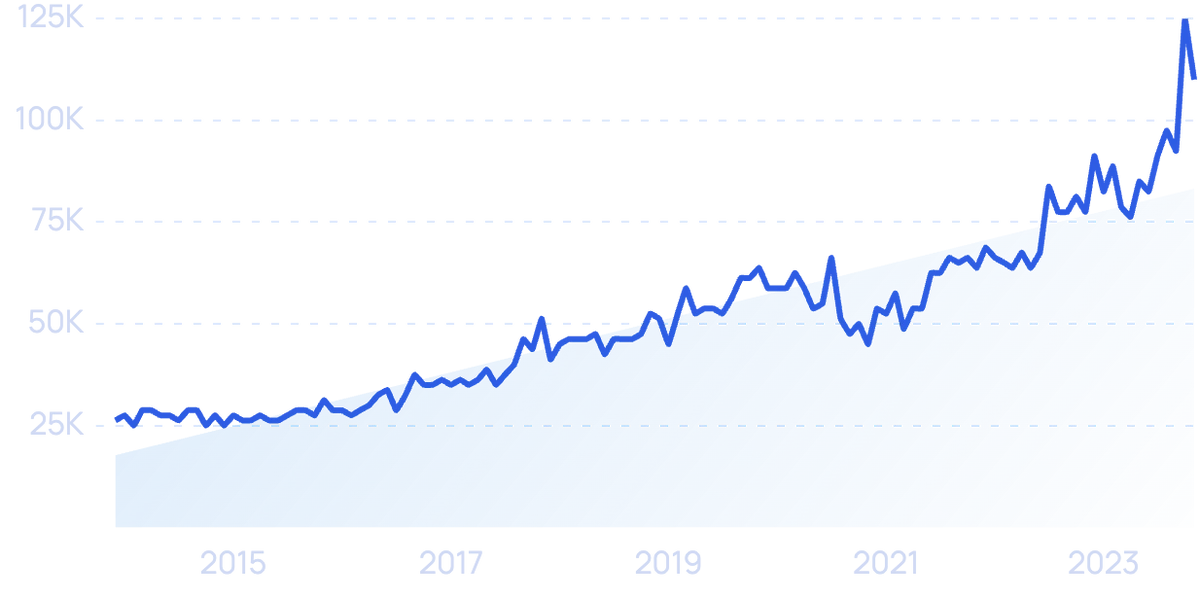
Searches for “Self-Checkout” have risen by 146% over the last 10 years.
96% of consumer goods brands, 86% of financial services businesses, 78% of travel and hospitality businesses, and 68% of professional service businesses report adopting various forms of contactless selling.
What’s more, these changes are here to stay: 79% of businesses state that they will continue to offer contactless methods even after the pandemic.
In a surprising find, a McKinsey analysis of 3,600 businesses across 12 sectors and 11 countries, revealed that China and India show the highest growth in adoption of self-service tools.
It’s no surprise then that the value of the global market for self-service systems is expected to exceed $6.5 billion by 2027.
3. Greater Focus on Reducing Buyer’s Remorse
Steve Jobs famously did not trust focus group studies, often expressing the view that people don’t know what they want until someone shows them.
When it comes to sales, new consumer research seems to validate that view.
Although both B2B and B2C buyers express a preference for buying without interacting with sales reps, post-purchase buyer remorse increases drastically with unaided buying experiences.
A report by Gartner describes customers as being their own worst enemies.
Customers' preference for unassisted channels corresponds with 23% higher purchase regret, compared to purchases that involve human interaction.
This leads to negative outcomes for both buyers and sellers, which can be avoided by providing customers with a more meaningful and differentiated buying experience.
A look at roadblocks to possible sales.
As of 2020, 64% of customers couldn’t tell the difference between the digital buying experiences of most brands. This is changing rapidly, with businesses focusing on a variety of measures to create unique customer experiences.
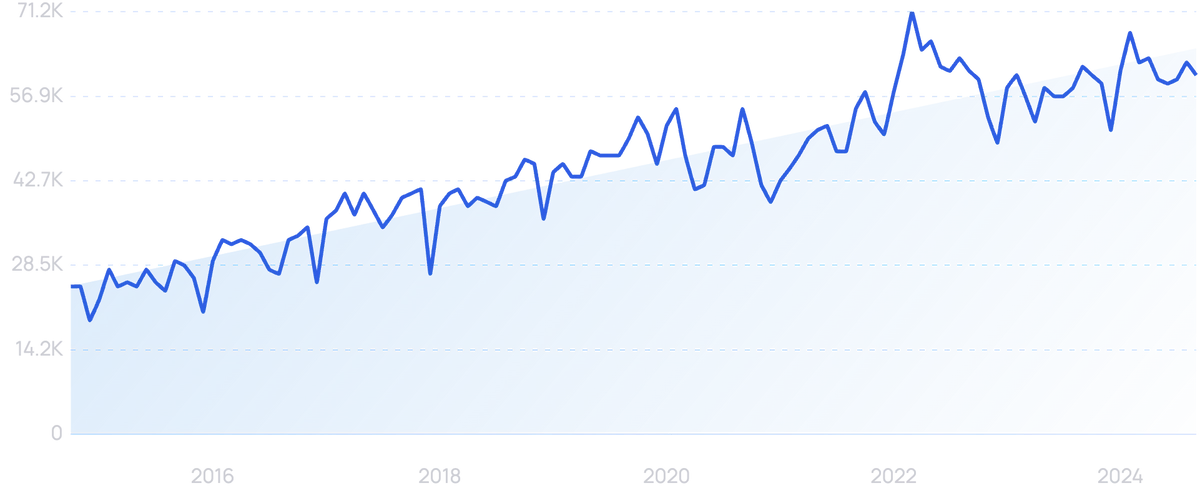
Searches for “Customer Experience” have grown by 143% over the past decade.
For example, Protolabs – a manufacturing services provider – developed a sales process that provides customers expert advice and specialist recommendations, without the need for appointments, meetings, or phone calls.
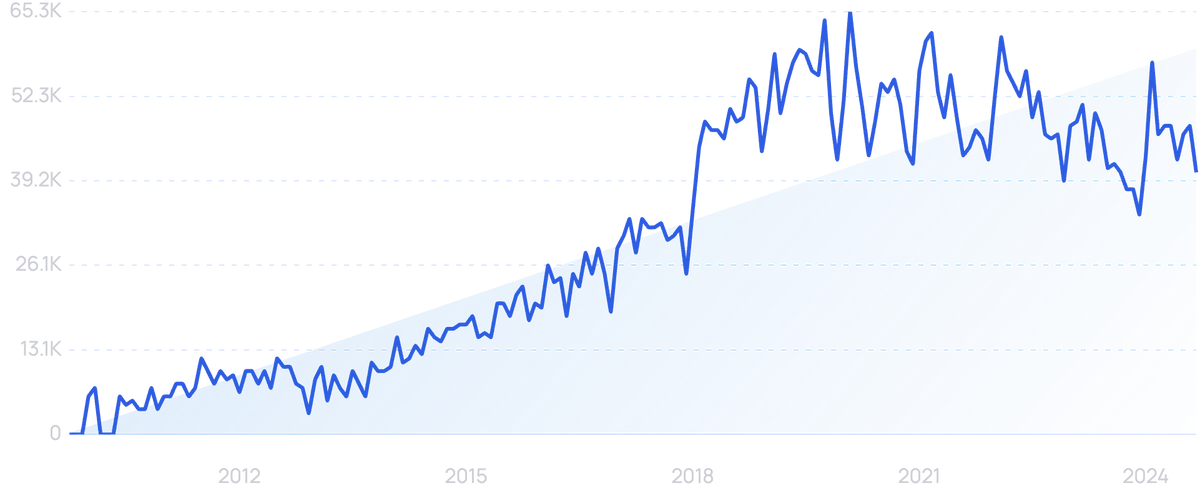
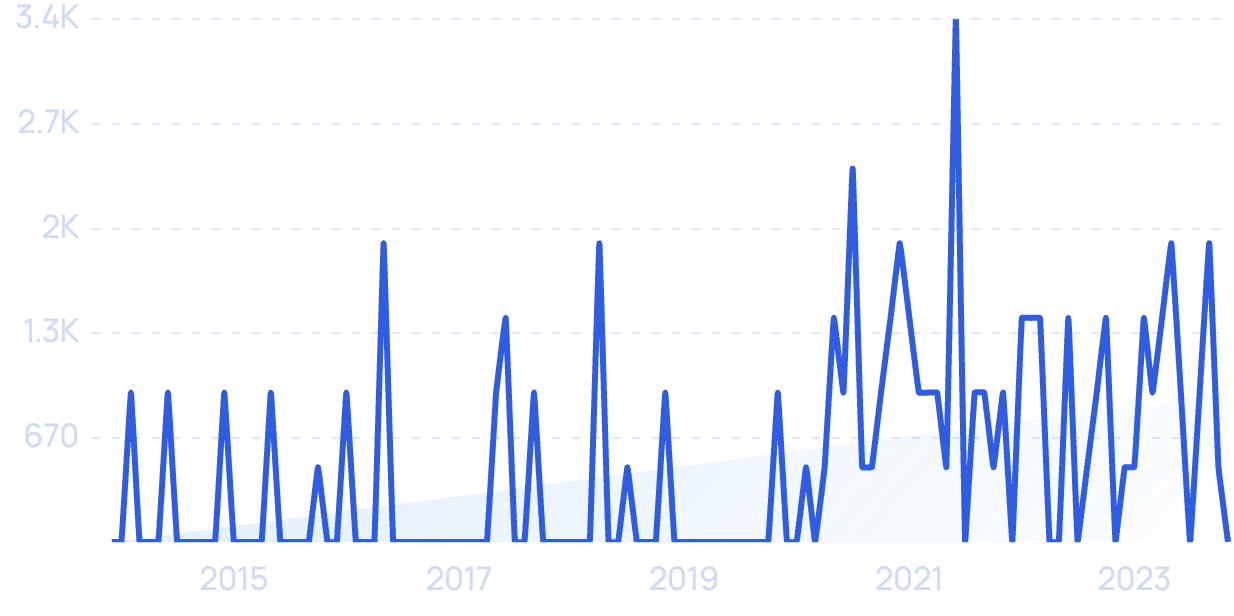
Searches for “Protolabs” grew by 6,100% over the last 15 years.
Protolabs’ software enables their engineers to audit models of parts uploaded by customers, for manufacturing readiness, in a matter of minutes.
This shortens the quoting process from three weeks to 12 hours, providing a win-win for both the business and its customers.
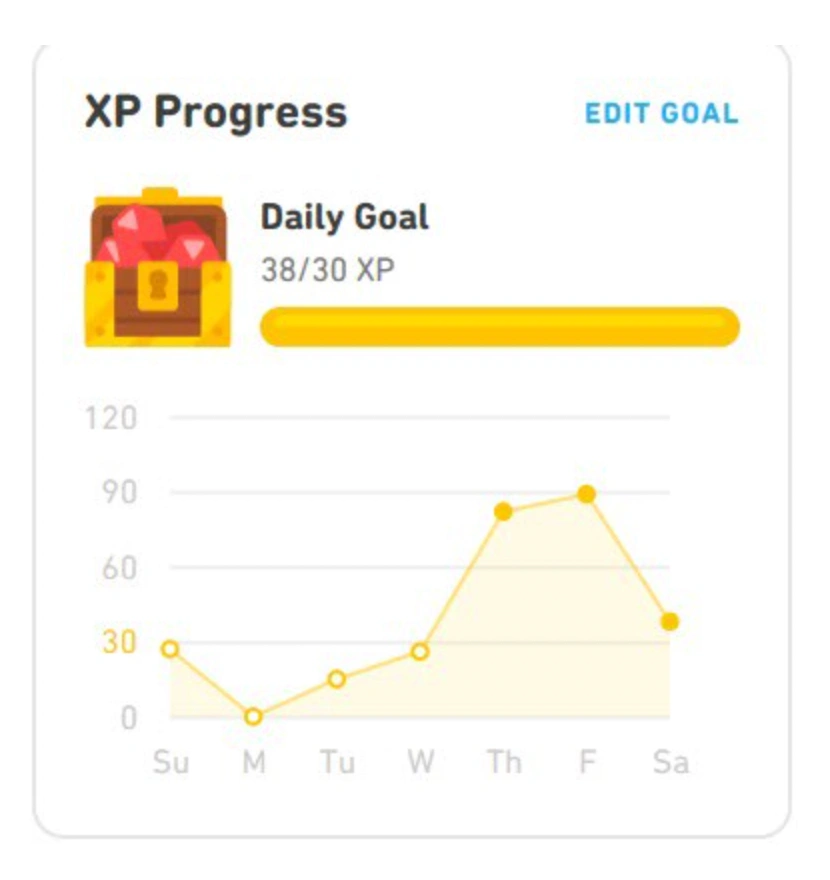
Tim Horton's also overhauled and gamified its mobile app, engaging customers with games and offering rewards on purchases.
Language learning app, Duolingo, reinvented its onboarding process to reduce the high customer churn rate that plagues the sales of subscription products, particularly in education.
Snapshot of Duolingo’s gamified mobile app.
4. Sales Automation Is the Key to Boosting Revenue
In 2020, McKinsey found that businesses that adopted sales automation consistently saw sales uplifts of up to 10%, alongside improvements in efficiency of up to 15%.
In addition, sales teams at automation-focused organizations also reported higher rates of customer satisfaction and more customer-facing time.
Roughly a third of all tasks in sales operations can be automated with technology, according to estimates from McKinsey Global Institute.
Investments in technology and automation have typically been led by large enterprises, but COVID has accelerated adoption even among SMBs.
More than 50% of growing SMBs increased their investments in sales technology in 2020.
And 62% cite improvements in productivity as the main objective for doing so, while 60% did so to improve business agility.
According to Salesforce, of the 2,534 businesses studied worldwide, technology investments in the area of sales correlated more strongly with business growth than investments in marketing, customer service, or operations.
53% of companies that increased automation in their sales processes reported increased revenues.
Growth of sales automation software also surged to 10.9% in 2020, reaching a value of $8.15 billion.
Forecasts predict that it will continue at a compounded annual growth rate of 8.3%, exceeding $14.2 billion by 2027.
5. AI Aids Sales Teams
In 2013, the University of Oxford released the first study of its kind, profiling the extent to which jobs across 702 occupations were at risk of being replaced by artificial intelligence (AI).
The risk profile for sales jobs was diverse. The vulnerability to AI of sales engineers, sales managers, and jobs in financial services sales, was estimated at less than 2%, while real estate, insurance, retail, and parts sales were extremely at risk — between 86% and 98%.
More recently, a 2018 McKinsey study reaffirmed those predictions: sales jobs that involve a lot of repetition and little to no social intelligence, will become obsolete.
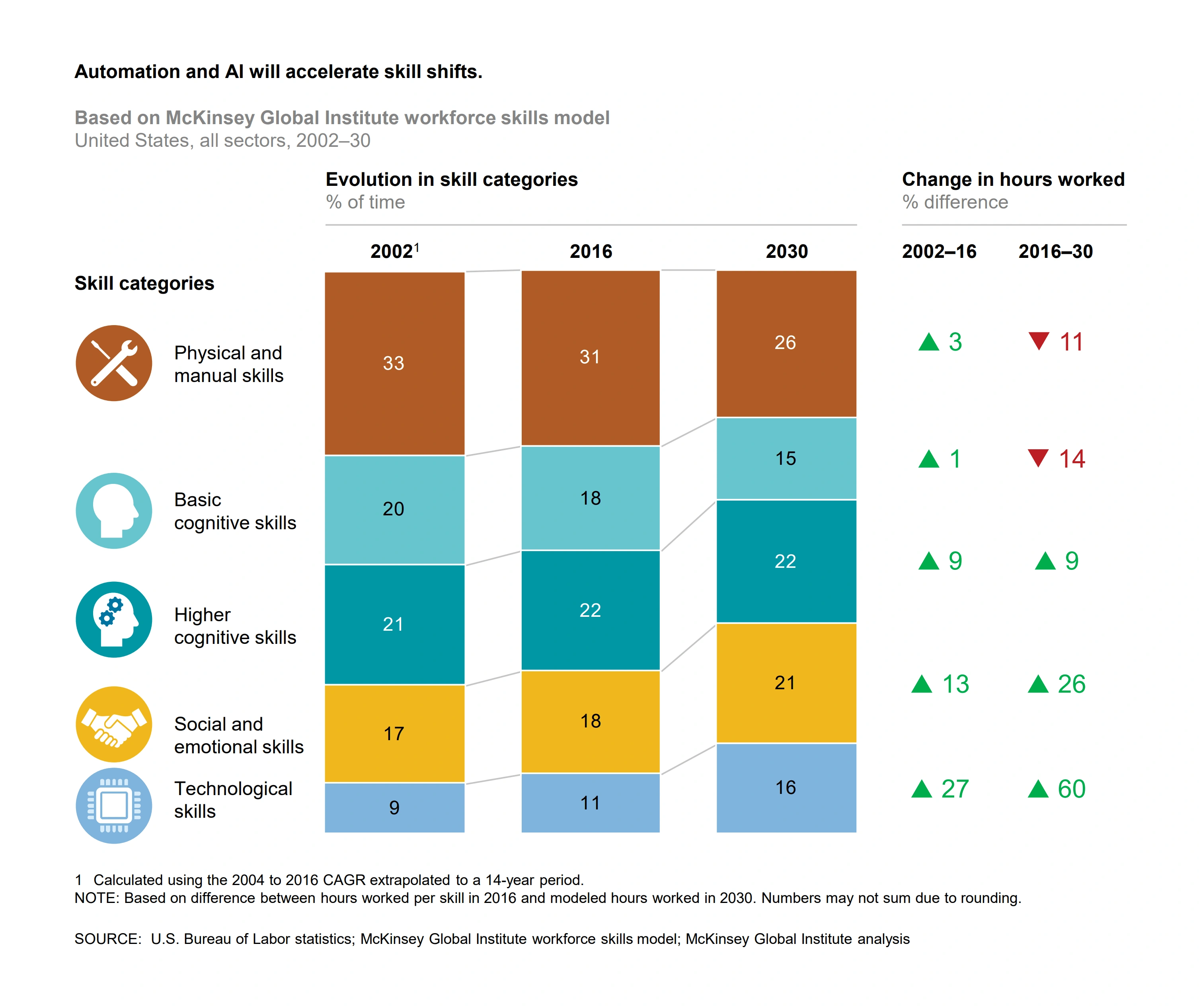
The good news is that the number of sales jobs that demand a high degree of social intelligence and interpersonal connection is expected to grow by more than 7.9% by 2030.
A large portion of the workforce is expected to shift towards jobs prioritizing social and emotional skills by 2030
Between 2018 and 2020, the number of sales teams using AI shot up 155%.
The top five areas where sales tasks are being handed over to AI are logging sales data, recording customer information, drafting proposals, scoring leads, and determining actions to take on customer accounts, with 63% to 69% of businesses saying they prioritize AI in these areas.
Chatcompose is one of the beneficiaries of this shift.
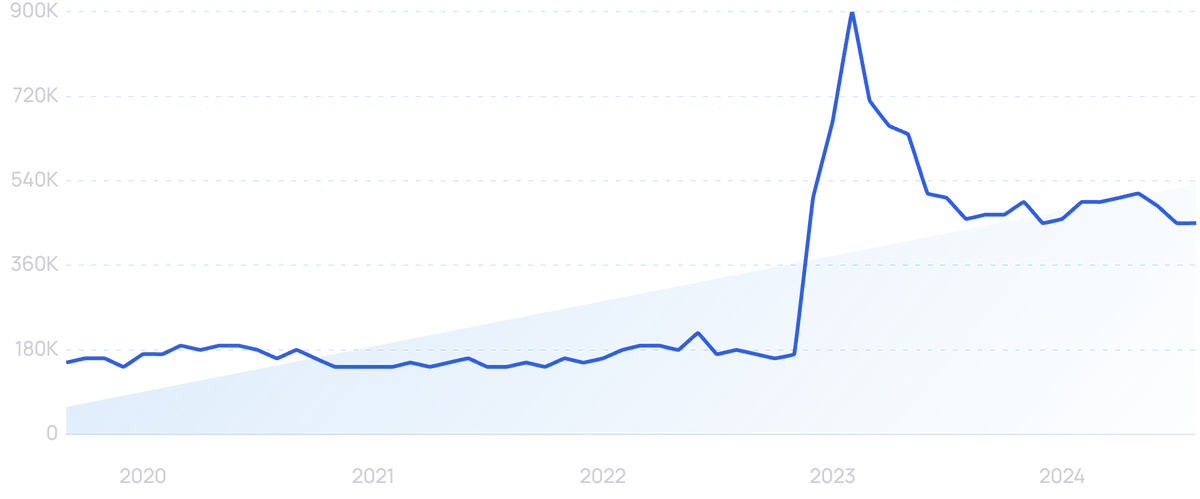
Searches for “Chatcompose” over the past 10 years.
The company allows users to develop and deploy custom-made chatbots across a wide variety of communication channels.
As a result of technologies like this, 42% of sales professionals in the US say that their organizations are working with fewer sales personnel compared to pre-COVID levels.
Overall, 57% of businesses plan to increase investments in AI-driven sales in the coming year, allowing sales reps the benefit of more time to conduct deeper customer research and forge meaningful connections with buyers.
6. Diversified Sales Channels and Tactics
Sales experimentation is at an all-time high as businesses hasten to grow more resilient.
Traditionally, most businesses have confined themselves to just two sales channels — typically, e-commerce and physical stores.
A Forrester study finds that this is changing, with most businesses having increased to three sales channels on average, in 2020.
Consistent with the imperative to reduce risk, most organizations indicated a fairly even revenue split of about 39% to 45% across these channels.
In addition to the two usual suspects, 48% of sales leaders indicated that they would invest more in post-sale / service as a channel in the coming months.
This is followed by direct sales (47%), distributor sales (42%), in-app sales (41%), and third-party marketplaces (38%).
This trend of adding more sales channels is expected to increase in the coming year.
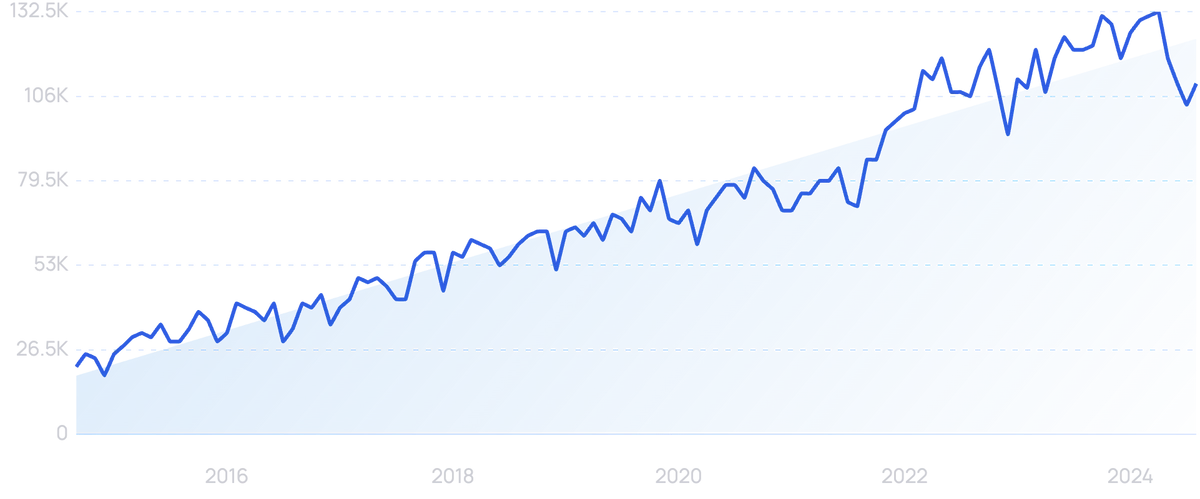
Search interest in the term “Omnichannel” has risen by 419% over the last decade.
The increased focus on service as an avenue for sales revenue puts the spotlight on live chat as a tool that can deliver those outcomes.
When researching suppliers, buyers rate live chat as their most preferred tool.
Searches for “Chatbot” have jumped by 194% over the last 5 years.
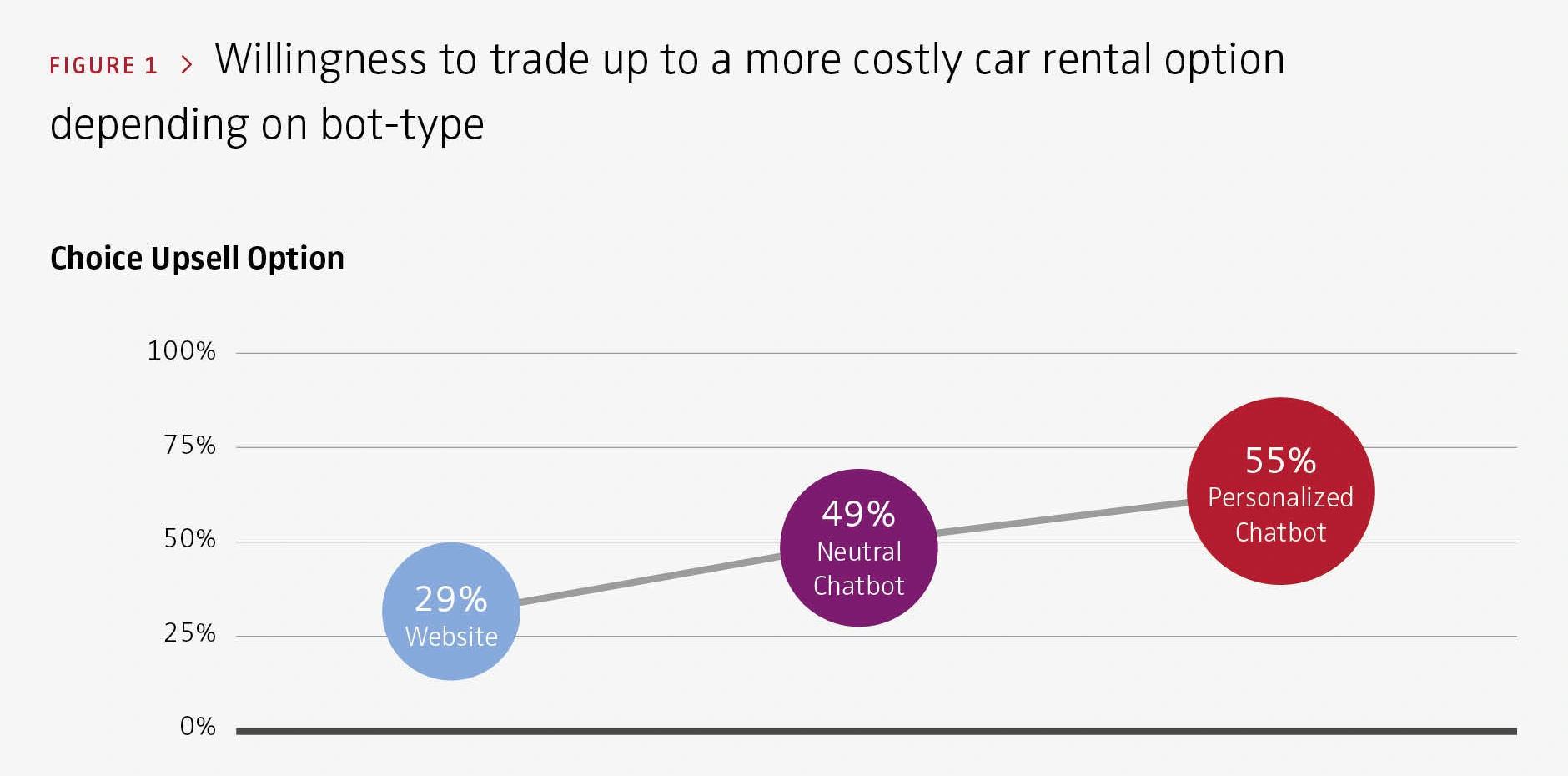
Recent data indicates that personalized, AI-driven chatbots are 55% more successful at upselling.
As such, it’s no surprise that more than 80% of businesses intend to use chatbots for sales within the next five years.
A study by the Nuremberg Institute for Market Decisions found that personalized chatbots are more likely than other digital options to influence upsells in car rentals.
That said, for sales teams to actually realize results from non-traditional sales channels, greater collaboration between departments is going to be essential.
After surveying 800 companies across 15 countries and 19 industries, Zendesk reports that 32% of sellers say their customers expect vendor sales reps to have the context of the problems they (customers) are trying to solve.
And 26% find that customers expect a close collaboration between the vendor’s internal teams.
These shifts toward omnichannel, AI adoption, and growing customer expectations have set the stage for data-driven selling.
88% of sales reps rate the ability to anticipate customer needs as very important amidst the current economic conditions.
Local, national, international, and industry news have always been data sources that sales teams utilize.
However, modern sales tools now also glean insights from communication and purchase history, customers’ competitor activity, and customer staffing changes.
These data points will become more central to sales decisions over the next five years.
Conclusion
As employees and workers both increasingly realize that they enjoy working from home, and businesses see the cost efficiency of remote work, virtual selling is here to stay.
Meanwhile, the rise of AI looks to reduce sales interactions in the physical world, with more sales tasks being automated than ever before.
At the same, businesses are also exploring ways to fight increased rates of post-purchase regret that comes with impersonal, undifferentiated selling.
This suggests that sales reps are far from obsolete — at least for now — but they will be working with more software robots and sales analytics in the years to come.
Stop Guessing, Start Growing 🚀
Use real-time topic data to create content that resonates and brings results.
Exploding Topics is owned by Semrush. Our mission is to provide accurate data and expert insights on emerging trends. Unless otherwise noted, this page’s content was written by either an employee or a paid contractor of Semrush Inc.
Share
Newsletter Signup
By clicking “Subscribe” you agree to Semrush Privacy Policy and consent to Semrush using your contact data for newsletter purposes
Written By


Josh is the Co-Founder and CTO of Exploding Topics. Josh has led Exploding Topics product development from the first line of co... Read more